This "All about PHP"-repository catches up its focus on all the PHP I've learned, commented and written through the years as a SAE-Web Development student with exercise lessons every week as well as tutorial videos on Youtube.
Direct Link to the place where I'm studying are you going to find HERE
What is PHP ?
-
PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely used and general-purpose open source scripting language that is specifically suited for web programming and can be embedded in HTML. GET MORE DETAILS HERE
-
PHP can generate dynamic page content
-
PHP can create, open, read, write, delete, and close files on the server
-
PHP can collect form data
-
PHP can send and receive cookies
-
PHP can add, delete, modify data in your database
-
PHP can be used to control user-access
-
Are you new to PHP? Check out the PHP DOCUMENTATION HERE
⚫🔴🟡 IMPORTANT: Comments in each file are commented in german⚫🔴🟡
| Topic | Content |
|---|---|
| Week 01 | direction , errortest , hello world , include() vs require() vs require_once() |
| Week 02 | Schreibweisen PHP - 3 Ways to integrate Arrays[] , Associative and Mutlidimensional Arrays[] , Blog Layout , include() folder |
| Week 03 | Reg-Formvalidation with style and basic design , $_get() vs $_post() Request , filter_var() + isset() vs empty() + implode() vs explode() |
| Week 04 | login.php WITH protected area , login.php (hashed) WITH protected area , login.php WITHOUT protected area , login.php with timeout session , hashing encryption lab , session vs cookie |
| Week 05 | Structure (Front Controller) , Structure (Basic) , Structure (Basic) + Dynamic Navigation + Admin Area |
| Week 06 | MySQL Database (Blog "Musteraufbau") , (demo files) working with MyPHPAdmin MySQL Database (CRUD Operations) |
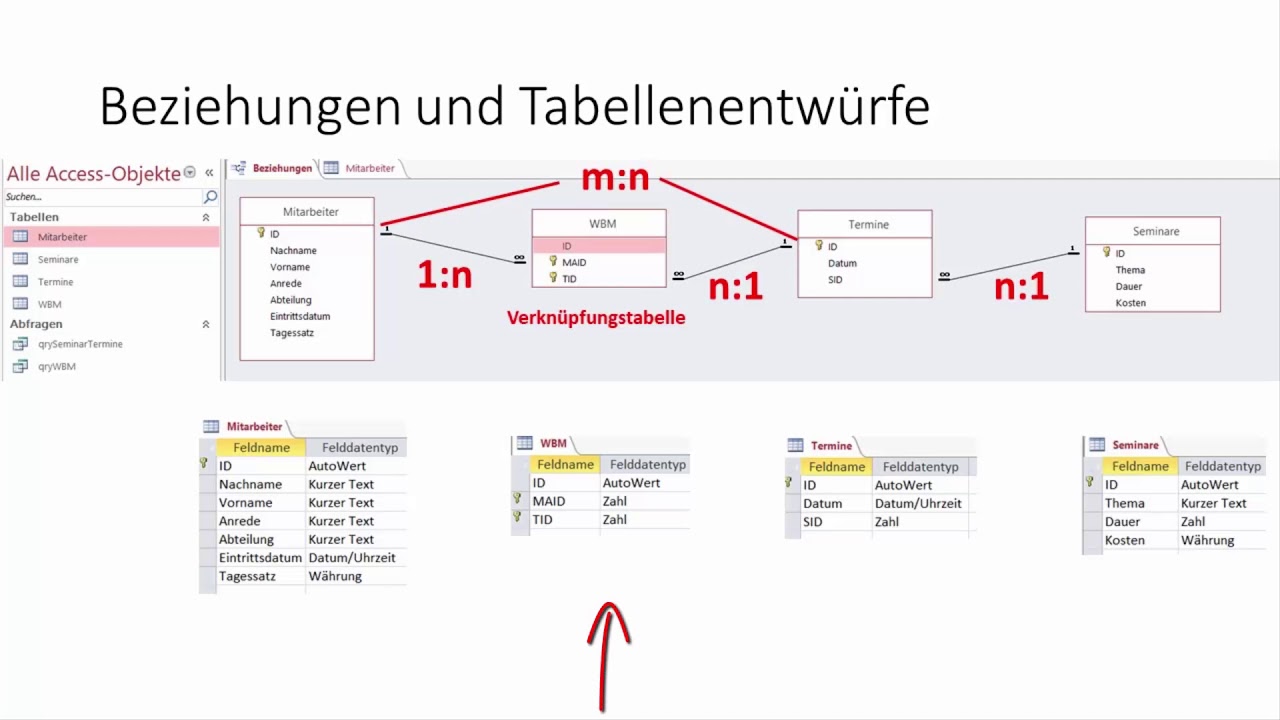
| Week 07 | TableReferences 1:1 / 1:N / N:M |
| Week 08 | MySQLi prepare()-statement to make user inputs more secure against SQL-Injections |
| Week 09 | "All in One"-File with: Registration and Login with MySQL Database management |
| Week 10 | Image Upload Basic Variant |
| Week 11 | Image Upload Advanced Variant |
