Add cache abstraction and method annotations for controlling cache. The current implementation of the Cache component is a wrapper (proxy) for Doctrine\Common\Cache.
The TbbcCacheBundle integrates Symfony with a non-instrusive applicative cache management system. It gives to the developer annotation driven cache control by using AOP mechanisms and PHP language expressions.
<?php
namespace My\Manager;
use My\Model\Product;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\Cacheable;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\CacheUpdate;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\CacheEvict;
class ProductManager
{
/**
* @Cacheable(caches="products", key="sku")
*/
public function getProduct($sku, $type = 'book')
{
// fetch a product from a repository or whatever
$product = $this->productRepository->getByType($sku, 'book');
return $product;
}
/**
* @CacheUpdate(caches="products", key="product.getSku()")
*/
public function updateProduct(Product $product)
{
$product = $this->productRepository->save($product);
return $product;
}
/**
* @CacheEvict(caches="products", key="product.getSku()")
*/
public function removeProduct(Product $product)
{
$product = $this->productRepository->remove($product);
}
}@Cacheable,@CacheUpdate,@CacheEvictannotation support- TTL strategy, allow you to customize cache retention
- Namespaced cache manager
- Multiple cache managers:
- Doctrine/ArrayCache
- Doctrine/ApcCache
- Doctrine/MemcachedCache
- Doctrine/RedisCache
- Symfony Debug Toolbar integration
- Installation
- Configuration
- Usage
- Symfony debug toolbar integration
- Known limitations
- Testing
- License
First, install the bundle package with composer:
$ php composer.phar require tbbc/cache-bundleNext, activate the bundle into app/AppKernel.php:
<?php
// ...
public function registerBundles()
{
$bundles = array(
//...
new Tbbc\CacheBundle\TbbcCacheBundle(),
);
// ...
}services:
my_manager.product:
class: My\Manager\ProductManager
tags:
- { name: tbbc_cache.cache_eligible }
tbbc_cache:
annotations: { enabled: true }
manager: simple_cache
key_generator: simple_hash
metadata:
use_cache: true # Whether or not use metadata cache
cache_dir: %kernel.cache_dir%/tbbc_cache
cache:
products:
type: memcached
servers:
memcached-01: { host: localhost, port: 11211 }Note: The tbbc_cache.cache_eligible tag is mandatory in your service definition if you want to be able to use
annotation for this service.
Recommended
If some prefer to avoid repeating code each time they want to add some caching logic, the bundle can automate the process by using AOP approach and annotations.
The bundle provides the following annotations:
@Cacheable annotation is used to automatically store the result of a method into the cache.
When a method demarcated with the @Cacheable annotation is called, the bundle checks if an entry exists in the cache before executing the method. If it finds one, the cache result is returned without having to actually execute the method.
If no cache entry is found, the method is executed and the bundle automatically stores its result into the cache.
<?php
namespace My\Manager;
use My\Model\Product;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\Cacheable;
class ProductManager
{
/**
* @Cacheable(caches="products", key="sku")
*/
public function getProduct($sku, $type = 'book')
{
// fetch a product from a repository or whatever
$product = $this->productRepository->getByType($sku, 'book');
return $product;
}
}@CacheEvict annotation allows methods to trigger cache population or cache eviction.
When a method is demarcated with @CacheEvict annotation, the bundle will execute the method and then will automatically try to delete the cache entry with the provided key.
<?php
namespace My\Manager;
use My\Model\Product;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\CacheEvict;
class ProductManager
{
/**
* @CacheEvict(caches="products", key="product.getSku()")
*/
public function removeProduct(Product $product)
{
// saving product ...
}
}It is also possible to flush completely the caches by setting allEntries parameter to true
allEntries option you have to be really careful, if you
use the same cache manager for different namespace, the whole cache manager will be flushed. This is currently
a limitation of the underlying Doctrine Cache library.
<?php
namespace My\Manager;
use My\Model\Product;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\CacheEvict;
class ProductManager
{
/**
* @CacheEvict(caches="products", allEntries=true)
*/
public function removeProduct(Product $product)
{
// saving product ...
}
}Note: If you also provide a key, it will be ignored and the cache will be flushed.
