Any kinds of contributions including pull requests, registering new issues, sending me personal emails are always welcome. Let me know if you have any idea about basic utils for Android development.
- Get started
- Utils
- Base
- LogUtil (L)
- LogHelper
- ContextUtil (Ctx)
- ResourcesUtil (Res)
- PreferencesUtil (Pref)
- ExtrasBinder
- UnitConverter (Unit)
- KeyboardUtil (Keyboard)
- APILevel
- DisplayUtil
- ViewUtil
- ServiceUtil
- ThemeUtil
- ActivityBuilder
- BundleBuilder
- PackageUtil
- VibratorUtil
- ClipboardManagerUtil
- TypedValueUtil
- WindowManagerUtil
- IntArrayUtil
- SparseArrayUtil
- ThreadUtil
- Contributors
- License
Release is in process...
buildscript {
dependencies {
classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
}
}
apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt'
dependencies {
compile 'com.thefinestartist:utils:0.9.5'
apt 'com.thefinestartist:compilers:0.9.5'
}Call Base.initialize(context) within your Application onCreate() method.
public class App extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Base.initialize(this);
}
}Base helps to get Context, Resources, Assets, Configuration and DisplayMetrics in any class.
void Base.initialize(Context context);
Context Base.getContext();
Resources Base.getResources();
Theme Base.getTheme();
AssetManager Base.getAssets();
Configuration Base.getConfiguration();
DisplayMetrics Base.getDisplayMetrics();LogUtil helps to deal with Log conveniently.
L is abbreviation class of LogUtil. You can extends LogUtil to create your own L.
Settings L.getDefaultSettings();
LogHelper L.tag(String tag);
LogHelper L.tag(@StringRes int tagRes);
LogHelper L.tag(Class clazz);
LogHelper L.showThreadInfo(boolean showThreadInfo);
LogHelper L.stackTraceCount(int stackTraceCount);
LogHelper L.logLevel(LogLevel logLevel);
LogHelper L.showDivider(boolean showDivider);
LogHelper L.logPrinter(LogPrinter logPrinter);
void L.v(byte message);
void L.v(char message);
void L.v(short message);
void L.v(int message);
void L.v(long message);
void L.v(float message);
void L.v(double message);
void L.v(boolean message);
void L.v(String message);
void L.v(JSONObject message);
void L.v(JSONArray message);
void L.v(Exception message);
void L.v(Object message);
// and so on...
void L.json(String jsonString);
void L.json(LogLevel logLevel, String jsonString);
void L.xml(String xmlString);
void L.xml(LogLevel logLevel, String jsonString);// Set default settings at your Application.
L.getDefaultSettings()
.setTag(LogUtil.class)
.setShowThreadInfo(false)
.setStackTraceCount(0)
.setLogLevel(LogLevel.FULL)
.setShowDivider(false)
.setLogPrinter(new AndroidLogPrinter());
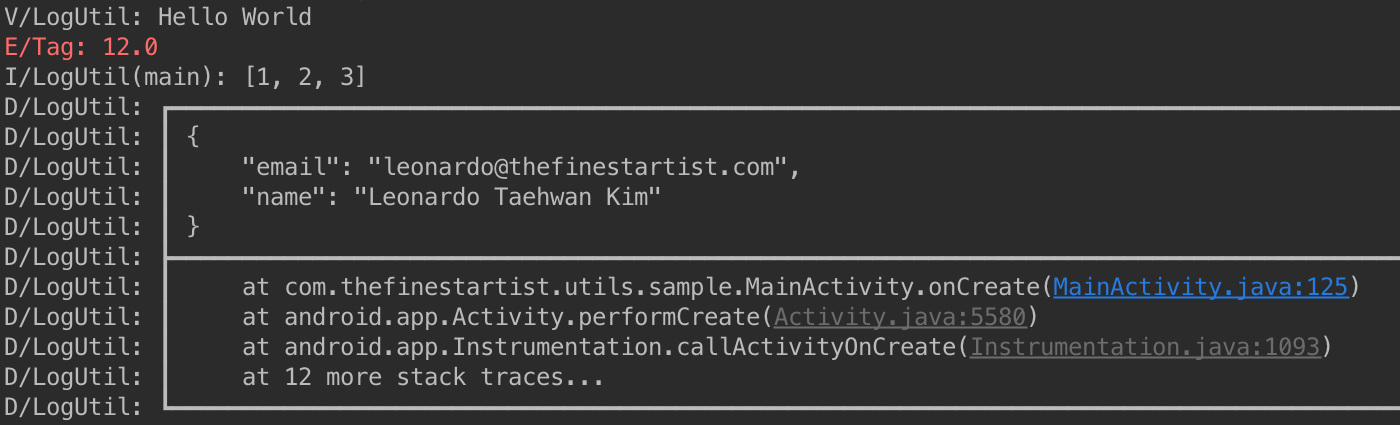
L.v("Hello World");
L.tag("Tag").e(12.0f);
L.showThreadInfo(true).i(new int[]{1, 2, 3});
