Implementation of Learning Sleep Quality from Daily Logs in Tensorflow.
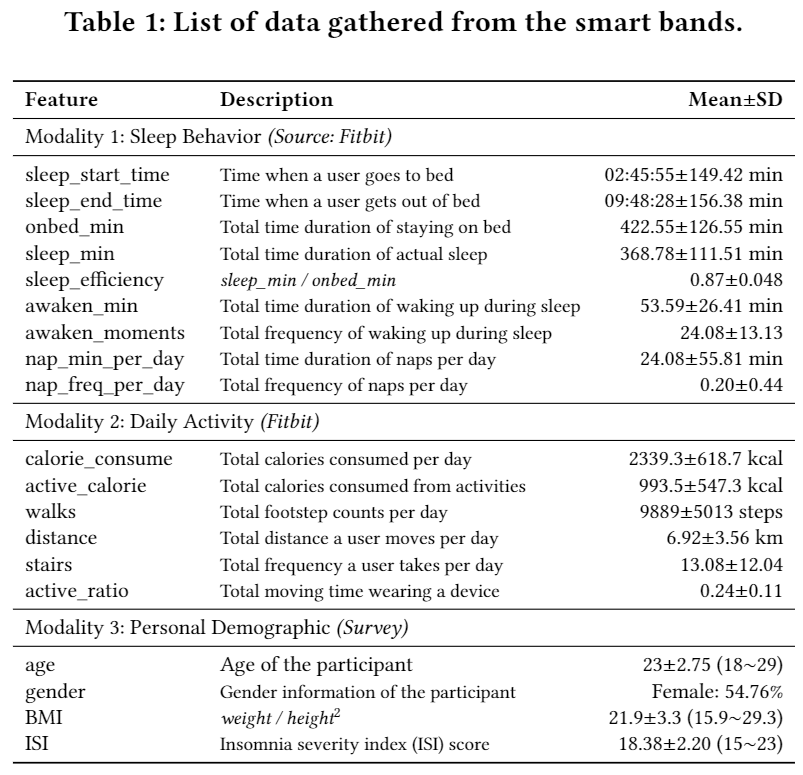
Table 1 displays the list of data features gathered by the Fitbit device and the user surveys. All features without "onbed_min" (which was excluded due to its strong correlation with other sleep features.) were used in this project. Sample data from four randomly selected users is uploaded in data folder. sample_data_sleeps_ORIGINAL.csv includes the data from Modality 1 and 2, and sample_meta-data_sleeps.csv includes the data from Modality 3.
The code has been tested running under Python 3.6.6. with the following packages installed (along with their dependencies):
- numpy == 1.16.0
- pandas == 0.23.4
- pyprind == 2.11.2
- tensorflow == 1.12.0
- scikit-learn == 0.20.2
You can set parameter by modifying GAIN/parameter.json file. In our paper, to make an imputation , we used parameters as follows.
"GAIN":
{"file_path": "....../sample_data_sleeps_ORIGINAL.csv", "save_path": "....../impute_data.csv", "epoch": 20000}
1. Setting the path of parameter.json in main.py
(For example : If your parameter.json is located in 'user/Documents/data/parameter.json',you should set it as json_path in
main.py)
2. Setting parameter in parameter.json:
(For example : If your sample_data_sleeps_ORIGINAL.csv is saved in 'user/Documents/data/sample_data_sleeps_ORIGINAL.csv',
you should set it as parameter in parameter.json ; If you want to save imputed data,you should set the path whwere you
want to save a parameter in parameter.json)
3. python main.py -- After you finish step 1,2 , you can execute main.py and get imputed data.
You can set parameter by modifying Sleep_Efficiency_Prediction/model_parameter.json file. In our paper, to make a prediction, we used parameters as follows.
