D language bindings for the Godot Engine's GDExtension API.
Originally a fork of godot-d
WIP: These bindings are still under development. Until v1.0.0, expect breaking changes, bugs, and missing documentation. Please report any issues and confusing or undocumented features on the GitHub page.
- Usage
- Dependencies
- Install
- Manually building (advanced)
- Generating Godot Bindings
- Manually creating project
- Creating project by using init script
- Extend as you wish!
- D compiler:
- DUB package/build tool (usually included with both compilers)
- Godot 4 editor (standard version)
Before you start please keep in mind that this is purely experimental unstable volatile WIP project intended for those brave people who would like to try D and Godot.
In no situation do not use it to ship your product, doing so of course is possible but by no means the author is responsible for the consequences.
This will download and cache dub package
- Run
dub fetch godot-dlang
Proceed to Manually creating project for adding it to your D project.
Normaly one would use dub package, this section is for advanced users who would like to develop or hack godot-dlang.
- Clone git repo
git clone https://github.com/godot-dlang/godot-dlang.git - Switch it to master branch
git checkout master - Use dub local project version lock file
dub.selections.jsonto specify where to look for your local copy
Note that if you have strange errors in
dub runyou might have godot-dlang cached in dub, you might need to remove it by usingdub remove godot-dlang
- Download godot 4 editor and place it in somewhere like
C:\godot - Step into that directory and open terminal
- Generate script API information with command
godot.exe --dump-extension-api - Run binding generator (-j tells where to look for script API and -o tells to overwrite any existing bindings)
dub run godot-dlang:generator -- -j extension_api.json -o
This step is one time process, though you would need to re-generate API and bindings for every godot release
- Open Godot editor, and create a new project in some known location like
C:\godot\mycoolgame - Open it now and let Godot do initial loading
- Open your newly created project in terminal
- Run
dub init, make sure to give it a name for examplemydplugin - Add Godot-dlang master dependency
dub add godot-dlang@~master - (optional) (Windows) If you use
ldc2as compiler, then add"dflags-windows-ldc": ["-dllimport=defaultLibsOnly"]to yourdub.json, or you will have linker errors - Open up
dub.jsonand add"targetType": "dynamicLibrary",afterauthorsfield your dub.json file should look like this now:
dub.json:
{
"authors": [
"Godot-DLang"
],
"targetType": "dynamicLibrary",
"dflags-windows-ldc": ["-dllimport=defaultLibsOnly"],
"copyright": "Copyright © 2022, Godot-DLang",
"dependencies": {
"godot-dlang": "~master", <!--DEPRECATED-->
},
"description": "A minimal D application.",
"license": "proprietary",
"name": "mydplugin"
}- Do a test build
dub build, you might see some warnings but that's ok
- Rename
source/app.dfile into something likesource/greeter.d - Open
source/greeter.din your favorite text/code editor and add following content:
source/greeter.d:
import godot;
// import godot.api.script; // for GodotScript!
// import godot.api.register; // for GodotNativeLibrary
// import godot.string; // for gs!
import godot.node;
// minimal class example with _ready method that will be invoked on creation
class Greeter : GodotScript!Node {
@Property String name;
// this method is a special godot entry point when object is added to the scene
@Method
void _ready() {
// 'gs' is a string wrapper that converts D string to godot string
// usually there is helper functions that takes regular D strings and do this for you
print(gs!"Hello ", name);
}
}
// register classes, initialize and terminate D runtime, only one per plugin
mixin GodotNativeLibrary!(
// this is a name prefix of the plugin to be acessible inside godot
// it must match the prefix in .gdextension file:
// entry_symbol = "mydplugin_gdextension_entry"
"mydplugin",
// here goes the list of classes you would like to expose in godot
Greeter,
);- Build plugin again
dub build, in some rare cases you might do a full rebuild by adding--forceswitch, build should be ok
You would need to build your plugin every time you have modified the code in order to see changes
Currently AFAIK there is no way to unload/reload GDExtension, because of that on Windows it will prevent rebuilding plugin until you close the editor!