L.stackTraceCount(3).showDivider(true).json("{\"name\":\"Leonardo Taehwan Kim\",\"email\":\"leonardo@thefinestartist.com\"}");LogHelper helps to deal with Log conveniently.
LogHelper new LogHelper();
LogHelper new LogHelper(String tag);
LogHelper new LogHelper(@StringRes int tagRes);
LogHelper new LogHelper(Class clazz);
LogHelper tag(String tag);
LogHelper tag(@StringRes int tagRes);
LogHelper tag(Class clazz);
LogHelper showThreadInfo(boolean showThreadInfo);
LogHelper stackTraceCount(int stackTraceCount);
LogHelper logLevel(LogLevel logLevel);
LogHelper showDivider(boolean showDivider);
LogHelper logPrinter(LogPrinter logPrinter);
void v(byte message);
void v(char message);
void v(short message);
void v(int message);
void v(long message);
void v(float message);
void v(double message);
void v(boolean message);
void v(String message);
void v(JSONObject message);
void v(JSONArray message);
void v(Exception message);
void v(Object message);
// and so on...
void json(String jsonString);
void json(LogLevel logLevel, String jsonString);
void xml(String xmlString);
void xml(LogLevel logLevel, String jsonString);// Set default settings at any Class.
LogHelper logHelper = new LogHelper(MainActivity.class).showThreadInfo(true);
logHelper.v("Hello World");
logHelper.e(12.0f);
logHelper.json("{\"name\":\"Leonardo Taehwan Kim\",\"email\":\"leonardo@thefinestartist.com\"}");ContextUtil helps to use Context conveniently.
Ctx is abbreviation class of ContextUtil. You can extends ContextUtil to create your own Ctx.
boolean Ctx.bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags);
int Ctx.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(String permission);
int Ctx.checkSelfPermission(@NonNull String permission);
void Ctx.enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(String permission, String message);
void Ctx.enforceCallingOrSelfUriPermission(Uri uri, int modeFlags, String message);
ApplicationInfo Ctx.getApplicationInfo();
File Ctx.getCacheDir();
File Ctx.getExternalCacheDir();
File Ctx.getExternalFilesDir(String type);
Looper Ctx.getMainLooper();
Object Ctx.getSystemService(String name);
void Ctx.sendBroadcast(Intent intent, String receiverPermission);
void Ctx.sendBroadcast(Intent intent);
boolean Ctx.startActivities(Intent[] intents, Bundle options);
boolean Ctx.startActivities(Intent[] intents);
void Ctx.startActivity(@NonNull Intent intent);
void Ctx.startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options);
ComponentName Ctx.startService(Intent service);
boolean Ctx.stopService(Intent service);
void Ctx.unbindService(ServiceConnection conn);
// and so on...ResourcesUtil helps to use Resources conveniently.
Res is abbreviation class of ResourcesUtil. You can extends ResourcesUtil to create your own Res.
