This "All about React"-repository catches up its focus on all the Projects and Excercises I've made with React through the coding years, which is a good way to keep track of my progress. I will also add some useful information about React and its usage.
What is REACT?
React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It is maintained by Facebook and a community of individual developers and companies. React can be used as a base in the development of single-page or mobile applications. Its aim is to allow developers to easily create fast user interfaces for websites and applications alike.
| Topic | Content |
|---|---|
| 00_Basics | Basic React Testing with the combination of Tailwind CSS |
| 01_TodoList | Created a simple todo list with React and Tailwind CSS to learn how it works |
| 02_AI_Powered3DWebsite | Build and deploy an AI-Powered 3D Website using REACT.js and THREE.js - UNDONE |
Node.js - INSTALLATION: (Used for runtime environment for Javascript, script performs directly on the computer and not just on a web browser)
- https://nodejs.org/en/ (Recommend LTS = Long Term Support for an unbuggy / non-risky experience)
- Open a command line on your computer like BASH or CMD or POWERSHELL to check with "node --version" if you installed it correctly
- Node works via the command lines and is not executed via graphical components.
- Together with NODE we also get the tool "Node Package Manager" = NPM. NPM is used to install additional libraries and frameworks. You can check the version with "npm --version"
VSC REACT EXTENSION (Some react snippets)
-
Look for: ES7+ React/Redux/React-Native snippets in the extensions tab of Visual Studio Code
-
With those extensions you can use the following shortcuts to create a react component for example: rafc = React Arrow Function Component rafce = React Arrow Function Component with Export
TAILWINDCSS with Create React App (Slightly deprecated)
- Direct Link: https://tailwindcss.com/docs/guides/create-react-app
TAILWINDCSS with VITE (Up to date!)
- Direct Link: https://tailwindcss.com/docs/guides/vite
| STEP | COMMAND | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| X | Open in integrated terminal | Opens the terminal in VSC |
| X | $ node --version | Checks the node.js version (None if you havent installed it) |
| X | $ npm --version | Checks the NPM Version (Node Package Manager) |
| X | $ npx create-react-app todoapp --use-npm | Initializes your Project with a PRE-DEFINED WORKSPACE which I've called "todoapp" |
| X | $ cd todoapp | Changes the directory to the "todoapp" folder to start |
| X | $ npm start | Starts the React App |
| X | ctrl + c | Stops the React App |
VITE = Is a faster way to install the package to start a project. Vite uses a native ES module based build pipeline that is significantly faster than traditional bundlers like Webpack or Parcel. The browser refreshes as you edit files, which means you can develop without waiting for a build to finish.
NOTE: Step 1 to 4 are only needed if you havent installed Vite before. If you have installed it before and want to START A NEW PROJECT, you can skip to step 5! But first create a new MAIN FOLDER to integrate your project in like "01_React" or "02_TodoApp" and so on.
| STEP | COMMAND | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Open in integrated terminal | Opens the terminal in VSC |
| 2 | $ node --version | Checks the node.js version (None if you havent installed it) |
| 3 | $ npm --version | Checks the NPM Version (Node Package Manager) |
| 4 | $ npm install -g vite | Installs Vite |
| 5 | $ npm create vite@latest | Asks for a project name. Choose a name and type in like for example "todoapp" > asks for a "selection of framework" > "react" > "Javascript" |
| 6 | $ cd todoapp | Changes the directory to the "todoapp" folder to start |
| 7 | $ npm install | Installs all the dependencies |
| 8 | $ npm run dev | Starts the React App |
| 9 | ctrl + Click on the localhost link | Given in the terminal, click on the link like "http:// localhost:5173/" to open a new window in the browser |
| 0 | ctrl + c | Stops the React App |
DOM = The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming API for HTML and XML documents. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated.
=> VITE will overwrite some folderstructure names, so don't be confused if it looks different than the general structre as shown down below!
FOLDERSTRUCTURE or a project with React:
- node_modules = All additional external Libraries used for our React App which are installed and handeled via NPM. No need to touch this folder.
- public = All the files which are public and can be accessed by everyone
- favicon.ico = Icon for our Webpage
- index.html = FIRST OPENING FILE and binds the
<body>-part from index.js. Everything will be integrated in this id="root" div down below this script. No further changes needed. - manifest.json = Configuration for our Webapp (Name, Description, Icon, etc.)
- robots.txt = Configuration for Search Engines (What should be indexed and what not)
- src = All the files which are private and can only be accessed by us (this is our workspace)
- App.css = Styling for our App.js
- App.js = Main Component which is called in index.js
- App.test.js = Testfile for our App.js
- index.css = Styling for our index.js
- index.js = ROOT COMPONENT: First opening file which binds the
<body>-part from index.html. Everything will be integrated in this id="root" div down below this script. No further changes needed. - logo.svg = Logo for our Webpage
- reportWebVitals.js = Performance measurement for our Webpage
- setupTests.js = Testfile for our App.js
What are COMPONENTS?
