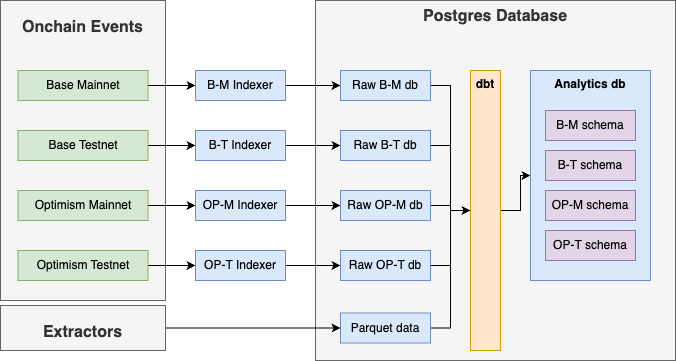
A collection of services to index, store, and transform data related to Synthetix smart contracts. A summary of each service is provided below. If you would like more information about running each of these services, visit the README in the respective directory.
At a high level, the data stack contains a set of services to listen to onchain events, store that event data in a Postgres database, then transform and aggregate that data into a format that is useful for analytics.
Read more about each service:
- Database - A Postgres database used to store raw and transformed data.
- Indexers - Blockchain indexers using Subsquid archives to index Synthetix smart contracts. These indexers are used to populate a Postgres database with raw event log data.
- Extractors - Scripts that extract blockchain data using
eth_callRPC calls and cryo. Data is stored in the aparquet-datadirectory, and will be imported into the Postgres database using the Transformers service. - Transformers - Services that transform raw event log data into a format that is more useful for querying. These services are used to populate a Postgres database with transformed data using dbt.
The services are all managed using docker compose. Review the docker-compose.yml file to view the services that will run on startup. Some of these services require configuration through environment variables, which should be copied and populated in a .env file. In the root directory use these to configure your environment:
NETWORK_X_RPC: The RPC endpoint for a specified network. ReplaceXwith the network id (ex. 1 for Ethereum mainnet, 10 for Optimism mainnet).PG_PASSWORD: The password for the admin user of the Postgres database.READONLY_PASSWORD: The password for a configured read-only user, used for dashboards. Change this password and runmake reset-pwto update the user's password.DB_PORT: The port that will be used to expose the Postgres database. If left blank, the database will only be exposed to the docker network.
Once you have configured your environment, run docker compose up -d --build to build and run the services in detached mode. By default, the service will start a Postgres database, indexers for each network, and an instance of Airflow. Each indexer will write data to a database corresponding with the network name (ex. base_mainnet). You can view the logs for each service using docker compose logs -f <service-name>.
See the data tools for dashboards that consume this data.
To populate the parquet-data directory with data, you must run the extractors. These scripts will run the eth_call RPC method for each of the specified calls in the extractors/main.py file. To run the extractors, use the following command:
make extractYou can view the data in the parquet-data directory, which should contain both raw and clean directories populated with data for each network.
To simplify queries and transformed data, you must run the transformers to populate the analytics database. This happens in two steps, first by wrapping the raw tables as foreigns tables in the analytics database, then running dbt for each of the relevant schemas. To do this, run:
make build # build the docker image for the transformers
make wrap # wrap the raw tables as foreign tables in the analytics database
make import # import the data from the parquet files into the database
make dbt # run dbt for each networkYou should see output confirming that dbt has run for each network, and created a set of tables and views in the analytics database.