{
"phase1_parameter": {
"batch_size" : 35,
"learning_rate" : 1e-4,
"epoch" : 400,
"keep_prob" : 0.8,
"step1_hidden_size": 200,
"step2_hidden_size": 75,
"step3_hidden_size": 50,
"step4_hidden_size": 100,
"step5_hidden_size": 90,
"step6_hidden_size": 100,
"step7_hidden_size": 500,
"optimizer": "AdamOptimizer"
},
"phase2_parameter": {
"batch_size" : 35,
"learning_rate" : 1e-4,
"epoch" : 400,
"keep_prob" : 0.8,
"query_size" : 70,
"metadata_hidden_size1": 90,
"metadata_hidden_size2": 50,
"optimizer": "AdamOptimizer"
}
}
usage: main.py [-h] [--model_name MODEL_NAME] [--impute IMPUTE] [--load] [--printlog]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--model_name MODEL_NAME
Name of the model
--impute IMPUTE Method for filling data, select from BLANK, AVERAGE,
and GAIN
--load With this option, load trained phase 1 and phase 2
model. Otherwise, train new one
--printlog With this option, print train log in the prompt.
Otherwise, no logs are printed
$ cd Sleep_Efficiency_Prediction
$ python main.py --model_name TEST_MODEL --impute GAIN --printlog
Result files are saved in Sleep_Efficiency_Prediction/result Log files(with --printlog option) are saved in Sleep_Efficiency_Prediction/log. Models are saved in Sleep_Efficiency_Prediction/model. You can load model with --load option with proper MODEL_NAME and corresponding parameter file.
Our two attention mechanisms can be used to explore general sleep patterns among participants.
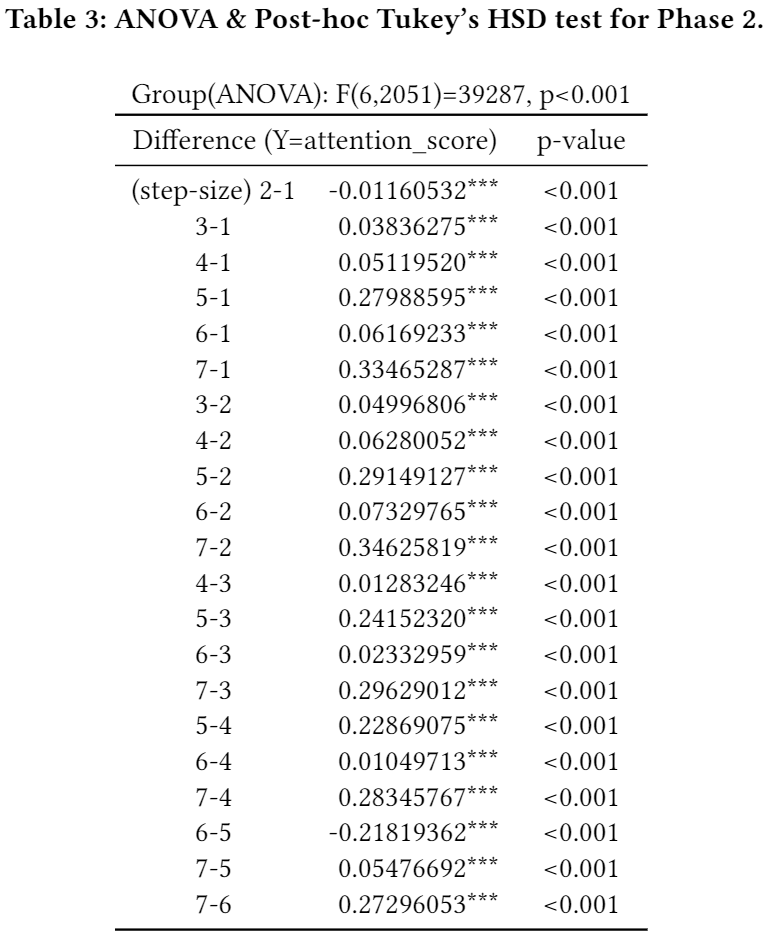
- (Phase 2) Especially, reporting ranks among step-sizes (s) can exhibit what time-frame (i.e., weekly-base) would be the most suitable for predicting sleep efficiency, in general. For 294 test chunks (7 chunks from each 42 users, c.f., 1 chunk is composed by 8 consecutive day-vectors), we recorded all attention scores (score ∈ [0,1]) among 7 step-sizes per chunk then averaged the recorded scores per step-size: the highest attention score value means the corresponding step-size is the most important for predicting sleep efficiency whereas the lowest value means the corresponding step-size is the least important. The below table presented the mean, SD, and 95% confidence interval of averaged attention score per step-size. Overall, s=7 and s=5 take the first and the second places that many users are attended on (see Table 2). ANOVA test and the post-hoc Tukey's honest significant difference (HSD) test (see Table 3) confirms the averaged attention scores of all step-sizes are statistically different from each others.