| Week 12 | CKEditor for < textareas > , 2 versions included: WITH and WITHOUT Database |
| Week 13 | Datetime |
XAMPP - INSTALLIZATION:
- Use XAMPP Windows Systems. Its a local web-server (stack) for your local ideas and projects. DOWNLOAD XAMPP HERE
- Use MAMP if you're working on a MAC: DOWNLOAD MAMP HERE
- Use WAMP if you want to work with another stack: DOWNLOAD WAMP HERE
XAMPP - FIRST STEPS:
- Download and open xampp-control.exe
- Start Apache and MySQL
- Empty htdocs for the very first use. This will be your index
- Adjust XAMPP control panel for the very first use as well:
- Apache > Config > php.ini > Change to:
- I) display_error: on
- II) error_reporting: E_ALL
- Navigate through the files via htdocs and open it via Visual Studio Code to work with
- Visit your work in your browser. Lifeserver doesnt work, so write "localhost" in your URL of your browser instead
XAMPP - RUN YOUR FILES:
-
Open XAMPP control panel and start Apache and MySQL
-
Add the files you want to display in your browser to the htdocs folder by copying and pasting them there:
2.1 Explorer > htdocs > right click > paste
-
Open your browser and type in "localhost" in the URL of your browser > Click on the file you want to display (If you want to display a file in a subfolder, you have to type in the name of the subfolder in the URL of your browser)
-
To STOP XAMPP: stop Apache and MySQL in the XAMPP control panel again
💥TROUBLESHOOTING in XAMPP:
PROBLEM A: "How to Fix the XAMPP Error “MySQL Shutdown Unexpectedly”? SOLUTION
SOLUTION A:
1) XAMPP > Explorer > mysql > data > Make a copy of it and call it "data-old"
2) Delete the content in the "data" folder
3) Copy the content of the backup and paste it into the new "data" folder
🔵 CREATE DATABASE in PHPMyAdmin:
PHPMyAdmin = Web Based Tool // MySQL Workbench = Desktop Tool
- Open MyPhpAdmin within your URL window:
http://localhost/phpmyadmin/. Now you can create and structurize databases! - "Databases" > "Create New Database" (give server a command where to fetch data) > "select default charset" > "utf8-unicode-ci" > "Create"
- Additional infos about the path system:
- The file path is shown above (...)>(...)>(...)