@CacheUpdate annotation is useful for cases where the cache needs to be updated without interfering with the method execution.
When a method is demarcated with @CacheUpdate annotation, the bundle will always execute the method and then will automatically try to update the cache entry with the method result.
<?php
namespace My\Manager;
use My\Model\Product;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\CacheUpdate;
class ProductManager
{
/**
* @CacheUpdate(caches="products", key="product.getSku()")
*/
public function updateProduct(Product $product)
{
// saving product....
return $product;
}
}For key generation, Symfony Expression Language can be used.
/**
* @CacheUpdate(caches="products", key="product.getSku()")
*/
public function updateProduct(Product $product)
{
// do something
}The Expression Language allow you to retrieve any arguments passed to your method and use it to generate the cache key.
CacheManager instance must be injected into services that need cache management.
The CacheManager gives access to each configured cache (see Configuration section).
Each cache implements CacheInterface.
Usage:
<?php
namespace My\Manager;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Annotation\Cacheable;
class ProductManager
{
private $cacheManager;
private $keyGenerator;
public function __construct(CacheManagerInterface $cacheManager, KeyGeneratorInterface $keyGenerator)
{
$this->cacheManager = $cacheManager;
$this->keyGenerator = $keyGenerator;
}
public function getProduct($sku, $type = 'book')
{
$cacheKey = $this->keyGenerator->generateKey($sku);
$cache = $this->cacheManager->getCache('products');
if ($product = $cache->get($cacheKey)) {
return $product;
}
$product = $this->productRepository->findProductBySkuAndType($sku, $type);
$cache->set($cacheKey, $product);
return $product;
}
public function saveProduct(Product $product)
{
$this->productRepository->save($product);
$cacheKey = $this->keyGenerator->generateKey($product->getSku());
$cache = $this->cacheManager->getCache('products');
$cache->delete($cacheKey);
}
}Out of the box, the bundle provides a SimpleCacheManager, but custom cache managers can be used instead of the default one and must implement the CacheManagerInterface.
Key generation is up to the developer, but for convenience, the bundle comes with some key generation logic.
Note: When using Annotation based caching, usage of Key generators is mandatory.
Out of the box, the bundle provides a SimpleHashKeyGenerator which basically adds each param encoded using md5 algorithm, and returned a md5 hash of the result.
For testing purpose you may also use LiteralKeyGenerator which build a slug-like key.
Note: Both generators does not support non-scalar keys such as objects.
You can override the Key Generator by setting the key_generator key in your config.yml
Allowed values are: simple_hash, literal or the id of the service of your custom Key generator
Custom key generators can be used instead of the default one and must implement the KeyGeneratorInterface.