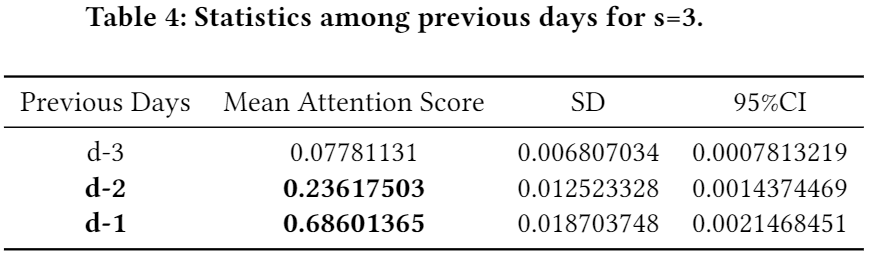
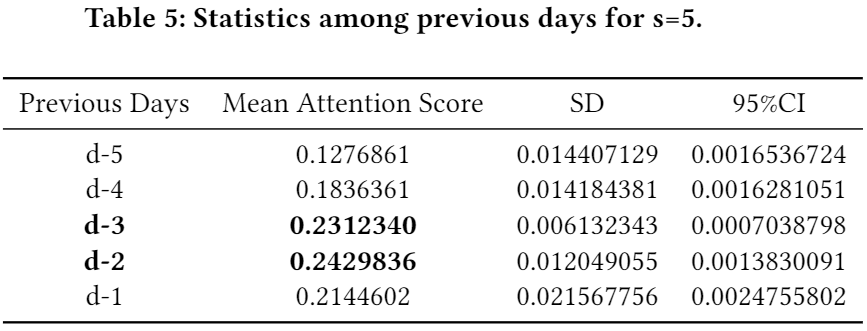
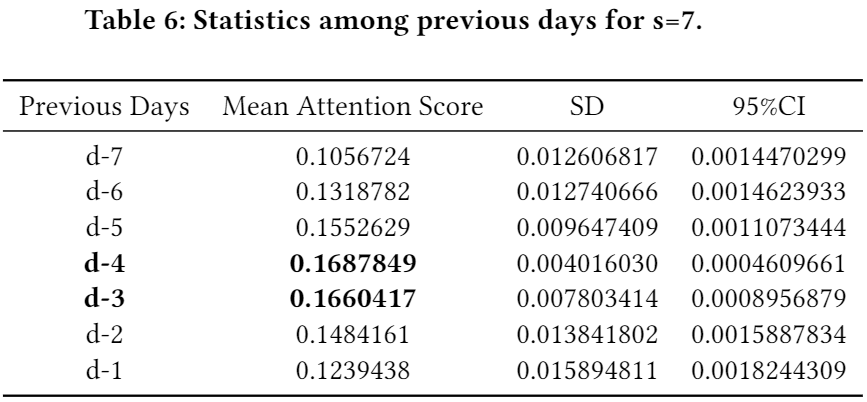
- (Phase 1) We also investigated which days are the most crucial within the chosen step-sizes in general. The below three tables show the results in regard to s=3, 5, and 7, respectively. (a) inside s=3, the first and the second ranks go to d-1 (i.e., the most recent day from the target day d and d-2; (b) inside s=5, the first and the second ranks go to d-2 and d-3; (c) inside s=7, the first and the second ranks go to d-4 and d-3.
You can set parameter by modifying Isomnia_Ranking/parameter.json file. In our paper, to rank users, we used parameters as follows.
"Isomnia_Ranking":
{"file_path": "....../sample_data_sleeps_Imp-GAIN.csv", "threshold": 0.006, "main_effect_location": 4}
1. Setting the path of parameter.json in main.py
(For example : If your parameter.json is located in 'user/Documents/data/parameter.json',you should set it as json_path in
main.py)
2. Setting parameter in parameter.json:
(For example : If your sample_data_sleeps_Imp-GAIN.csv is saved in 'user/Documents/data/sample_data_sleeps_Imp-GAIN.csv',
you should set it as parameter in parameter.json ; If you want to save imputed data,you should set the path whwere you
want to save a parameter in parameter.json)
3. python main.py -- After you finish step 1,2 , you can execute main.py and get rank result.