XmlResourceParser Res.getAnimation(@AnimRes int animRes);
boolean Res.getBoolean(@BoolRes int boolRes);
int Res.getColor(@ColorRes int colorRes);
int Res.getColor(@ColorRes int colorRes, Resources.Theme theme);
ColorStateList Res.getColorStateList(@ColorRes int colorRes);
ColorStateList Res.getColorStateList(@ColorRes int colorRes, Resources.Theme theme);
float Res.getDimension(@DimenRes int dimenRes);
int Res.getDimensionPixelOffset(@DimenRes int dimenRes);
int Res.getDimensionPixelSize(@DimenRes int dimenRes);
DisplayMetrics Res.getDisplayMetrics();
Drawable Res.getDrawable(@DrawableRes int drawableRes);
int Res.getIdentifier(String name, String defType, String defPackage);
int[] Res.getIntArray(@ArrayRes int arrayRes);
int Res.getInteger(@IntegerRes int integerRes);
XmlResourceParser Res.getLayout(@LayoutRes int layoutRes);
String Res.getQuantityString(int id, int quantity, Object... formatArgs);
CharSequence Res.getQuantityText(int id, int quantity);
String Res.getResourceEntryName(@AnyRes int anyRes);
String Res.getResourceName(@AnyRes int anyRes);
String Res.getResourcePackageName(@AnyRes int anyRes);
String Res.getResourceTypeName(@AnyRes int anyRes);
String Res.getString(@StringRes int stringRes);
String Res.getString(@StringRes int stringRes, Object... formatArgs);
String[] Res.getStringArray(@ArrayRes int arrayRes);
CharSequence Res.getText(@StringRes int stringRes, CharSequence def);
CharSequence Res.getText(@StringRes int stringRes);
CharSequence[] Res.getTextArray(@ArrayRes int arrayRes);
void Res.getValue(String name, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs);
void Res.getValue(@AnyRes int anyRes, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs);
void Res.getValueForDensity(@AnyRes int anyRes, int density, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs);
XmlResourceParser Res.getXml(@XmlRes int xmlRes);
TypedArray Res.obtainAttributes(AttributeSet set, int[] attrs);
TypedArray Res.obtainTypedArray(@ArrayRes int anyRes);
InputStream Res.openRawResource(@RawRes int rawRes);
AssetFileDescriptor Res.openRawResourceFd(@RawRes int rawRes);
int[] Res.getColorArray(@ArrayRes int array);
// and so on...PreferencesUtil helps to manage application-wide preferences conveniently.
Pref is abbreviation class of PreferencesUtil. You can extends PreferencesUtil to create your own Pref.
String Pref.getDefaultName();
void Pref.setDefaultName(String name);
boolean Pref.get(String key, boolean defValue);
int Pref.get(String key, int defValue);
float Pref.get(String key, float defValue);
long Pref.get(String key, long defValue);
String Pref.get(String key, String defValue);
Set<String> Pref.get(String key, Set<String> defValue);
C Pref.get(String key, C defValue);
boolean Pref.get(String name, String key, boolean defValue);
int Pref.get(String name, String key, int defValue);
float Pref.get(String name, String key, float defValue);
long Pref.get(String name, String key, long defValue);
String Pref.get(String name, String key, String defValue);
Set<String> Pref.get(String name, String key, Set<String> defValue);
C Pref.get(String name, String key, C defValue);
void Pref.put(String key, boolean value);
void Pref.put(String key, int value);
void Pref.put(String key, float value);
void Pref.put(String key, long value);
void Pref.put(String key, String value);
void Pref.put(String key, Set<String> value);
void Pref.put(String key, C value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, boolean value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, int value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, float value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, long value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, String value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, Set<String> value);
void Pref.put(String name, String key, C value);
void Pref.remove(String key);
void Pref.remove(String name, String key);
void Pref.clear();
void Pref.clear(String name);Simply call ExtrasBinder.bind(this) in your Activity or Fragment. ExtrasBinder binds data from Intent or Bundle to matching variable. ExtrasBinder will consider annotation variable as key. If there is no annotation variable, it will consider variable name as key.
