This package contains utilities for prepping PyTorch audio models for use in Audacity. More specifically, it provides abstract classes for you to wrap your waveform-to-waveform and waveform-to-labels models (see the Deep Learning for Audacity website to learn more about deep learning models for audacity).
- Downloading Audacity with Deep Learning
- Installing
- Contributing Models to Audacity
- Choosing an Effect Type
- Model Metadata
- Making Your Model Built-In to Audacity
- Debugging Your Model in Audacity
- Example - Waveform-to-Waveform
- Examples
Our work has not yet been merged to the main build of Audacity, though it will be soon. You can keep track of its progress by viewing our pull request. In the meantime, you can download an alpha version of Audacity + Deep Learning here.
You can install audacitorch using pip:
pip install audacitorch
audacitorch requires for your model to be able to run in Torch 1.9.0, as that's what the Audacity torchscript interpreter uses.
Audacity is equipped with a wrapper framework for deep learning models written in PyTorch. Audacity contains two deep learning tools: Deep Learning Effect and Deep Learning Analyzer.
Deep Learning Effect performs waveform to waveform processing, and is useful for audio-in-audio-out tasks (such as source separation, voice conversion, style transfer, amplifier emulation, etc.), while Deep Learning Analyzer performs waveform to labels processing, and is useful for annotation tasks (such as sound event detection, musical instrument recognition, automatic speech recognition, etc.).
audacitorch contains two abstract classes for serializing two types of models: waveform-to-waveform and waveform-to-labels. The classes are WaveformToWaveformBase, and WaveformToLabelsBase, respectively.
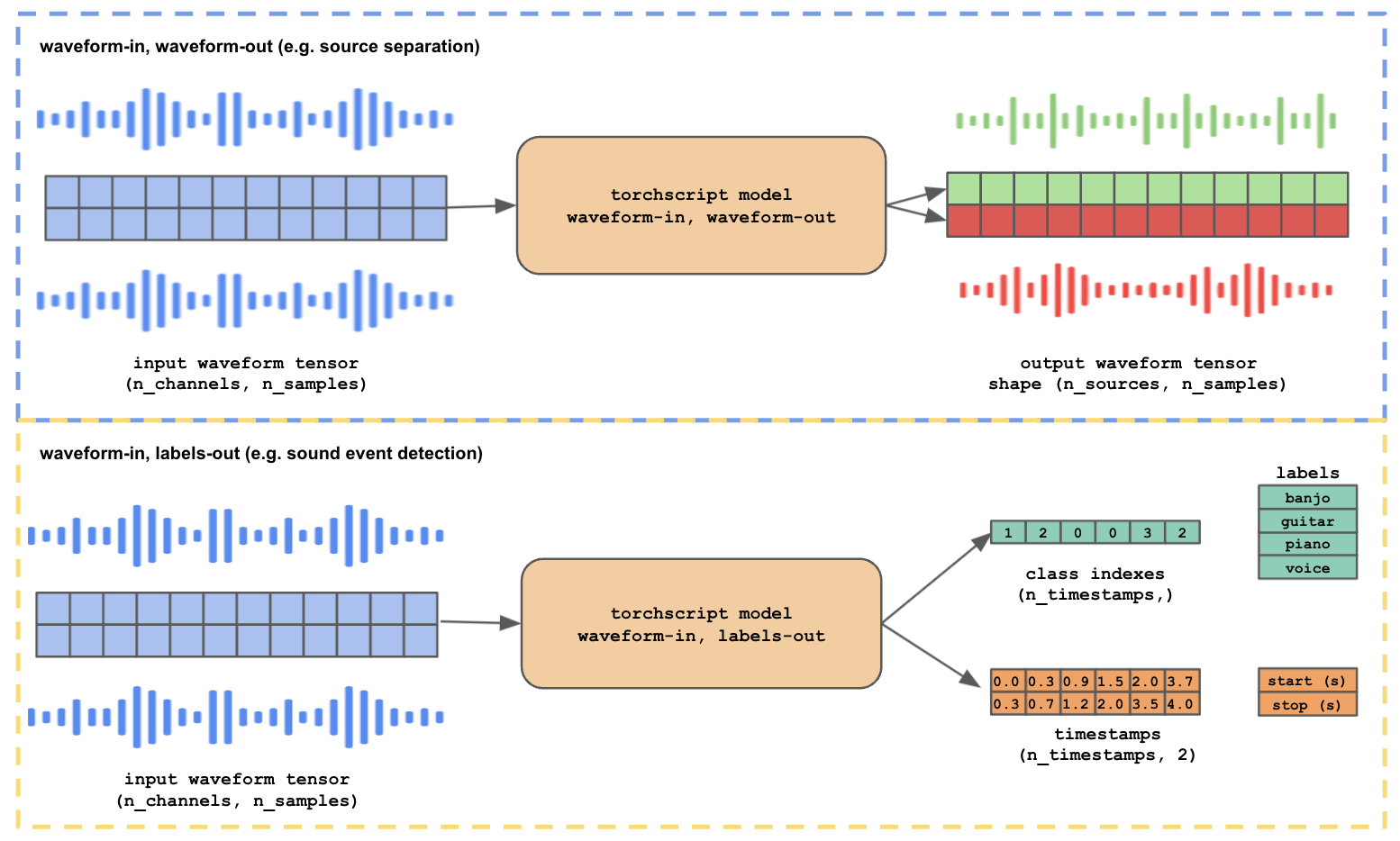
As shown in the effect diagram, Waveform-to-waveform models receive a single multichannel audio track as input, and may write to a variable number of new audio tracks as output.
Example models for waveform-to-waveform effects include source separation, neural upsampling, guitar amplifier emulation, generative models, etc. Output tensors for waveform-to-waveform models must be multichannel waveform tensors with shape (num_output_channels, num_samples). For every audio waveform in the output tensor, a new audio track is created in the Audacity project.
As shown in the effect diagram, Waveform-to-labels models receive a single multichannel audio track as input, and may write to an output label track as output. The waveform-to-labels effect can be used for many audio analysis applications, such as voice activity detection, sound event detection, musical instrument recognition, automatic speech recognition, etc. The output for waveform-to-labels models must be a tuple of two tensors. The first tensor corresponds to the class indexes for each label present in the waveform, shape (num_timesteps,). The second tensor must contain timestamps with start and stop times for each label, shape (num_timesteps, 2).