- Path overview for selections is also displayed on the left in a tree diagram
- TIP: Use "right klick" on the desired subpage in the navigation on the left and open in new tab to work faster and cleaner
🔵 CREATE TABLE (contains all the data):
1.1 (Option 1): Create a table (make sure that you are in the database folder) by clicking the SQL field and use your SQL skills such as this example here:
CREATE TABLE users (
usersId int(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
usersName varchar(128) NOT NULL,
usersEmail varchar(128) NOT NULL,
usersUid varchar(128) NOT NULL,
usersPwd varchar(128) NOT NULL
);
1.2 (Option 2): "Create Table" (erzeuge Tabelle) > Select name column with appropriate labels for your project:
- A_I (AUTO INCREMENT) = "Incrementing itself" > Click on the first field of "IDcomment" = It becomes Primary (it receives a PRIMARY KEY)
- Add the suitable DATATYPES, here is a very short overview:
- VARCHAR is variable character limit. You should enter this, e.g. maximum 100 characters for the name (String based)
- TEXT = Write a lot of text without restriction. (String based)
- BOOLEAN = True or False as confirmation
- INT = data capability (length) of the ID. Be on the safe side with INT: If the character capacity is exceeded, there is no room for any further saving data (Numeric)
- TINYINT = (1 byte, 255 integer data) vs BIGINT (8 byte, Billions of integer data #) (Numeric)
- TIMESTAMP = as well as the default with "current_time": Display the current time on every save. (Dates) The "default" is an additional possibility to influence the default value (e.g. as defined: 0 = false)
- IMPORTANT: there are exact number data types that use integer data: To save space in the database, use the smallest data type that can reliably contain all possible values. For example, TINYINT would suffice for the age of a person, since no one can live more than 255 years. However, tinyint would not suffice for the age of a building, since a building can be more than 255 years old.
🟤 PRIMARY KEY vs FOREIGN KEY in PHPMyAdmin:
-
A key must be UNIQUE (A) and MINIMALLY (B) equipped with attributes. It is best to set the PRIMARY KEY at the ID, because:
A) IDs are most UNIQUE for the respective column and content
B) Attributes such as name, street etc. can occur twice. It is best to restrict ourselves to only one attribute
PRIMARY KEY = attribute which a line can be uniquely identified
FOREIGN KEY = Attribute that refers to the primary key of another table
=> courseId from the upper table receives a foreign key. It thus refers to the primary key of the smaller lower table, which happens to have the same name (but does not have to). We clearly refer to the primary key of the smaller table (contents of the columns also occur above, clear indication that it fits).=> Fun Fact: Underline means "Primary Key" in the table. It is therefore clear that studentId from the upper table is a primary key.
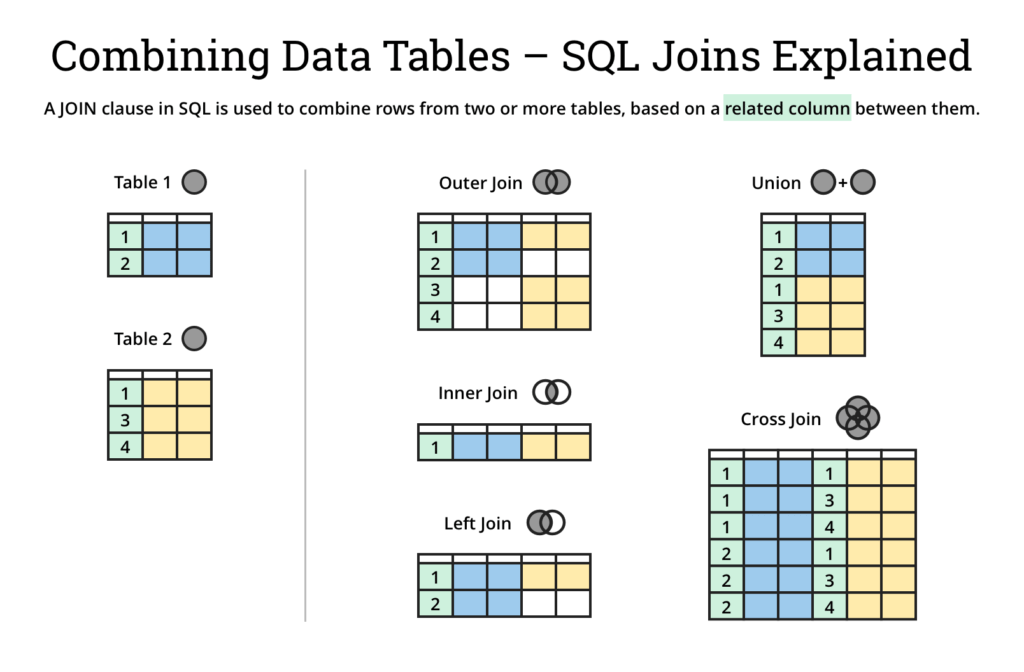
🟣 JOIN TABLES (Take care writing SQL)
- If TABLE1 and TABLE2 has the same name of the attribute, like "Hersteller" it's IMPORTANT you write the name like: TABLE1.Hersteller
IN GENERAL - The grey area means: Output matching values:
INNER JOIN = If the columns to be checked do not have a common value, the row is discarded (only column 1 in green is a RELATED COLUMN, 2,3,4 therefore are discarded and not shown):
SELECT *
FROM Table1 join Table2 (Table1,Table2 = Neue Schreibweise)
WHERE Table1.SpalteRelatedColumn = Table2.SpalteRelatedColumn
