Learning project to build a tiny LLM model from scratch.
Got problems or have some time to help? Please open an Issue to tell us!
Polaris Baby is a custom language model developed using PyTorch. This project encompasses scripts for training the model on a character-level dataset and executing inference with the trained model. The development of Polaris Baby LLM serves educational purposes.
| Original Input | Latest Inference |
|---|---|
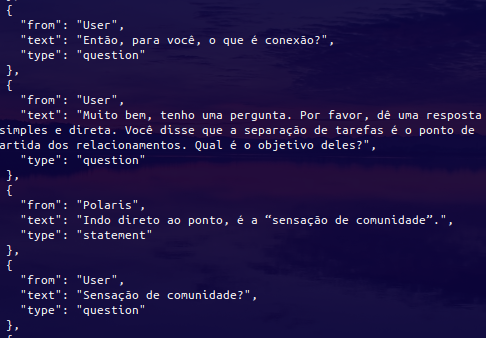 |
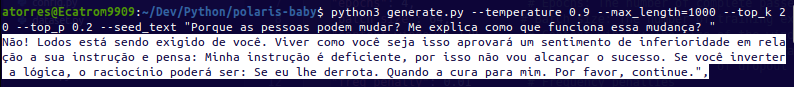 |
- Python 3.x
- PyTorch
- NumPy
- Pandas
- Word2Vec
Clone the repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/Tech-Tweakers/polaris-baby.git
cd polaris-baby1 - Prepare your dataset: The dataset should be a text file where the text data is used for training the model. The input file should be placed in the root directory. In the Makefile there is some functions to improve the dataset, like removing special characters, strings, add tags, etc.
2 - Adjust the training configuration: The training configuration can be adjusted in the config.py file. The configuration includes parameters like batch size, learning rate, and number of epochs.
# config.py
HP = {
"embed_dim": 256, # Embedding dimension: Size of the embedding vectors.
"hidden_dim": 512, # Hidden dimension: Size of the hidden layers in the model.
"num_layers": 16, # Number of layers: The number of layers in the model (e.g., in LSTM or Transformer models).
"num_heads": 32, # Number of heads: The number of heads in the multi-head attention mechanism.
"learning_rate": 0.005, # Learning rate: The step size at each iteration while moving toward a minimum of a loss function.
"epochs": 3, # Epochs: The number of complete passes through the training dataset.
"batch_size": 64, # Batch size: The number of training examples utilized in one iteration.
"context_window": 64, # Context window: The size of the window of context used for models that require a fixed input size.
"log_interval": 128, # Log interval: The interval (in iterations) at which training progress (e.g., loss) is logged.
"dropout": 0.5, # Dropout: The probability of dropout for regularization in the model.
}3 - Run the training script: The training script will train the model and save the trained model to the models directory. The script will also monitor performance metrics. The script can be run with the following command:
python main.pyAfter training, use the generate.py script for generating text:
1 - Load the trained model: Ensure that the trained model .pth file is accessible to the script.
2 - Run the inference script:
usage: generate.py [-h] [--seed_text SEED_TEXT] [--max_length MAX_LENGTH] [--temperature TEMPERATURE] [--top_k TOP_K] [--top_p TOP_P]
Generate text using a trained model.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--seed_text SEED_TEXT
Initial text to start generating from.
--max_length MAX_LENGTH
Maximum length of the generated text.
--temperature TEMPERATURE
Temperature for sampling.
--top_k TOP_K Top-k filtering threshold.
--top_p TOP_P Top-p (nucleus) filtering threshold.
Polaris LLM demonstrates the process of building a language model from the ground up, showcasing the intricacies of model architecture and training. It provides hands-on experience with advanced concepts in natural language processing and deep learning. The main focus is to process a brazilian portuguese dataset and generate text in the same language with all the challenges that comes with it.
This repository provides a complete setup for processing text data, constructing a vocabulary, and integrating Word2Vec embeddings for use in natural language processing tasks. Below are the components and functionalities encapsulated in the code:
- Vocabulary Construction: Upon initialization, the class reads text from a file (input.txt), constructs a sorted vocabulary, and logs the vocabulary size and a preview of its contents using colored console outputs for clarity.
- Word2Vec Training and Loading: Integrates with a custom Word2VecTrainer class to train a Word2Vec model from the input text, subsequently loading the trained model to access word vectors.
- Embedding Preparation: Generates a weight matrix for the vocabulary based on the embeddings from the Word2Vec model, converting it to a PyTorch tensor for further use in neural networks.
- Text Encoding: Encodes the entire text using the vocabulary, converting characters to indices, which are then used to create sequences of a specified length (defined by context_window).
The standalone function load_embeddings further facilitates the process of loading and preparing embeddings from an existing Word2Vec model. It adjusts the weight matrix to accommodate vocabulary and potentially a padding token, ensuring the embeddings are ready for integration into various types of neural network architectures.
Utilization of a config module allows for easy management of model parameters and configurations (CC and HP). The code also employs color-coded console logs (Colors class) to provide clear, real-time feedback about the status of operations such as vocabulary construction, model training, and embedding initialization.
This setup is ideal for researchers and developers working on projects that require efficient text processing and utilization of neural network embeddings. Whether the goal is to perform text classification, generation, or another form of analysis, this codebase provides a robust foundation for handling textual data and embedding integration.
The dataset file used for training must be the same file to be used for the Vocabulary. The Vocabulary is generated from the dataset file and is used to encode the text data into integers. If you train the model on one dataset and then try to use a different Vocabulary for inference, the model will not be able to decode the text data.
The Polaris Baby LLM model architecture is designed to handle character-level text generation tasks, leveraging recurrent layers, attention mechanisms, and advanced activation units to capture complex patterns in the data. The model comprises the following key components:
The SwiGLU class implements an enhanced version of the Gated Linear Unit (GLU) with a swish-based gating mechanism. It comprises dual linear transformations: one for gating and another for data transformation. The gating output is modulated by a sigmoid function scaled by a learnable parameter, and the result is multiplied by the output of the second transformation. This module is crucial for enhancing the model's ability to capture complex patterns in the data.
The MultiHeadAttention class facilitates the model's focus on different parts of the input sequence simultaneously. It splits the input into multiple heads, processes each head through a separate linear transformation, and then concatenates the results. This mechanism is essential for improving the model's interpretability and performance on tasks requiring nuanced understanding of contextual relationships.
The EnhancedRNNModel class integrates multiple components into a cohesive sequence processing model. It supports the use of pre-trained embeddings to leverage prior knowledge, which can be particularly beneficial for natural language processing tasks. The architecture includes an LSTM layer for learning long-term dependencies, followed by a SwiGLU activation unit for additional non-linearity and a multi-head attention layer for focused contextual processing. Layer normalization and a fully connected output layer finalize the model structure.
This architecture is designed to effectively handle complex sequence modeling tasks, providing robustness and flexibility through its integration of recurrent layers, attention mechanisms, and advanced activation units. Whether you are tackling language modeling, text generation, or any other sequence-based problem, this model provides a strong foundation for developing high-performing algorithms.