If your model uses a spectrogram as input/output, you'll need to wrap your forward pass with some torchscript-compatible preprocessing/postprocessing. We recommend using torchaudio, writing your own preprocessing transforms in their own nn.Module, or writing your PyTorch-only preprocessing and placing it in WaveformToWaveform.do_forward_pass or WaveformToLabels.do_forward_pass. See the compatibility section for more info.
Once you have chosen the appropriate class type for your model from the provided audacitorch Deep Learning Effect and the Deep Learning Analyzer classes, you will need to create a model file for use in Audacity. This model file allows a trained model to be executed in Audacity.
There are several methods available to create a file for an executable deep learning model. The purpose of serializing the model into a file is to enable our C++ code to execute your model. To serialize a model, our framework utilizes files generated from TorchScript. An important note is that TorchScript does not facilitate model training. When investigating TorchScript, you may also come across the term LibTorch, which is a PyTorch C++ API. LibTorch contains the core components of PyTorch, allowing TorchScript files to be executed in C++. However, you do not need to interact directly with LibTorch to serialize your model.
TorchScript enables the serialization of PyTorch code and is included with the PyTorch module - no additional modules are required. Currently, the deep learning tools for Audacity do not support models running on the GPU. More information on TorchScript can be found in the PyTorch documentation.
TorchScript features a JIT module, where JIT stands for Just-In-Time Compiler. The TorchScript JIT analyzes PyTorch code and translates it into TorchScript. There are two methods for converting PyTorch code into TorchScript:
-
Tracing: torch.jit.trace constructs the computational graph of your model by tracing the path of sample inputs through your model.
-
Scripting: This method parses the PyTorch code to compile a graph for TorchScript. Scripting is a more robust method for generating a TorchScript version of your model, as tracing can overlook certain logic embedded in the Python code of your model.
These two approaches can be combined, with more information available in the TorchScript documentation. We recommend using TorchScript scripting whenever possible for more robust model serialization.
Serializing a model can be a challenging task with many unique edge cases. To help you navigate this process, we have provided several examples.