- Currently there is no UI for that AFAIK, so lets do that manually
- Create a file in your Godot project root called
mydplugin.gdextensionand fill with following content:
mydplugin.gdextension:
[configuration]
entry_symbol = "mydplugin_gdextension_entry"
compatibility_minimum = "4.1"
[libraries]
linux.64 = "libmydplugin.so"
windows.64 = "mydplugin.dll"
Note that entry_symbol should match class registration in D inside of
GodotNativeLibrarydeclaration
- If you still have godot editor open reload project by using main menu
Project->Reload Current Project - In editor now create an empty
3D Nodescene - Select root object and attach new
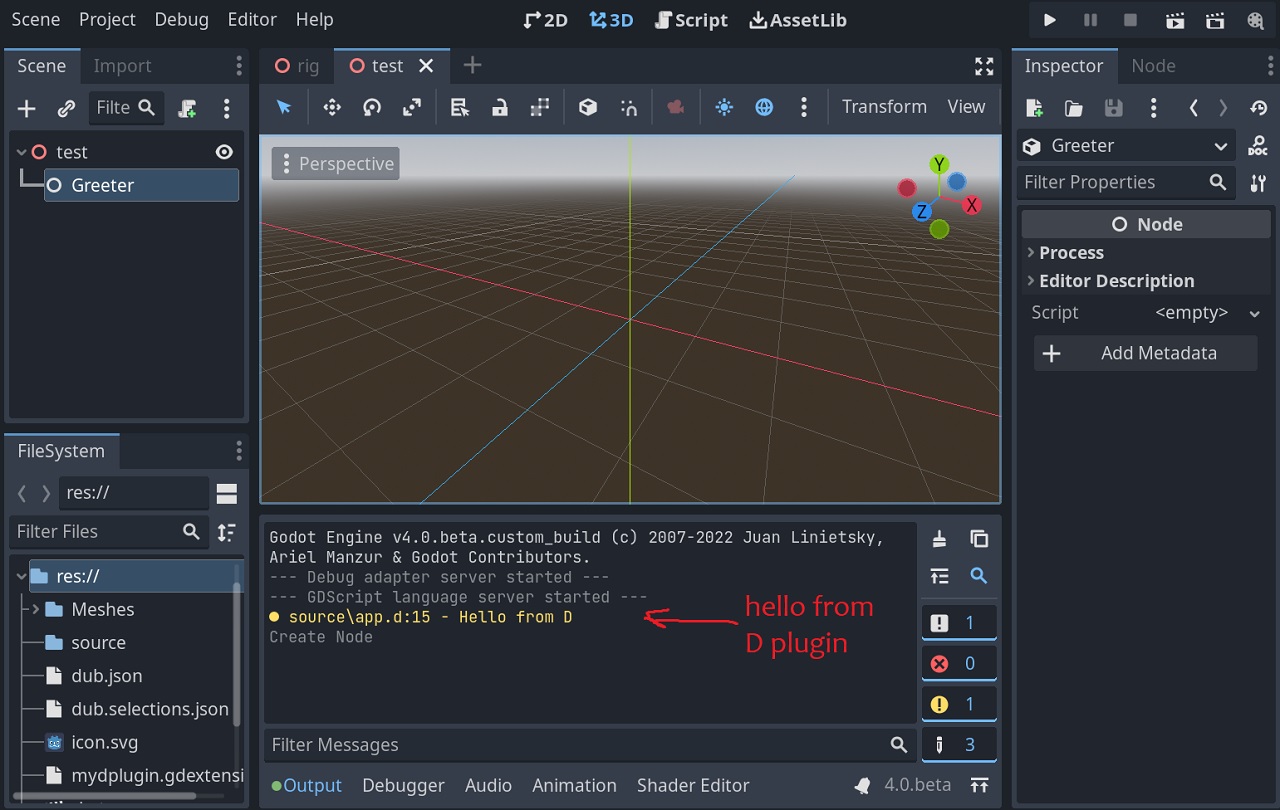
Nodeentity, navigate and pickGreeterclass - As soon as it gets added to the scene you should see Hello message in log in the panel below.
Run command dub run godot-dlang:init to initialize new project in current folder. This script will walk you through standard dub project set up and will create dub config, library entrypoint and gdextension plugin.
It is important that you use this script after creating godot project since you can't create godot project in non-empty directory.
Arguments:
-p, --path- Sets path for project to be initialized in.-i, --importc- Adds dflag to use C header instead of D bindings (advanced, use only if you know what you're doing).-c, --custom- Sets custom path for godot-dlang, can be used if you've cloned master branch.
Example:
# Initialize project in current directory:
dub run godot-dlang:init
# Initialize project in custom directory:
dub run godot-dlang:init -- --path path/to/folder
# Initialize project with custom godot-dlang path:
dub run godot-dlang:init -- --custom path/to/godot/dlang
# Initialize project with custom godot-dlang path in custom directory:
dub run godot-dlang:init -- -p folder/ -c godot-dlang/After running this script you'll have theese new files in selected folder:
├── dub.json/sdl # - Your dub config
├── projectname.gdextension # - GDExtension plugin
└── source/
└── lib.d # - Library entrypoint that contains "mixin GodotNativeLibrary!"- Remember that there still might be some bugs, sometimes confusing, sometimes blocking your progress, and sometimes even missing features
Enjoy your new game!
Godot's full script API can be used from D:
Godotsubmodules contain container, math, and engine structs likeVector3andString.- Other submodules of
Godotcontain bindings to Godot classes, auto-generated from the engine's API. These are the native classes scripts can be attached to. - These bindings use camelCase instead of snake_case.
// Change window to fullscreen example: // GDScript OS.set_window_fullscreen(false) // Would be: // D OS.setWindowFullscreen(false);
- D code should use D naming conventions (PascalCase for classes, camelCase for properties and methods).
The GDExtension API should be binary-compatible between Godot minor versions as in SemVer convention, so a D library built for Godot v4.0.0 should work with any v4.0.x versions but not guaranteed to work with v4.1.0 or later.
D bindings must be generated for your target Godot minor release version
(godot.exe --dump-extension-api).
Extension version properties can be checked to prevent newer functions from being called with older Godot binaries. For example:
import godot.apiinfo; // contains version information about bindings
if(VERSION_MINOR > 0) useNewGodotFunctions();
else doNothing();MIT - https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT
- GitHub repository - https://github.com/godot-dlang/godot-dlang
- GDExtension repository - https://github.com/godotengine/godot-headers
- C++ bindings these are based on - https://github.com/godotengine/godot-cpp
- D bindings these are based on - https://github.com/godot-d/godot-d
- Godot Engine - https://godotengine.org
- D programming language - https://dlang.org