Python script for illustrating Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). Inspired by the draw_convnet project [1].
Models can be visualized via Keras-like (Sequential) model definitions. The result can be saved as SVG file or pptx file!
python-pptx (if you want to save models as pptx)
pip install python-pptxKeras (if you want to convert Keras sequential model)
pip install kerasmatplotlib (if you want to save models via matplotlib)
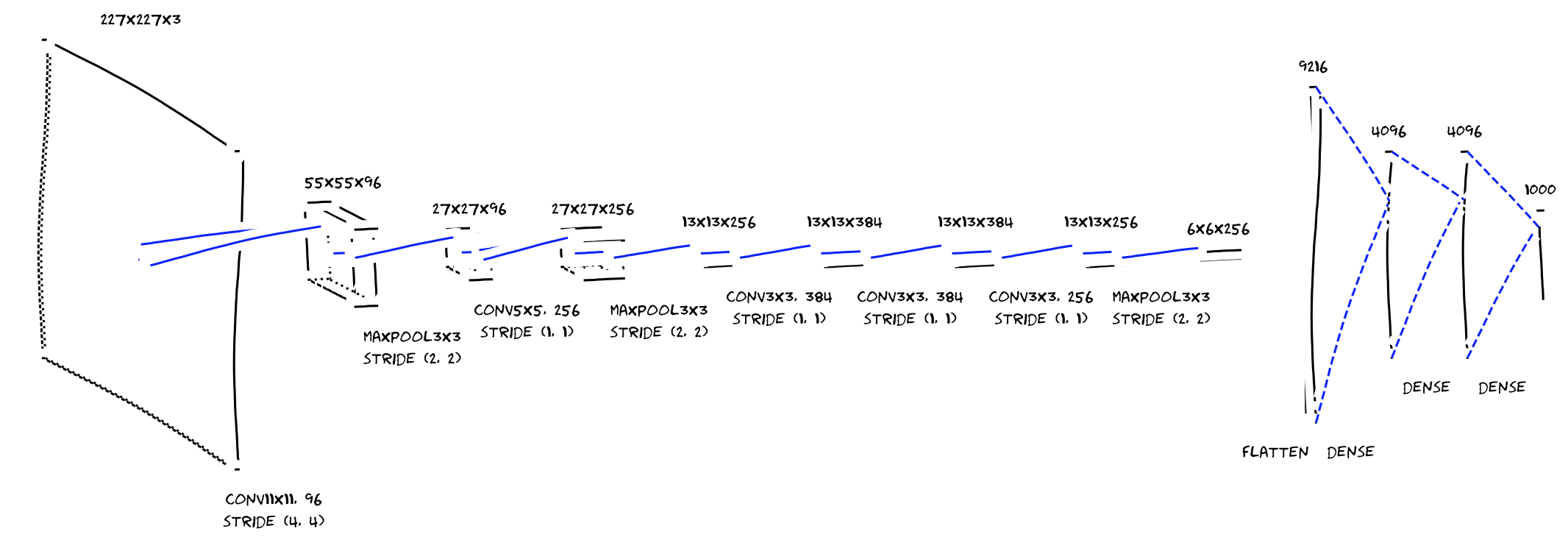
pip install matplotlibWrite a script to define and save a model. An example of visualizing AlexNet [2] is as follows.
from convnet_drawer import Model, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense
from pptx_util import save_model_to_pptx
from matplotlib_util import save_model_to_file
model = Model(input_shape=(227, 227, 3))
model.add(Conv2D(96, (11, 11), (4, 4)))
model.add(MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2)))
model.add(Conv2D(256, (5, 5), padding="same"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2)))
model.add(Conv2D(384, (3, 3), padding="same"))
model.add(Conv2D(384, (3, 3), padding="same"))
model.add(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2)))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(4096))
model.add(Dense(4096))
model.add(Dense(1000))
# save as svg file
model.save_fig("example.svg")
# save as pptx file
save_model_to_pptx(model, "example.pptx")
# save via matplotlib
save_model_to_file(model, "example.pdf")Result:
The other examples can be found here.
Keras sequential model can be converted to convnet_drawer.Model (thanks to @wakamezake).
Only Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense layers are supported for this conversion.
from keras_util import convert_drawer_model
from keras_models import AlexNet
from pptx_util import save_model_to_pptx
from matplotlib_util import save_model_to_file
# get Keras sequential model
keras_sequential_model = AlexNet.get_model()
model = convert_drawer_model(keras_sequential_model)
# save as svg file
model.save_fig("example.svg")
# save as pptx file
save_model_to_pptx(model, "example.pptx")
# save via matplotlib
save_model_to_file(model, "example.pdf")- Conv2D
Conv2D(filters=None, kernel_size=None, strides=(1, 1), padding="valid")- e.g.
