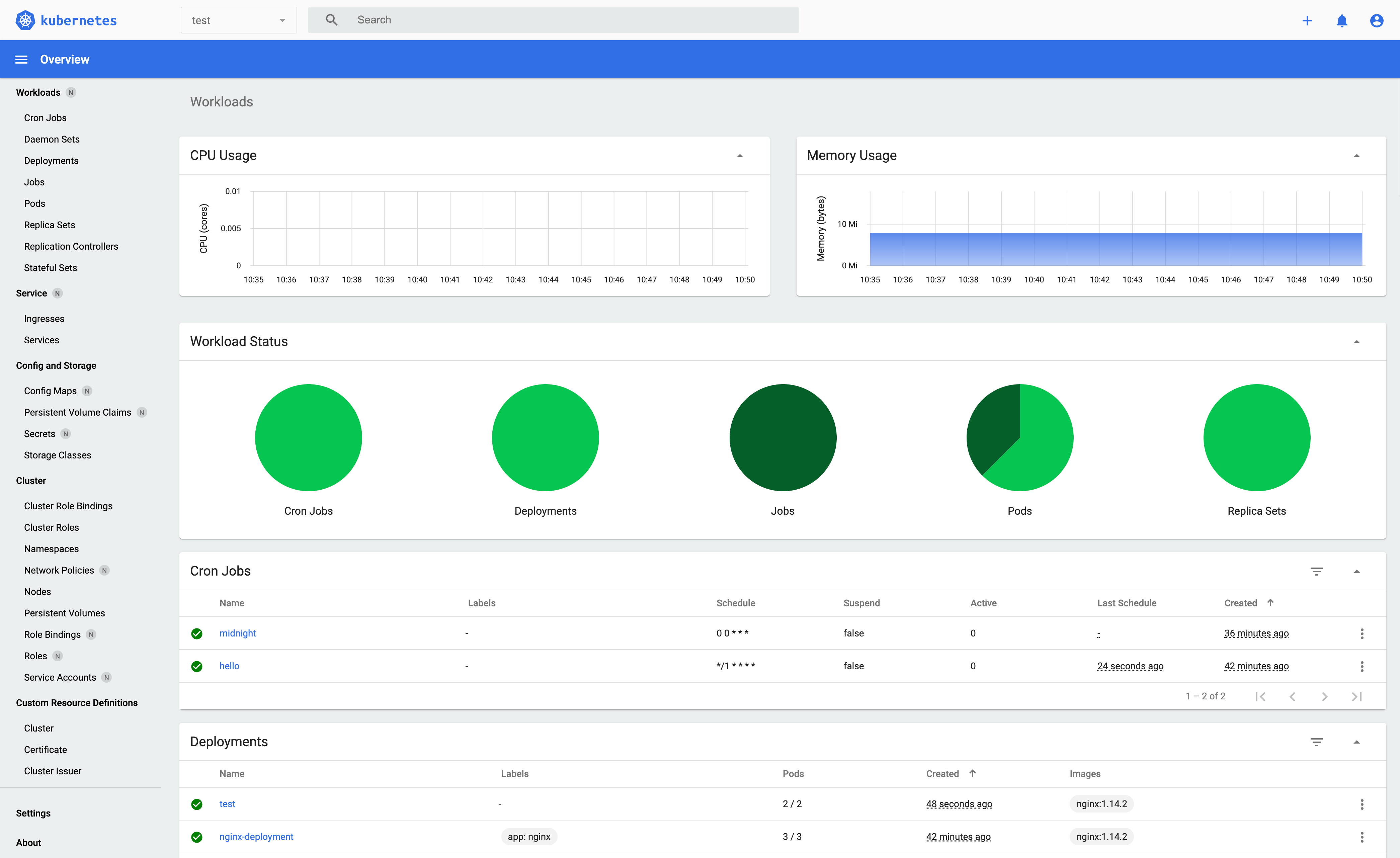
Kubernetes Dashboard
Introduction
Kubernetes Dashboard is a general purpose, web-based UI for Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to manage applications running in the cluster and troubleshoot them, as well as manage the cluster itself.
Getting Started
IMPORTANT: Read the Access Control guide before performing any further steps. The default Dashboard deployment contains a minimal set of RBAC privileges needed to run.
Install
To deploy Dashboard, execute following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.7.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yamlAlternatively, you can install Dashboard using Helm as described at https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/k8s-dashboard/kubernetes-dashboard.
Access
To access Dashboard from your local workstation you must create a secure channel to your Kubernetes cluster. Run the following command:
kubectl proxyNow access Dashboard at:
Create An Authentication Token (RBAC)
To find out how to create sample user and log in follow Creating sample user guide.
NOTE:
- Kubeconfig Authentication method does not support external identity providers or certificate-based authentication.
- Metrics-Server has to be running in the cluster for the metrics and graphs to be available. Read more about it in Integrations guide.
Documentation
Dashboard documentation can be found on docs directory which contains:
- Common: Entry-level overview.
- User Guide: Installation, Accessing Dashboard and more for users.
- Developer Guide: Getting Started, Dependency Management and more for anyone interested in contributing.
Community, discussion, contribution, and support
Learn how to engage with the Kubernetes community on the community page.
You can reach the maintainers of this project at:
Contribution
Learn how to start contribution on the Contributing Guideline.
Code of conduct
Participation in the Kubernetes community is governed by the Kubernetes Code of Conduct.
License
Copyright 2019 The Kubernetes Dashboard Authors