Certain details about the model, such as its sample rate, tool type (e.g. waveform-to-waveform or waveform-to-labels), list of labels, etc. must be provided by the model contributor in a separate metadata.json file. In order to help users choose the correct model for their required task, model contributors are asked to provide a short and long description of the model, the target domain of the model (e.g. speech, music, environmental, etc.), as well as a list of tags or keywords as part of the metadata. Note that you do not need to manually create a metadata file, we provide utility function to automatically create and test metadata files from a Python dictionary. For an example of creating a metadata file from a Python dictionary, see here.
required fields:
sample_rate(int)- range
(0, 396000) - Model sample rate. Input tracks will be resampled to this value.
- range
domains(List[str])- List of data domains for the model. The list should contain any of the following strings (any others will be ignored):
["music", "speech", "environmental", "other"]
- List of data domains for the model. The list should contain any of the following strings (any others will be ignored):
short_description(str)- max 60 chars
- short description of the model. should contain a brief message with the model's purpose, e.g. "Use me for separating vocals from the background!".
long_description(str)- max 280 chars
- long description of the model. Shown in the detailed view of the model UI.
tags(List[str])- list of tags (to be shown in the detailed view)
- each tag should be 15 characters max
- max 5 tags per model.
labels(List[str)- output labels for the model. Depending on the effect type, this field means different things
- waveform-to-waveform
- name of each output source (e.g.
drums,bass,vocal). To create the track name for each output source, each one of the labels will be appended to the mixture track's name.
- name of each output source (e.g.
- waveform-to-labels:
- This should be classlist for model. The class indexes output by the model during a forward pass will be used to index into this classlist.
effect_type(str)- Target effect for this model. Must be one of
["waveform-to-waveform", "waveform-to-labels"].
- Target effect for this model. Must be one of
multichannel(bool)- If
multichannelis set totrue, stereo tracks are passed to the model as multichannel audio tensors, with shape(2, n). Note that this means that the input could either be a mono track with shape(1, n)or stereo track with shape(2, n). - If
multichannelis set tofalse, stereo tracks are downmixed, meaning that the input audio tensor will always be shape(1, n).
- If
By default, users have to click on the Add From HuggingFace button on the Audacity Model Manager and enter the desired repo's ID to install a community contributed model. If you, instead, would like your community contributed model to show up in Audacity's Model Manager by default, please open a request here.
Here's a minimal example for a model that simply boosts volume by multiplying the incoming audio by a factor of 2.
We can sum up the whole process into 4 steps:
- Developing your model
- Wrapping your model using
audacitorch - Creating a metadata document
- Exporting to HuggingFace
First, we create our model. There are no internal constraints on what the internal model architecture should be, as long as you can use torch.jit.script or torch.jit.trace to serialize it, and it is able to meet the input-output constraints specified in waveform-to-waveform and waveform-to-labels models.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MyVolumeModel(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# do the neural net magic!
x = x * 2
return xPyTorch makes it really easy to deploy your Python models in C++ by using torchscript, an intermediate representation format for torch models that can be called in C++. Many of Python's built-in functions are supported by torchscript. However, not all Python operations are supported by the torchscript environment, meaning that you are only allowed to use a subset of Python operations in your model code. See the torch.jit docs to learn more about writing torchscript-compatible code.
If your model computes spectrograms (or requires any kind of preprocessing/postprocessing), make sure those operations are compatible with torchscript, like torchaudio's operation set.
Useful links:
- Torchscript reference
- Pytorch's tutorial on torchscript models
- A 1:1 mapping of the features in python to their support in torchscript
- (recommended) Mastering Torchscript: Tracing vs Scripting, Device Pinning, Direct Graph Modification
Now, we create a wrapper class for our model. Because our model returns an audio waveform as output, we'll use WaveformToWaveformBase as our parent class. For both WaveformToWaveformBase and WaveformToLabelsBase, we need to implement the do_forward_pass method with our processing code. See the docstrings for more details.
from audacitorch import WaveformToWaveformBase
class MyVolumeModelWrapper(WaveformToWaveformBase):
def do_forward_pass(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# do any preprocessing here!