// Start YourActivity with extras
Intent intent = new Intent(this, YourActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(YourActivity.EXTRA_TITLE, "Activity title");
intent.putExtra("ids", new ArrayList<Integer>());
startActivity(intent);public class YourActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
public static final String EXTRA_TITLE = "TITLE";
@Extra(EXTRA_TITLE) String title;
@Extra ArrayList<Integer> ids;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ExtrasBinder.bind(this);
// do something...
}
}// Show YourFragment with extras
YourFragment fragment = new YourFragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("Name", "Fragment name");
fragment.setArguments(bundle);public class YourFragment extends Fragment {
@Extra("NAME") String name;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
ExtrasBinder.bind(this);
// do something...
}
}Proguard
-keep class com.thefinestartist.annotations.** { *; }
-keep class **$$ExtraBinder { *; }
-keepclasseswithmembernames class * {
@com.thefinestartist.annotations.Extra <fields>;
}UnitConverter helps to convert dp or sp size into pixel.
Unit is abbreviation class of UnitConverter. You can extends UnitConverter to create your own Unit.
float Unit.dpToPx(float dp);
int Unit.dpToPx(int dp);
float Unit.pxToDp(float px);
int Unit.pxToDp(int px);
float Unit.spToPx(float sp);
int Unit.spToPx(int sp);
float Unit.pxToSp(float px);
int Unit.pxToSp(int px);KeyboardUtil helps to show and hide keyboard conveniently.
Keyboard is abbreviation class of KeyboardUtil. You can extends KeyboardUtil to create your own Keyboard.
void Keyboard.show(View);
void Keyboard.showImmediately(View); // Call this method if your activity or fragment is resumed.
void Keyboard.hide(View);
void Keyboard.hide(View, clearFocus);
void Keyboard.hide(Activity);
void Keyboard.hide(Activity, clearFocus);
void Keyboard.hide(Fragment);
void Keyboard.hide(Fragment, clearFocus);
void Keyboard.hide(Dialog);
void Keyboard.hide(Dialog, clearFocus);APILevel helps to check device API Build.VERSION conveniently.
- Update your Android Studio lint option before you use this class. Show Image
→ Android Studio
→ Preferences...
→ Editor
→ Inspections
→ Android Lint
→ Calling new methods on older versions
→ Set Severity as Warning.boolean APILevel.require(int level); // Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= level
boolean APILevel.requireCupcake();
boolean APILevel.requireDonut();
boolean APILevel.requireEclair();
boolean APILevel.requireFroyo();
boolean APILevel.requireGingerbread();
// and so on...
boolean APILevel.deprecatedAt(int level); // Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < level
boolean APILevel.deprecatedAtCupcake();
boolean APILevel.deprecatedAtDonut();
boolean APILevel.deprecatedAtEclair();
boolean APILevel.deprecatedAtFroyo();
boolean APILevel.deprecatedAtGingerbread();
// and so on...DisplayUtil helps to calculate screen size conveniently.
int DisplayUtil.getWidth();
int DisplayUtil.getHeight();
Rotation DisplayUtil.getRotation();
boolean DisplayUtil.isDisplayPortrait();
boolean DisplayUtil.isDisplayLandscape();
int DisplayUtil.getStatusBarHeight();
int DisplayUtil.getToolbarHeight();
int DisplayUtil.getActionBarHeight();
int DisplayUtil.getNavigationBarHeight(); // Navigation bar is located bottom of device for `back`, `home` and `menu` buttons.ViewUtil helps to set background drawable conveniently.
void ViewUtil.setBackground(View view, Drawable drawable);
void ViewUtil.setBackground(View view, int drawableRes);ServiceUtil helps to get Android system service conveniently.