LEFT JOIN = The numbers in the first table (Table1) are focussed and listed. In addition, the overlapping contents (Table1 and Table2) are shown as we already know from the inner join:
SELECT *
FROM Table1 left join Table2
WHERE Table1.SpalteRelatedColumn = Table2.SpalteRelatedColumn
🟠 RENAME DATABASE in PHPMyAdmin:
PHPMyAdmin = Web Based Tool // MySQL Workbench = Desktop Tool
- click on your database which you want to rename > "Operationen"
- Scroll down to: "Datenbank umbenennen in"
- Rename it and confirm with "OK"
- IMPORTANT: Don't forget to rename your $dbname in your PHP-File as well if you have worked with VSC. This guarantees a perfect connection from VSC to your database at PHPMyADmin
🔵 CREATE ADDITIONAL TABLES in PHPMyAdmin:
1.1 (Variant 1): Open the database on the navigator on the left > Click "Neu" to ADD ANOTHER TABLE + FIELDS to your chosen database
1.2.(Variant 2): Open the database on the navigator on the left > Select "Struktur" from above > "Erzeuge Tablle" > Chose the amout of columns you want at Anzahl der Spalten and fill in the fields.
🔵 CREATE ADDITIONAL FIELDS in PHPMyAdmin:
Did you forgot an additional row of your table inside your database? Or did you get the request from your boss to add a further field subsequently?
- Open the database on the navigator on the left > Click on your table inside the database > Select
"Struktur"from above > Right above the "Indizes"-section: choose the amout of columns and the place where it should be added in your table (above which field of your table) > "OK"
🟢 IMPORT SQL-CONTENT - PHPMyAdmin:
- Check if you are on right folder for import! The centered folder structure at the top shows you where you are and additonally where you will import the SQL file!
-
"Import" > Select File (SQL format = perfect) - If you choose .sql file: select "SQL" > OK
- Successful Safe: all boxes must be green, otherwhise you'll receive an error
- Never forget to create a valid database before you import a SQL file
- SQL files cannot be overwritten. They can only be adjusted or completely deleted to integrate a new SQL file into the database
🟡 EXPORT SQL-CONTENT - PHPMyAdmin (Usually used as a backup):
- "Export" > (Export selected pieces) as a Backup for safety:
- Exportmethod "angepasst" for more options:
- "Objekterstellungsoptionen" = "Create Table" should be checked
- "Datenerstellungsoptionen" = "TRUNCATE" = doesnt have to be checked (proves files of existance)
- "Ausgabe" = "Safe data as file" should be checked as well
- "OK" to export as an SQL
🔴 DELETE DATABASE / TABLE (warning: this will delete everything, table and all the content!)
- To delete the DATABASE at "SQL", write in the SQL field => DROP DATABASE `` ; (Be sure to add the database name in the ' ' signs!)
- To delete the TABLE at "SQL", write in the SQL field => DROP TABLE `` ; (Be sure to add the table name in the ' ' signs!)
MENU BAR IN PHPMyAdmin shortly explained:
- BROWSE = Overview
- STRUCTURE = Column editing
- SQL = Data management
MySQL Tables (Which can be integrated in relations to other tables in many ways, such as 1:N or N:M)
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row 1 | Field | Field | Field | Field |
| Row 2 | Field | Field | Field | Field |
-
If a primary key column is marked with "AUTO_INCREMENT", then no value has to be set for this column when creating a row. The database system then "automatically sets a value" = "Auto_Increment"
-
We can thus create several tables, for example USERS, and assign the primary key of this ID there. The second table POSTS also receives an ID, a foreign key. We can relate these to each other and query (ger: "auslesen") them from multiple tables:
What is SQL ?
