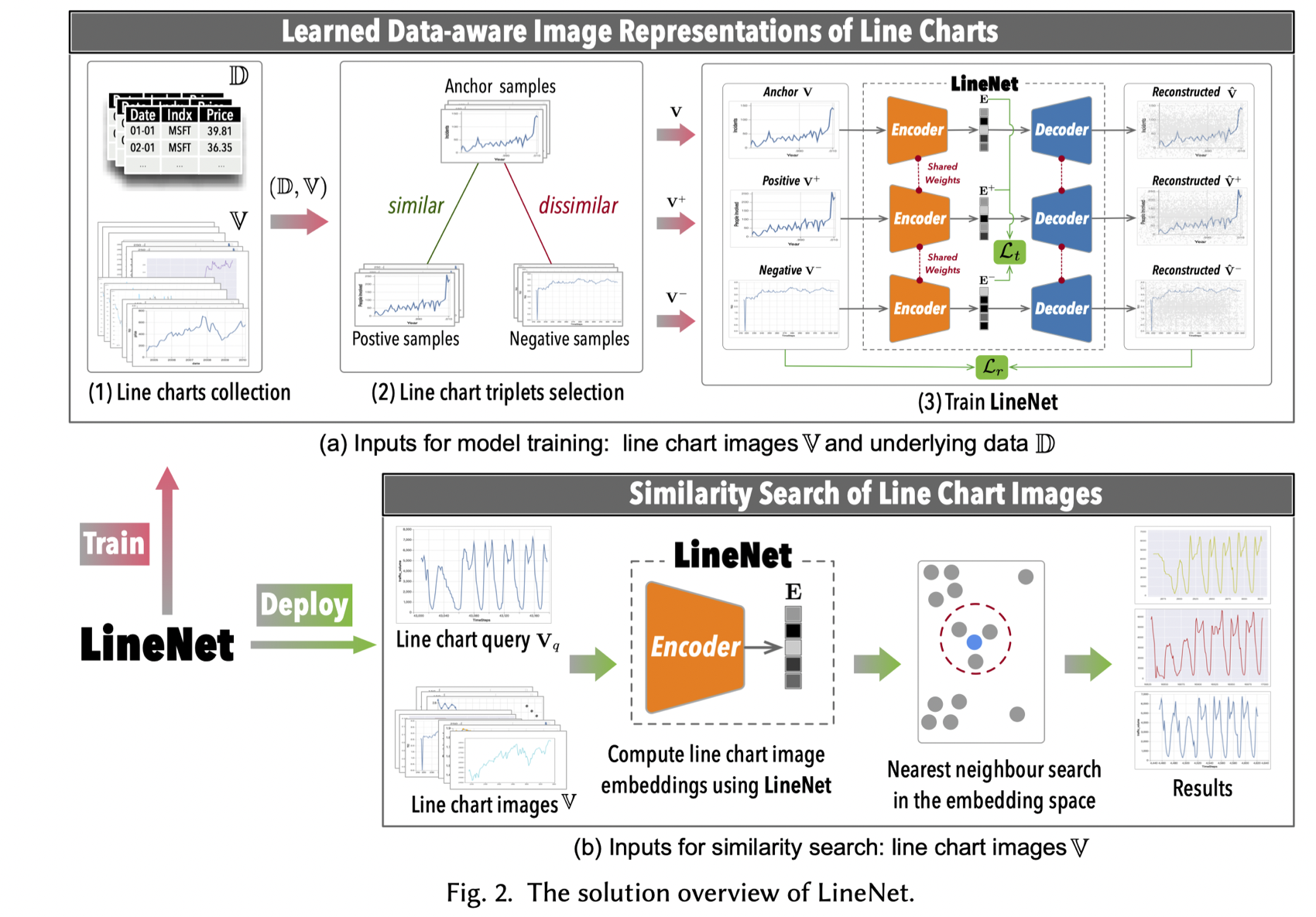
Finding line-chart images similar to a given line-chart image query is a common task in data exploration and image query systems. We study the scenario that during query time, only line-chart images are available. Our goal is to train a neural network that can turn these line-chart images into representations that are aware of the data used to generate these line charts, so as to learn better representations. Our key idea is that we can collect both data and line-chart images to learn such a neural network (at training step), while during query (or inference) time, we support the case that only line-chart images are provided.
To this end, we present LineNet, a Vision Transformer-based Triplet Autoencoder model, to learn data-aware image representations of line charts for similarity search.
LineNet is built using a Triplet Autoencoder architecture, which consists of three identical autoencoders. For each autoencoder, it consists of an Encoder and a symmetric Decoder. At the training phase, LineNet takes as input a line chart image triplet
We first propose a triplets selection algorithm to automatically select a set of training samples (i.e., a set of triplets). This algorithm can produce a larger number of effective training samples for training LineNet.
Furthermore, we judiciously select a small set of most representative triplets to make the learning process more effective and efficient. Therefore, we further design a diversified triplets selection algorithm to pick a set of discriminative triplets from a mini-batch to optimize the learning process.
Suppose we have a well-trained LineNet that can map a line chart image
Therefore, once the embedding space is well-prepared, the top-k similarity search of line chart images problem can be tackled using
Please refer to our paper at SIGMOD 2023 for more details.
Please refer to the folder LineNet for details.
conda create -n linenet python=3.8
conda activate linenet
pip install -r <path-to-this-dir>/requirements.txt
In case you are using recent hardware with cuda version >= 12.1, use the following instructions instead:
conda create -n linenet python=3.8
conda activate linenet
pip install -r <path-to-this-dir>/requirements_cu12.txt
1.Place dataset under ./datasets folder.
2.Run the following scripts:
make run-aq-semihard
make run-eeg-semihard
make run-stocks-semihard
make run-traffic-semihard
make run-aq-diversified
make run-eeg-diversified
make run-stocks-diversified
make run-traffic-diversified
@article{10.1145/3588942,
author = {Luo, Yuyu and Zhou, Yihui and Tang, Nan and Li, Guoliang and Chai, Chengliang and Shen, Leixian},
title = {Learned Data-Aware Image Representations of Line Charts for Similarity Search},
year = {2023},
issue_date = {May 2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3588942},
doi = {10.1145/3588942},
journal = {Proc. ACM Manag. Data},
month = {may},
articleno = {88},
numpages = {29},
keywords = {similarity search, line charts, triplets selection, learned representations}
}If you have any questions, feel free to contact Yuyu Luo (luoyy18 [AT] mails.tsinghua.edu.cn).