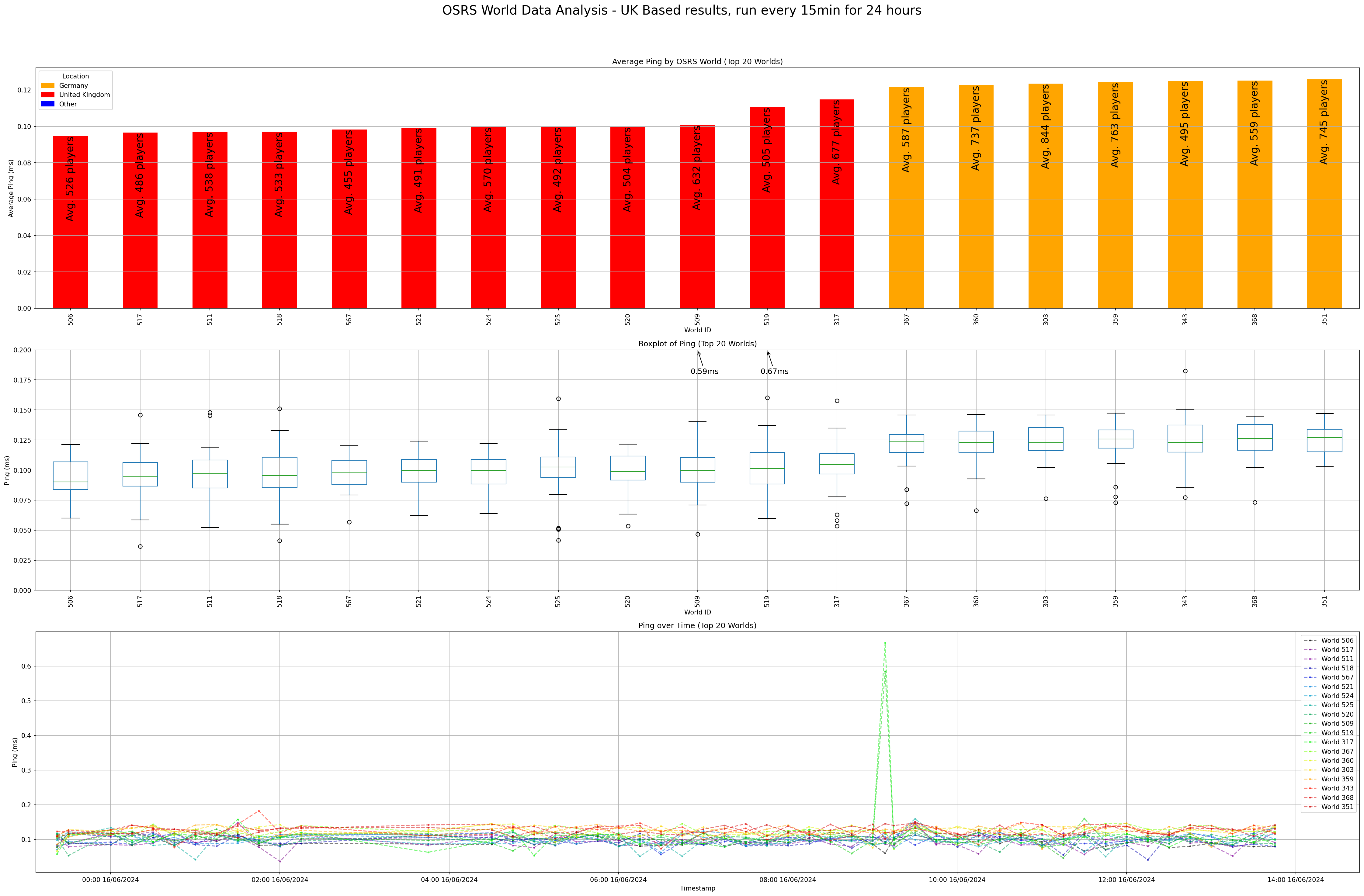
This Python script scrapes the Old School RuneScape (OSRS) world list and stores the data in a SQLite database.
The script uses the following Python libraries:
requestsfor making HTTP requestsbs4(BeautifulSoup) for parsing HTMLpandasfor data manipulationsqlalchemyfor database operationsmatplotlibfor plotting (jupyter notebook only)
The script first sends a GET request to the OSRS world list page and parses the HTML response using BeautifulSoup. It then extracts the world list table and converts it into a pandas DataFrame.
The DataFrame is processed to extract and format the necessary data, such as world ID, world URL, membership status, and player count. The processed data is then converted into a list of dictionaries.
The script then creates a SQLite database (if it doesn't exist) and inserts the world data into the OSRSWorlds table. If a world already exists in the database, it is not inserted again.
Finally, the script pings all member worlds located in Germany or the United Kingdom and stores the ping data and player count in the PingData table.
Run the script with the command python run.py.
-
Install Python: Download and install Python from the official Python website. Ensure to add Python to PATH during installation if you want to run Python from the command line without extra steps.
-
(Optional) Set Up a Virtual Environment: Create a virtual environment using
python -m venv .venvand activate it usingsource .venv/bin/activateon Linux or.\.venv\Scripts\activateon Windows. The Cronjob Management Script expects a virtual environment to be set up in the current directory. -
Clone the Repository: Download the code from this repository using
git cloneor by downloading it as a ZIP file from the repository page on GitHub. -
Install Dependencies: Navigate to the directory containing the code and run
python -m pip install -r requirements.txtto install the necessary Python libraries. -
Run the Script: In the terminal, navigate to the directory containing the code and run
python run.py. (Optionally specify the countries to ping as command line arguments.)
The script accepts several command-line arguments to customise its behavior:
-
--locations: This argument allows you to specify the locations of the worlds to ping. It accepts one or more values. By default, it pings worlds located in Germany and the United Kingdom. Example usage:
--locations Germany "United Kingdom". -
--members: This argument determines whether to ping members worlds. It's a boolean flag. If provided, the script will ping members worlds; if not, it won't. By default, it pings members worlds. Example usage:
--members 0. -
--activity: This argument allows you to filter worlds by activity. It accepts a string value. By default, it filters by
"-"which means no activity. Example usage:--activity "Bounty Hunter".
The cronjob.sh script is a utility for managing a cronjob that runs (run.py) in the current directory.
- Run the script using the command
./cronjob.sh. - When prompted, enter 'add' or 'a' to add the cronjob, or 'remove' or 'r' to remove it.
The script determines the full file path to run.py and uses it to add or remove the cronjob. It uses the crontab -l command to list the current cronjobs, the echo command to append the new cronjob to the list (when adding), and the grep -v command to filter out the cronjob (when removing). The updated list of cronjobs is then piped back to crontab - to update the cronjobs.
This script expects a python venv has been set-up in .venv in the current directory. If this is not the case, the script will not work.
The script logs its operations to both the console and a rotating log file (logs/world_scraper.log). The log file has a maximum size of 100KB and keeps the last 5 backups.
The database schema is defined in the utils/schema.py file. It consists of two tables: OSRSWorlds and PingData.
The script could easily be improved in the following ways:
- Make the countries to ping configurable via command line arguments or a configuration file.
- Add error handling for HTTP requests and database operations.
- Add more detailed logging and error messages.
- Add a scheduler to run the script at regular intervals. - Instead of casting to list then back to DataFrame from the get_worlds function, we could just return the DataFrame and use it directly in the insert_worlds function. This would save some processing time and memory, but it's not a big deal for the current number of worlds and list of dictionaries is convenient for the insert function.