- (I would personally recommend to create a folder called "components" in the "src" folder and add all your components in there. This way you can keep your code clean and structured).
-
React is a component based framework which means that we can create components and use them in other components. This is the way how we can create a modular and reusable code.
-
Components are independent and reusable bits of code. They serve the same purpose as JavaScript functions, but work in isolation and return HTML. Components come in two types, Class components and Function components.
-
Functional components are basically just JavaScript functions. They accept arbitrary inputs (called “props”) and return React elements describing what should appear on the screen.
What is JSX?
-
Combines HTML and JavaScript to get a a functionable application.
-
Usually, React components are written in JavaScript. But, JSX is a syntax extension to JavaScript. It is a syntax that allows us to write HTML elements in JavaScript and place them in the DOM without any createElement() and/or appendChild() methods. JSX is a preprocessor step that adds XML syntax to JavaScript. It is not necessary to use JSX, but it is recommended to use it with React to describe what the UI should look like. JSX may remind you of a template language, but it comes with the full power of JavaScript.
-
If you take a look at the components up there: app.js got such HTML content while App.css got the styling for it. Index.js imports the App.js and binds it to the id="root" div in index.html. This is the way how React works.
How do we STYLE COMPONENTS? (with TailwindCSS for example)
- ...
How do COMPONENTS COMMUNICATE?
- ...
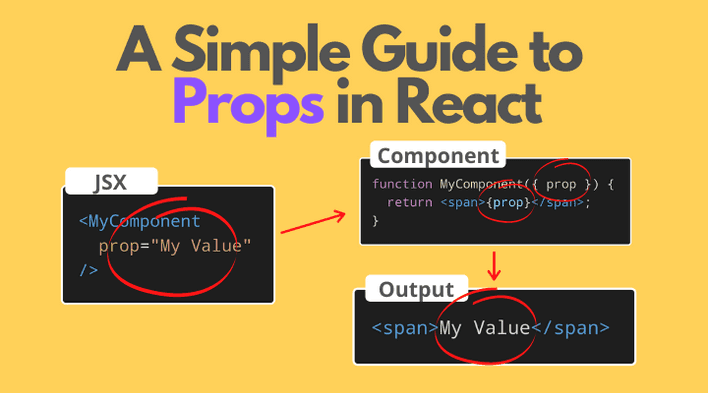
What are PROPS and STATES?
- ...
What are REACT HOOKS?
- ...
-
Get the documentation of installing HERE
-
Be sure to download the Tailwind CSS Extension for VS Code to get the IntelliSense for Tailwind CSS
-
IMPORTANT NOTE: If you're working with Tailwind CSS, the folder structure (as shown in Step 2 above) will be different:
-
src = Especially SRC will be a bit different after you've done step 1 to 6:
- App.css = Styling for our App.js (But not needed if you're working with utility classes)
- App.jsx = Main Component
- index.css = Where we now define utility base, components and utilities
- main.jsx = Root rendering component
- index.html = Where we import our main.jsx
- tailwind.config.js = Where we configure Tailwind CSS
| STEP | COMMAND | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $ npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer | Install Tailwind CSS |
| 2 | $ npx tailwindcss init -p | Initialize Tailwind CSS with a post config file to configurate stuff |
| 3 | Copy and replace the following code into the tailwind.config.js file: | Down below: |
/** @type {import('tailwindcss').Config} */
module.exports = {
content: [
"./src/**/*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}",
],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
}| STEP | COMMAND | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Copy and replace the following code into "src" > "index.css" | Down below: |
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;| STEP | COMMAND | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Copy the h1-html code below into "src" > "App.jsx" | Down below: |
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div className="App">
<!-- Over here we start using Tailwind’s utility classes to style our content -->
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold underline bg-red-500">Hello world!</h1>
<!-- Copy-END -->
</div>
);
}| STEP | COMMAND | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| x | $ npm run start | Run the process with create react app OR: |
| 6 | $ npm run dev | Run the process with VITE |
Feel free to contact me if you've seen something wrong, found some errors or struggled on some mistakes! Always happy to have a clean sheet here! :)
0 Questions have been asked, 0 answers have been given, 0 changes have been made.
| Questions | Anwers | Changes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
"How to fix Unknown at rule @tailwindcss (unknownAtRules) in VS Code?"
- Go to the settings of VS Code ("File" > "Preferences" > "Settings")
- Write "unkno" into the search bar for "unknownAtRules"
- Change "warning" to "ignore" and save the changes at "CSS > Lint: Unknown at rules"-section