💡 Our unforgeable watermark has been integrated into MarkLLM, an open-source toolkit for LLM watermarking. You can now try out our watermarking method in the MarkLLM repository!
- python 3.9
- pytorch
- others:
pip install -r requirements.txt
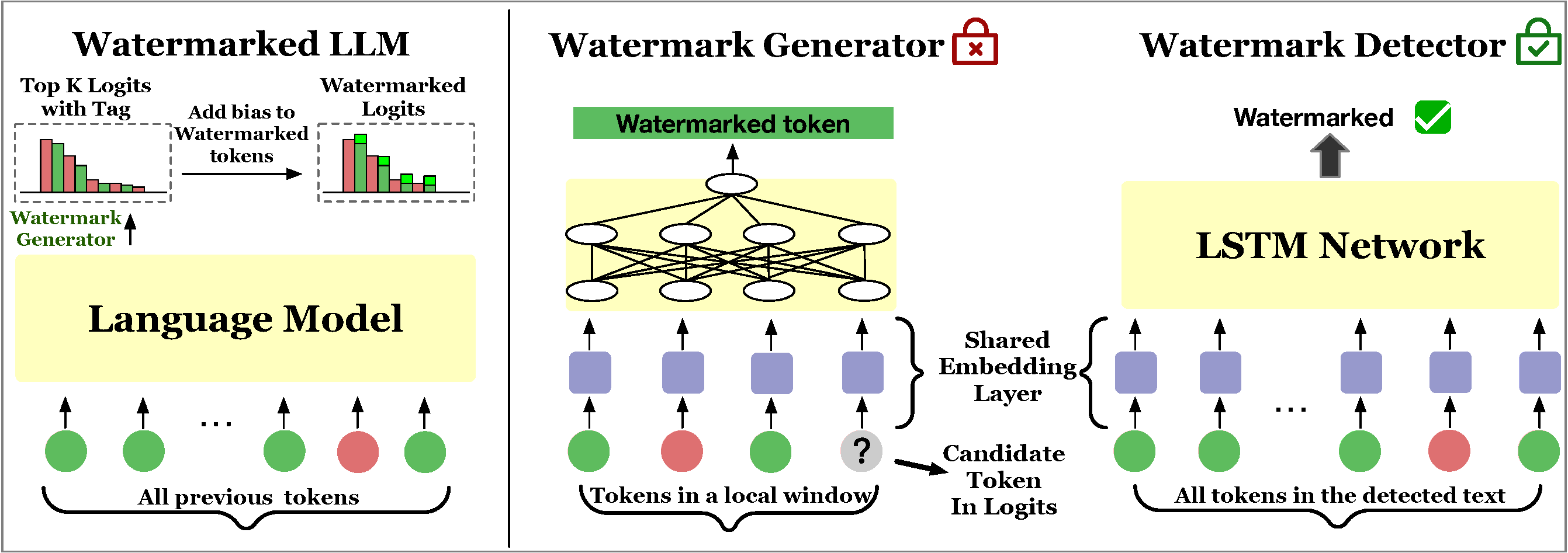
We need to train the watermark generator network in order to divide the red/green list evenly (approximately half green and half red).
python generate_data.py --bit_number 16 --window_size 3 --sample_number 2000 --output_file ./train_generator_data/train_generator_data.jsonlThe value of bit_number depends on the LLM you choose to use. For example, gpt2 has a vocabulary size of 50,257 (bit_number=16.
python model_key.py --data_dir ./train_generator_data/train_generator_data.jsonl --bit_number 16 --model_dir ./model/ --window_size 3 --layers 5-
generate training data:
watermark.generate_and_save_train_data(args.train_num_samples, args.output_dir)
- LLM is not used in this step.
- We randomly sample 10,000 token id sequences of length 200 and calculate z-score using the watermark generator (judging whether each token is green or not).
-
generate testing data:
watermark.generate_and_save_test_data(args.llm_name, args.dataset_name, args.output_dir, args.sampling_temp, args.max_new_tokens)
- LLM is used in this step.
- We use the validation set of c4 and dbpedia for experiments (you can find them in
./original_data). - Text 1-500 in c4 and text 1-500 in dbpedia are selected to generate testing data, with prompt length of 30 and new-generated text length of 200.
python watermark_model.py --bit_number 16 --train_num_samples 10000 --dataset_name c4 --llm_name gpt2 --output_dir ./data --model_dir ./model/ --window_size 3 --layers 5 --use_sampling True --sampling_temp 0.7 --n_beams 0 --max_new_tokens 200 --delta 2.0python detector.py --llm_name gpt2 --bit 16 --window_size 3 --input ./data --model_file ./model/sub_net.pt --output_model_dir ./model/ --layers 5 --z_value 4In directory ./experiments/main_experiments/, we provide the trained watermark generator model of main experiments, together with the training data and testing data that are already generated. For each experiment setting (llm: gpt2/opt-1.3b/llama-7b, top-k/beam search), 500 sentences of watermarked text (tagged as 1) and 500 sentences of the corresponding unwatermarked text (natural corpus, tagged as 0) are provided in test_data.jsonl.
You can train and test our private watermark detector simply by:
- changing line 122 in
detector.pyinto:
train_data = prepare_data(os.path.join('./experiments/train_and_test_data/', 'train_data.jsonl'), train_or_test="train", bit=_bit_number, z_value=z_value, llm_name=llm_name)
- running:
python detector.py --llm_name gpt2 --bit 16 --window_size 5 --input ./experiments/train_and_test_data/gpt2/c4_topk/ --model_file ./experiments/generator_model/sub_net.pt --output_model_dir ./experiments/detector_model/gpt2/c4_topk/ --layers 5 --z_value 1Tips:
- You may need to change llm tokenizer path in
detector.py, line 69, 72, 75. - You may need to set appropriate z_value in different experiment settings.
As for robustness against rewrite attack (corresponding to Appendix B in our paper), we observed varying performances in robustness among different watermark generator models. Consequently, we selected watermark generators that demonstrated relatively better performance. Trained generator models are provided in experiments/robustness/generator_model/. You can train your own detector based on the provided generators. Don't forget to set appropriate z_value according to the performance of key-based detector (i.e. public detector).
If you find this repo useful, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{
liu2024an,
title={An Unforgeable Publicly Verifiable Watermark for Large Language Models},
author={Aiwei Liu and Leyi Pan and Xuming Hu and Shuang Li and Lijie Wen and Irwin King and Philip S. Yu},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=gMLQwKDY3N}
}