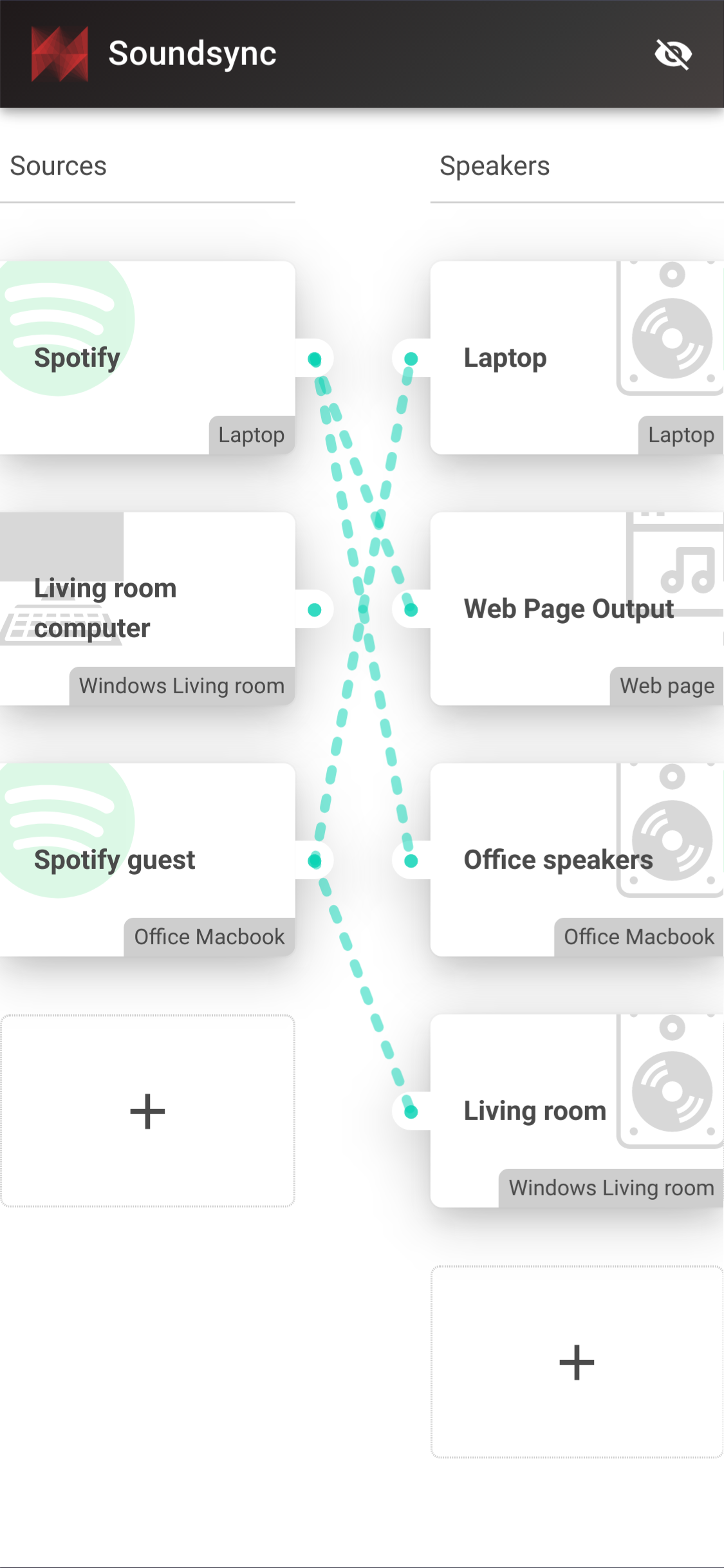
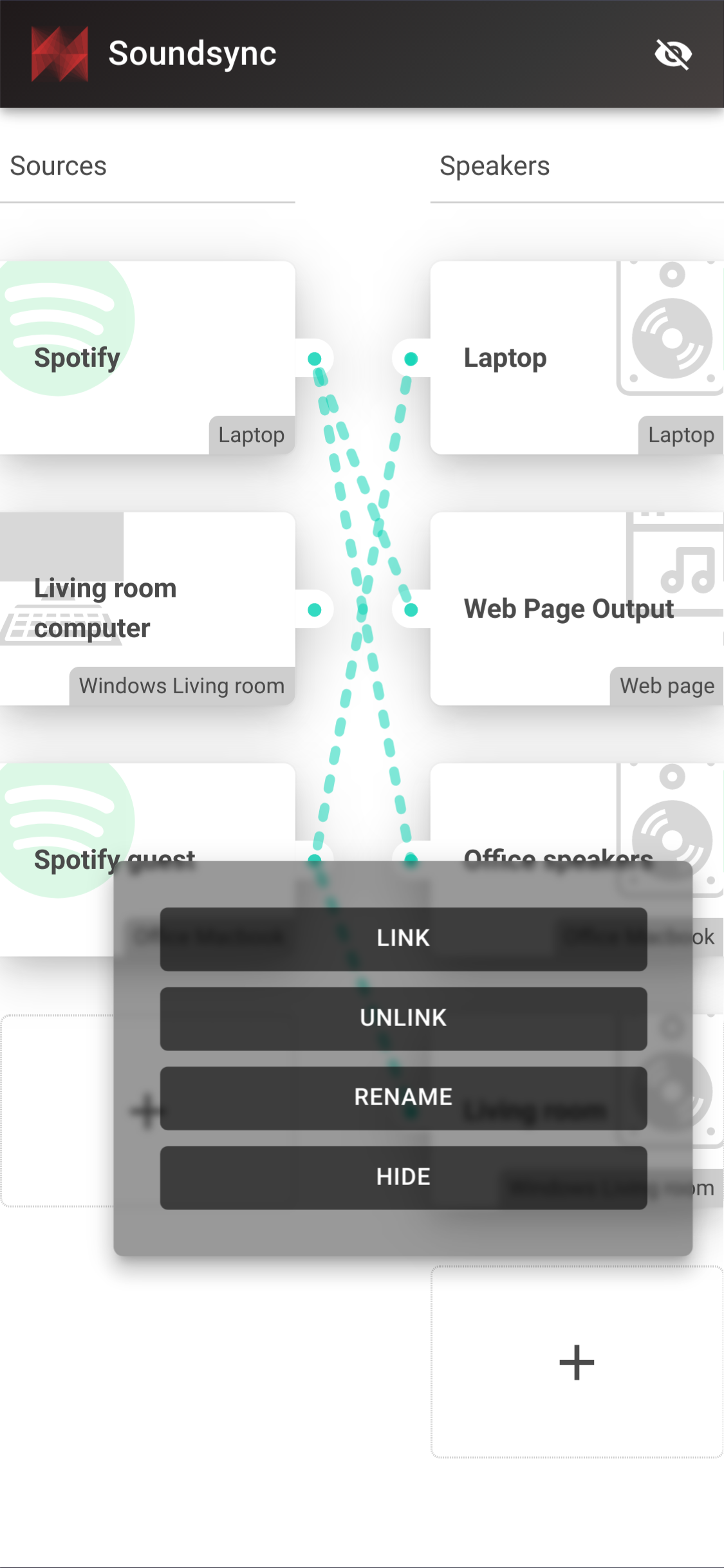
Connect virtual cables between any audio source and any audio output
Soundsync is a web and desktop app to manage every audio source and every audio output in your home from a single interface. Link any audio source to multiple speakers connected to any devices on your home network. Soundsync will keep the music synchronized between all of them.
- 🆓 Free to use
- 🕸️ Work with any number of connected devices, audio sources, audio outputs and every link of your choosing
- 🎶 Compatible with a lot of different audio sources (Spotify Connect with a premium account, Airplay, Hardware Audio input (line in / microphone), Linux system audio ; coming soon: Windows system audio, UPnP and more)
- 🔊 Broadcast sound to any speaker connected to a computer (Windows, MacOS, Linux, RapsberryPi), a web browser (Chrome, Firefox) or a Chromecast and soon more
- 🔗 Group speakers together to synchronize them to the same audio source
- 🎛️ Control everything from a web browser
- 🔓 Not linked to any external service, works offline, no account creation
Quick start
Download and install Soundsync for you operating system on every device in your home you want to use.
Windows |
MacOS |
Linux |
Linux ARM (Raspberry) |
Now go to https://soundsync.app/ to control every Soundsync install on your home network.
Download last development version
Want to try the latest features and help with debugging? Download the latest build! Each commit will generate a new installer with the latest version of the code (but the version number won't be increased).
Need help? Have new ideas? Want to contribute?