# expect x to be a waveform tensor with shape (n_channels, n_samples)
output = self.model(x)
# do any postprocessing here!
# the return value should be a multichannel waveform tensor with shape (n_channels, n_samples)
return outputAudacity models need a metadata file. See the metadata spec to learn about the required fields.
metadata = {
'sample_rate': 48000,
'domain_tags': ['music', 'speech', 'environmental'],
'short_description': 'Use me to boost volume by 3dB :).',
'long_description': 'This description can be a max of 280 characters aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.',
'tags': ['volume boost'],
'labels': ['boosted'],
'effect_type': 'waveform-to-waveform',
'multichannel': False,
}All set! We can now proceed to serialize the model to torchscript and save the model, along with its metadata.
from pathlib import Path
from audacitorch.utils import save_model, validate_metadata, \
get_example_inputs, test_run
# create a root dir for our model
root = Path('booster-net')
root.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
# get our model
model = MyVolumeModel()
# wrap it
wrapper = MyVolumeModelWrapper(model)
# serialize it using torch.jit.script, torch.jit.trace,
# or a combination of both.
# option 1: torch.jit.script
# using torch.jit.script is preferred for most cases,
# but may require changing a lot of source code
serialized_model = torch.jit.script(wrapper)
# option 2: torch.jit.trace
# using torch.jit.trace is typically easier, but you
# need to be extra careful that your serialized model behaves
# properly after tracing
example_inputs = get_example_inputs()
serialized_model = torch.jit.trace(wrapper, example_inputs[0],
check_inputs=example_inputs)
# take your model for a test run!
test_run(serialized_model)
# check that we created our metadata correctly
success, msg = validate_metadata(metadata)
assert success
# save!
save_model(serialized_model, metadata, root)At this point, your directory structure should look like this:
/booster-net/
/booster-net/model.pt
/booster-net/metadata.jsonThis will become the HuggingFace repository for your Audacity model.
Inside your HuggingFace repository, make sure to create a README.md file. After doing this, your directory structure should now look like:
/booster-net/
/booster-net/model.pt
/booster-net/metadata.json
/booster-net/README.mdIn your HuggingFace repository's README.md file, you'll need to add an audacity tag in the YAML metadata. This ensures that your model will appear under the "Explore" tab in Audacity's Deep Learning Tools. To add the audacity tag, insert the following lines at the top of your README.md file:
---
tags:
- audacity
---Great job! Now it's time to push your changes to HuggingFace. For more information on adding a model to the HuggingFace model hub, check out their documentation.
After serializing, you may need to debug your model inside Audacity, to make sure that it handles inputs correctly, doesn't crash while processing, and produces the correct output.
While debugging, make sure your model isn't available through other users through the Explore HuggingFace button by temporarily removing the audacity tag from your README file.
If your model fails internally while processing audio, you may see something like this:

To debug, you can access the error logs through the Help menu, in Help->Diagnostics->Show Log.... Any torchscript errors that may occur during the forward pass will be redirected here.
-
Demucs Denoiser: In this example, we guide you through implementing the
do_forward_passmethod of theWaveformToWaveformBaseclass, serializing the Demucs denoiser using the TorchScript scripting method, creating the model metadata (covered in the section below), and uploading to Huggingface. We illustrate how, in some instances, you may need to modify the original model code to properly serialize the model, this is done in the notebooks/denoiser/denoiser.py file. The model's source code is included for your reference. -
FCNF0 ++ Pitch Estimation: In this case, we guide you through implementing the
get_timestamps&do_forward_passmethods of theWaveformToLabelsBaseclass, serializing the FCNF0 ++ Pitch Estimator using the TorchScript scripting method, and creating the model metadata. The model's source code is also provided for your reference located in the file notebooks/pitch/pitch.py. -
Asteroid Source Separation Model: For this example, we download a pretrained model from the Asteroid Python module, create metadata for the model, inherit from the
WaveformToWaveformBaseclass, show you how to trace the model with dummy inputs, and demonstrate how to script the model. -
S2T-MEDIUM-LIBRISPEECH-ASR by Changhan Wang and Yun Tang and Xutai Ma and Anne Wu and Dmytro Okhonko and Juan Pino: In this last example, we guide you through the process of wrapping a language model in the
WaveformToLabelsBaseclass, creating model metadata, and tracing this model since scripting is not feasible in this case.