Conv2D(96, (11, 11), (4, 4)))
- MaxPooling2D, AveragePooling2D
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=None, padding="valid")- e.g.
MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2)) - If
strides = None, stride is set to bepool_size.
- GlobalAveragePooling2D
GlobalAveragePooling2D()
- Flatten
Flatten()
- Dense
Dense(units)- e.g.
Dense(4096)
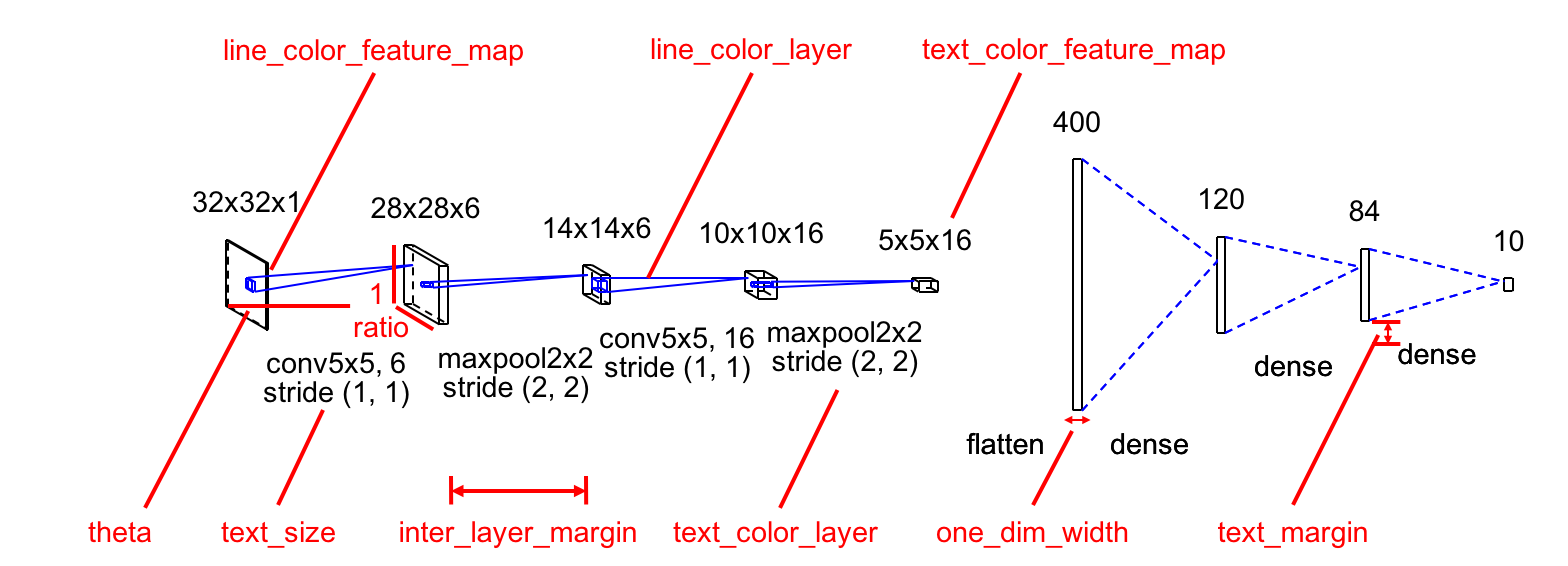
Visualization Parameters can be found in config.py.
Please adjust these parameters before model definition (see LeNet.py).
The most important parameter is channel_scale = 3 / 5.
This parameter rescale actual channel size c to c_ for visualization as:
c_ = math.pow(c, channel_scale)
If the maximum channel size is small (e.g. 512), please increase channel_scale.
Check how the other parameters works:
theta = - math.pi / 6
ratio = 0.7
bounding_box_margin = 10
inter_layer_margin = 50
text_margin = 10
channel_scale = 3 / 5
text_size = 14
one_dim_width = 4
line_color_feature_map = (0, 0, 0)
line_color_layer = (0, 0, 255)
text_color_feature_map = (0, 0, 0)
text_color_layer = (0, 0, 0)- Implement padding option for Conv2D and Pooling layers.
- Add some effects to Dense layer (and Flatten / GlobalAveragePooling2D).
- Automatically calibrate the scale of feature maps for better visibility.
- Move hard-coded parameters to a config file or options.
- Refactor Layer classes.
-
Draw with matplotlib? for other formats.The model is now directly saved as a pptx file.
LeNet
AlexNet
ZFNet
VGG16
AlexNet saved by matplotlib with plt.xkcd()
[1] https://github.com/gwding/draw_convnet
[2] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. E. Hinton, "ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks," in Proc. of NIPS, 2012.