Project status
Soundsync is still in an early stage. It's evolving quickly but there is still a lot to do. Here are some features that are being considered:
- Updating info for Spotify sink from WebUI
- Allow changing the name of a peer from the webui
- Group of sinks
- Use waveform-data to show activity on webui
- Integration of media info on webui
- Create a ready to use RaspberryPi image
- Allow devices on multiple networks to be connected together
- Improve linux script by detecting Pulseaudio process if run as root
- Add a option to start Soundsync in kiosk mode for rPi
- In kiosk mode, add a option to start Spotify WebUI in a BrowserView
- Find an alternative way to connect from rendez-vous service for device with DNS Rebinding Protection
- Adds audio visualization for Chromecast view and add an option to use this view from webui
- Resample the audio for each sink to handle drifting clocks instead of seeking to the corrected audio position and hearing an artifact
- Remember Chromecasts and add an option to auto-start them when the linked source become active
- Audio integration with:
- Bluetooth as a audio input
- Bluetooth as a audio output
- Windows monitor (in progress)
- UPnP
- Sonos (blocked: I do not own a test device)
- HEOS (blocked: I do not own a test device)
- Amazon Echo (blocked: I do not own a test device)
- Yamaha MusicCast (blocked: I do not own a test device)
FAQ
-
Is it Open-source ?
Soundsync code is released under the Business Source License. It is a special open-source compatible license which is 100% free to use as long as you don't use it for production work. It means you can use it at home, in your office but you cannot resell it or sell a service/product that directly use it. I'm open to licensing it for a business usage, contact me to work out the details. -
How to debug it?
You can activate the debug logs on the Webui with the commandwindow.soundsyncDebug(). For the desktop version, you need to start the process from the command line (/opt/Soundsync/soundsyncfor Linux). -
I need an integration with X!
Soundsync being a free to use project, I cannot invest money into buying every kind of speakers to build integration for them. I've listed the possible integrations above and you can create an issue if you do not see what you need. As the goal os Soundsync is to support every speaker combination, I'll be happy to work on the integration if someone sends me a compatible device. Contact me for the details. -
Is it available offline?
Every Soundsync peer (a device on which Soundsync is installed) can be used offline. Each peer will detect other peer on the local network with Bonjour and if connected to internet, will use a rendez-vous service to detect other peer with the same IP address. As Bonjour isn't available in a web browser, you need to connect to a peer on your local network with its IP and the port 6512 (for examplehttp://192.168.1.12:6512). Also note that you won't be able to use the webpage as an audio output because the page cannot be served in ahttpscontext. -
How to install on a headless RaspberryPi Install?
Assuming you're using raspbian, first download the package withwget https://soundsync.app/download/soundsync-deb-arm.deb, install it withsudo dpkg -i ./soundsync-deb-arm.deb, if some dependencies are missing install them withsudo apt-get install -fthan start Soundsync and activate it to be started at startup withsudo systemctl enable --now soundsync.service. -
How to disable telemetry?
Soundsync sends some non-identifiable information to our own usage tracker (based on Posthog and hosted on our own server). You can see the list of events sent in the Posthog integration file. If you want to disable this, you can set thedisableTelemetryflag in the config file totrue.
Development
To start Soundsync from the source code you'll need NodeJS and Git installed and then:
git clone https://github.com/geekuillaume/soundsync
cd soundsync
npm install
npm run build
npm run start
You can also use the command npm run start:electron to activate the Electron integrations (Systray icon, error tracking).
Building opus
git submodule update --init --recursive
cd src/utils/opus_vendor
./autogen.sh
emconfigure ./configure --disable-extra-programs --disable-doc --disable-intrinsics --disable-hardening --disable-rtcd --disable-stack-protector
emmake make
cd ../
emcc -s INITIAL_MEMORY=10MB \
-s MAXIMUM_MEMORY=10MB \
-O3 \
-o audio/opus_wasm.js \
-s EXPORT_ES6=1 \
-s MODULARIZE=1 \
-s EXPORT_NAME="Opus" \
-s USE_ES6_IMPORT_META=0 \
-s FILESYSTEM=0 \
-s NODEJS_CATCH_REJECTION=0 \
-s NODEJS_CATCH_EXIT=0 \
-s EXPORTED_RUNTIME_METHODS="['setValue', 'getValue', 'AsciiToString']" \
-s EXPORTED_FUNCTIONS="['_malloc', '_free', '_opus_decoder_create','_opus_decode_float','_opus_decoder_destroy','_opus_encoder_create','_opus_encoder_destroy','_opus_encode','_opus_encode_float','_opus_strerror']" \
-s ENVIRONMENT=node,web \
./opus_vendor/.libs/libopus.a
Attributions
- Speaker by Mestman from the Noun Project
- Slashed zero by Rflor from the Noun Project
- web browser by Iconstock from the Noun Project
- Computer by iconcheese from the Noun Project
- AirPlay by Michiel Willemsen from the Noun Project
- Icons made by Smashicons from www.flaticon.com
- Icons made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com
- Icons made by smalllikeart from www.flaticon.com
- Raspberry Pi by DesignBite from the Noun Project