Object ServiceUtil.getSystemService(Context.ServiceName);
AccessibilityManager ServiceUtil.getAccessibilityManager();
CaptioningManager ServiceUtil.getCaptioningManager();
AccountManager ServiceUtil.getAccountManager();
ActivityManager ServiceUtil.getActivityManager();
AlarmManager ServiceUtil.getAlarmManager();
AudioManager ServiceUtil.getAudioManager();
MediaRouter ServiceUtil.getMediaRouter();
// and so on...ThemeUtil helps to use Theme conveniently.
void ThemeUtil.applyStyle(int resId, boolean force);
void ThemeUtil.dump(int priority, String tag, String prefix);
int ThemeUtil.getChangingConfigurations();
Drawable ThemeUtil.getDrawable(@DrawableRes int drawableRes);
Resources ThemeUtil.getResources();
TypedArray ThemeUtil.obtainStyledAttributes(@StyleableRes int[] attrs);
TypedArray ThemeUtil.obtainStyledAttributes(@StyleRes int resid, @StyleableRes int[] attrs);
TypedArray ThemeUtil.obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet set, @StyleableRes int[] attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr, @StyleRes int defStyleRes);
boolean ThemeUtil.resolveAttribute(int resid, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs);
void ThemeUtil.setTo(Resources.Theme other);ActivityBuilder helps to build Activity Intent and start Activity.
Constructor ActivityBuilder(@NonNull Class<C> clazz);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.set(@NonNull String key, T value);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.set(@NonNull String key, Parcelable value);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.set(@NonNull String key, Parcelable[] value);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.set(@NonNull String key, ArrayList<T> value);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.remove(@NonNull String key);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.setFlags(int flags);
ActivityBuilder ActivityBuilder.addFlags(int flags);
Intent ActivityBuilder.buildIntent();
void ActivityBuilder.start();
void ActivityBuilder.startForResult(@NonNull Activity activity, int requestCode);
void ActivityBuilder.startForResult(@NonNull Activity activity, int requestCode, @Nullable Bundle options);new ActivityBuilder(YourActivity.class)
.set(YourActivity.TITLE, "Title")
.set(YourActivity.CONTENT, 1)
.set("values", new int[]{1, 2, 3})
.set(YourActivity.ARRAY_LIST, list)
.start();BundleBuilder helps to build Bundle conveniently.
BundleBuilder BundleBuilder.set(String key, T value);
T BundleBuilder.get(String key);
Bundle BundleBuilder.build();Bundle bundle = new BundleBuilder()
.set("values", new int[]{1, 2, 3})
.build();PackageUtil helps to handle methods related to package.
boolean PackageUtil.isInstalled(String packageName);
String PackageUtil.getPackageName();
void PackageUtil.openPlayStore();
void PackageUtil.openPlayStore(String packageName);VibratorUtil helps to use Vibrator conveniently.
void VibratorUtil.vibrate(); // vibrate device for 200 milliseconds
void VibratorUtil.vibrate(milliseconds);
// and more...ClipboardManagerUtil helps to use ClipboardManager conveniently.
void ClipboardManagerUtil.setText(CharSequence text);
boolean ClipboardManagerUtil.hasText();
CharSequence ClipboardManagerUtil.getText();TypedValueUtil helps to use TypedValue class conveniently.
float TypedValueUtil.applyDimension(int unit, float value);
float TypedValueUtil.complexToDimension(int data);
int TypedValueUtil.complexToDimensionPixelOffset(int data);
int TypedValueUtil.complexToDimensionPixelSize(int data);WindowManagerUtil helps to use WindowManager conveniently.
Display WindowManagerUtil.getDefaultDisplay();
void WindowManagerUtil.removeViewImmediate(View view);IntArrayUtil helps to deal with IntArray conveniently.
boolean IntArrayUtil.contains(int[] array, int value);
int[] IntArrayUtil.add(int[] array, int value);SparseArrayUtil helps to deal with SparseArray conveniently.
ArrayList<C> SparseArrayUtil.asArrayList(SparseArray<C> sparseArray);ThreadUtil helps to deal with thread conveniently.
boolean ThreadUtil.isMain();Leonardo Taehwan Kim
Min Kim
Robin Gustafsson
Marcos Trujillo
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2016 The Finest Artist
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.