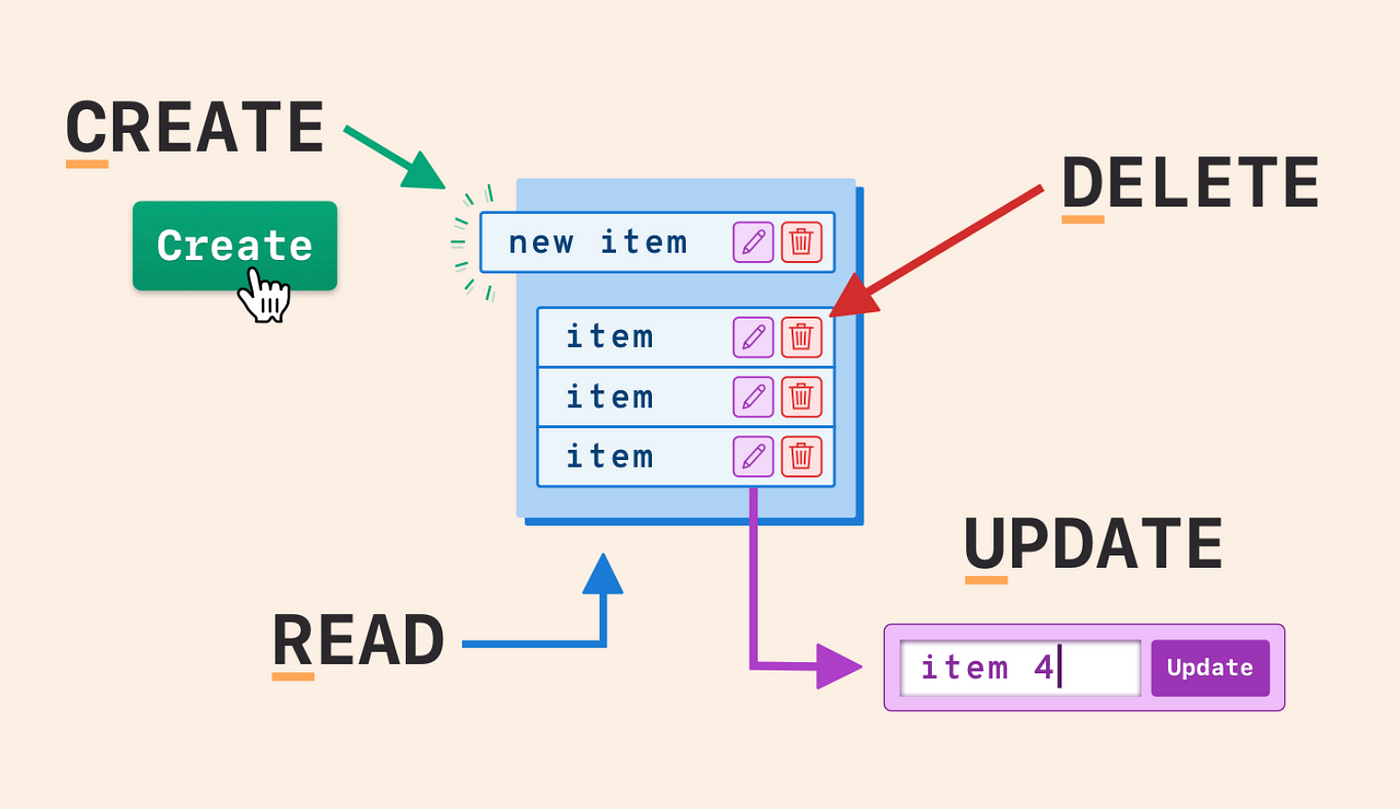
- As we know that we can use MySQL to use "structured query language" to store the data. SQL is the most popular language for adding, accessing and managing content in a database. MySQL provides a set of some basic but mostly essential operations that will help you to easily interact with the MySQL database at PHPMyAdmin. These operations are mostly known as CRUD, but I rather prefer to call them CUDR. Here is the reason why:
| Operation | Effect | Demo File |
|---|---|---|
| CREATE | Create Table Command | insert.php |
"INSERT INTO persons (familyname, firstname, place) VALUES ('peter', 'muster', 'mustertown')"; |
||
| UPDATE | Altering and changing content or structure of your table | edit.php |
"UPDATE persons SET familyname=`bohlen`, firstname=`dieter` WHERE id=201"; |
||
| DELETE | Delete Operations | delete.php |
"DELETE FROM persons WHERE id=201"; |
||
| READ | Retrieve and (re)-read the content of your table (*) | edit.php |
"SELECT * FROM persons WHERE familyname=`balboa` AND firstname= `rocky`"; |
||
| ---- | ------------------------------------------------------ | ---- |
| Connection to server database | connect.php | |
| Overview of the added data content | liste.php | |
| Delete a specific post (#) | delete.php?id= | |
| Edit a specific post (#) | edit.php?id= | |
| Delete a specific post (multiple functions in the script) | liste.php?delete= | |
| Edit a specific post (multiple functions in the script) | form.php?edit= |
-
The Demo Files are placed at Week_06
-
(*) CUDR instead of CRUD because you always OPERATE / MANIPULATE with "CDU" first and then (at the end) you "re-read" your changes to your table of your database with "R"!