Since this bundle provides a cache abstraction and not all cache providers support or handle TTL the same way, TTL strategy must be defined in each cache configuration options (when option is supported).
Example:
tbbc_cache:
annotations: { enabled: true }
manager: simple_cache
cache:
products:
type: memcached
ttl: 86400 # 1 day
servers:
memcached-01: { host: localhost, port: 11211 }
user_feeds:
type: memcached
ttl: 0 # infinite (same as omitting the option)
followers_list:
type: apc
ttl: 1296000 # 15 days
activity_counters:
type: redis
ttl: 3600 # 1 hour
server:
host: 127.0.0.1
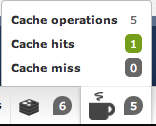
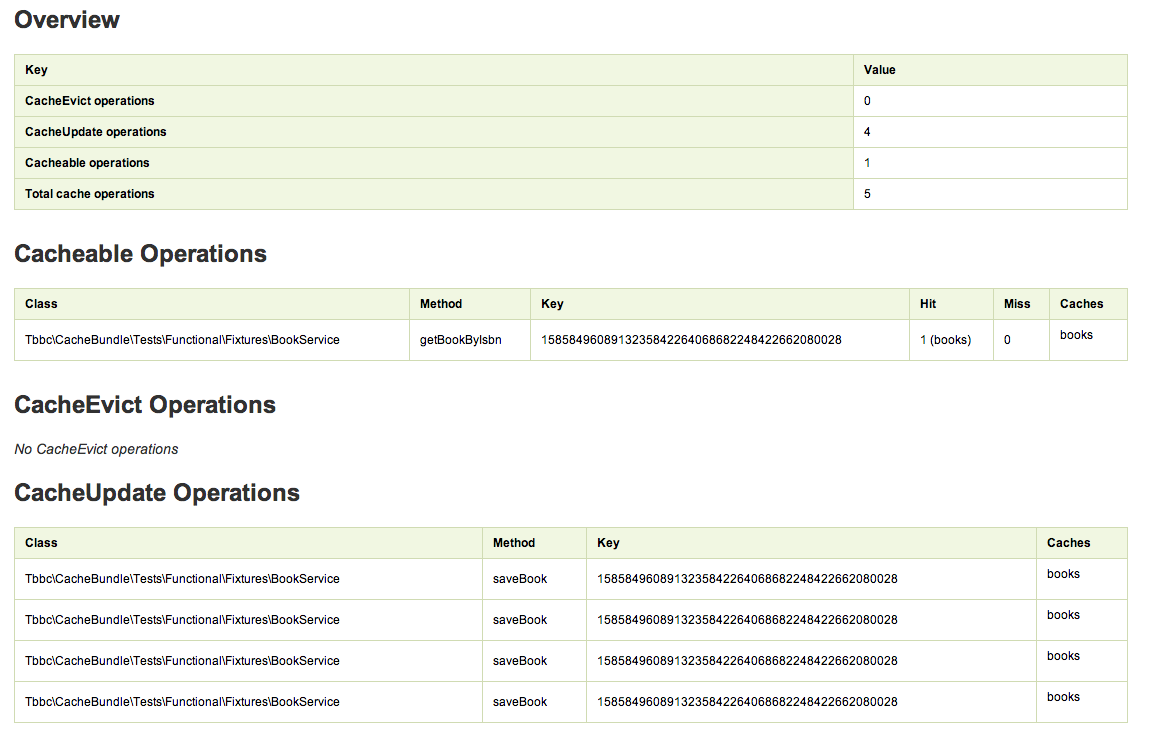
port: 6379Debugging cache operations is often a pain is the ass. In order to facilitate this work, the bundle adds some useful live information directly in the Symfony Debug Toolbar.
Here are some screenshots about the kind of information it will show:
Due to the way cache is managed in Doctrine and especially the way it is handled by the different cache systems, usage of the "CacheEvict" operation with the "allEntries" option can lead to undesired behaviour.
Be warned that if you use different cache namespaces but within the same cache instance (like a single memcached server for instance), the "allEntries" option will flush all cache entries in all namespaces. Meaning it will flush the entire instance cache.
Automatic caching of doctrine entities is not supported at this time. If you need to cache entities, you have to implement your own logic.
One way to do it would be to override annotations and metadatas for adding a serialization "type" option, and then hook in cache events to manually manage serialization/de-serialization operations:
<?php
namespace My\EventListener;
use My\CacheBundle\SerializedCacheValue;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Event\CacheHitEvent;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Event\CacheUpdateEvent;
use JMS\SerializerBundle\Serializer\SerializerInterface;
use Tbbc\CacheBundle\Cache\CacheManagerInterface;
class CacheEventListener
{
private $serializer;
private $cacheManager;
public function __construct(SerializerInterface $serializer, CacheManagerInterface $cacheManager)
{
$this->serializer = $serializer;
$this->cacheManager = $cacheManager;
}
public function onAfterCacheHit(CacheHitEvent $event)
{
$value = $event->getValue();
if ($value instanceof SerializedCacheValue) {
$value = $this->serializer->deserialize($value->data, $value->type, 'json');
$event->setValue($value);
}
}
public function onAfterCacheUpdate(CacheUpdateEvent $event)
{
$cache = $event->getCache();
$key = $event->getKey();
$metadata = $event->getMetadata();
if (null !== $metadata->type) {
$serializedValue = $this->serializer->serialize($event->getValue(), 'json');
$value = new SerializedCacheValue($metadata->type, $serializedValue);
$this->cacheManager->getCache($cache)->set($key, $value);
}
}
}Install development dependencies
$ composer install --devRun the test suite
$ vendor/bin/phpunitThis bundle is under the MIT license. See the complete license in the bundle:
Resources/meta/LICENSE