-
(#) Each post will get its own ID: "delete.php?id=4" will delete the post with its ID=4 by pressing a delete button for example. Same thing for the edit button, you update and read this specific post for editing!
-
"mysqli" is an improved object-oriented extension of PHP for accessing MySQL databases.
Here is a short list of errors I had while I was writing PHP. If some of these errors may appear...well...now you know what the problem is and how you can fix it (hopefully)
▸"signup=empty"
- Make sure you wrote "mysqli_connect" and NOT "mysql_connect" in the .php file!
▸"unexpected }"
- If you get this error message: Parse error: syntax error, unexpected '}' Then it is because you forgot to close a ) or ; somewhere.
▸"unexpected ;"
- If you get this error message: Parse error: syntax error, unexpected ';' Then it is because you forgot to close a } or ) somewhere. Probably because you made a mistake with your parenthesis near the "empty()" functions in your signup script.
▸"hashed pwd error"
- If you get an error in the script when you hash the password, then it is because you decided not to follow my steps exactly in the video when I created the database table. Make sure you DON'T set the varchar() to a lower value! When you hash the password it will take up a lot of space in this column, and if you set a lower number then it won't fit!
▸"signup=success but database is empty?"
- Here there might be a few reasons for your error. 1st is that you made a syntax/spelling mistake in your code. 2nd reason is that MAMP seems to cause a lot of issues for people. Therefore try using XAMPP and make sure you write the same as me in the .php file.
▸"HTTP ERROR 500"
- HTTP ERROR 500 is a server error, meaning that you are most likely using an outdated version of apache or mysql (or in case you've forgot to start your apache and mysql server). Try updating your servers and make sure that you are using the latest version of PHP.
▸"Fatal error: Call to a member function bind_param() on boolean"
- The prepare() method can return false and you should check for that. As for why it returns false, perhaps the table name or column names (in SELECT or WHERE clause) are not correct. There is an issue with your query. The prepare() might return FALSE (a Boolean), but this generic failure message doesn't leave you much in the way of clues. BUT HERE COMES A POSSIBLE SOLUTION FOR IT:
▸"mysqli_stmt::$error -- mysqli_stmt_error — Returns a string description for last statement error"
- To get more informations about the error itself, use this to return a string containing the error message for the most recently invoked statement function that can succeed or fail:
mysqli_stmt_error(mysqli_stmt $statement): string
Here is an example of how to use it:
$stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($connection);
if (!mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt, $sql)) {
echo 'sql prepare error';
echo mysqli_stmt_error($stmt); // => Gives you closer information
}
Feel free to contact me if you've seen something wrong, found some errors or struggled on some mistakes! Always happy to have a clean sheet here! :)
0 Questions have been asked, 0 answers have been given, 0 changes have been made.
| Questions | Anwers | Changes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
How to Fix the XAMPP Error “MySQL Shutdown Unexpectedly”?
=> https://kinsta.com/knowledgebase/xampp-mysql-shutdown-unexpectedly/ (Step 2 worked for me)