The course of Machine Learning System Designs (or MLOps) aims at enabling students to truly build fully functional "user-ready" ML systems. It will look at the whole lifecycle of building a real world ML application. At the end of the course, students will be familiar with key tools and frameworks of MLOps.
We are in the early days of the AI revolution, which is expected to bring a large impact to many industries. There is a large demand for skilled engineers who are able to build ML systems.
Bringing a Machine Learning application to production requires many more efforts than solely the ML model development. Famously, there is a large hidden technical debts in designing and implementing all the components coming around your model.
This course and material contained in this repo aims at closing that technical debt by providing essential tools and best practices in MLOps.
- Teaching Staff:
- Thomas Vrancken (Instructor): t.vrancken@uliege.be
- Matthias Pirlet (Teaching Assistant): Matthias.Pirlet@uliege.be
- Class time & place: Classes are held from 9:00 to 12:30 every Monday in B37 S.42 (-1/42) [Liège Sart-Tilman - Polytech]
- Note that it was changed from the original room B28 R.75 (0/75) as we were a too large group for it.
- The new room is not available on the 04/03/2024. That day we will be back in room B28 R.75 (0/75).- Support: You can ask any question by email, during (or after) classes or in person during open office hours every Monday till 18:00 in office 77B (building B28).
- Communication: Main communication point will be Discord (link). Official communication might also come by email.
Note that links to the lecture and labs slides will always be provided shortly before the actual date.
| Date | Week # | Sprint # | Description | Material (gradually added) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05/02/2024 | W0 | Sprint 0 | Course introduction | lecture slides |
| 12/02/2024 | W1 | Sprint 1 | Use case definition | lecture slides |
| 19/02/2024 | W2 | Sprint 1 | Project organisation Lab git code versioning |
lecture slides lab slides |
| 26/02/2024 | W3 | Sprint 2 | Data processing Lab YData-profiling |
lecture slides lab slides - lab notebook |
| 04/03/2024 | W4 | Sprint 2 | Model development(class in B28 R.75 (0/75)) | lecture slides lab folder |
| 11/03/2024 - 18/03/2024 | W4 | Sprint 2 | MS 1 presentations | See project section |
| 11/03/2024 | W5 | Sprint 3 | API implementation | lecture slides guest lecture lab folder |
| 18/03/2024 | W6 | Sprint 3 | Model serving & Cloud infrastructure | lecture slides guest lecture lab folder |
| 25/03/2024 | W7 | Sprint 4 | Serving & training optimisation | lecture slides lab folder |
| 01/04/2024 | No Class | No Class | No Class | No Class |
| 08/04/2024 | W8 | Sprint 4 | Model Pipeline | lecture slides lab folder |
| 15/04/2024 | W9 | Sprint 5 | Monitoring & dashboarding | lecture slides lab folder |
| 22/04/2024 | No Class | No Class | No Class | No Class |
| 29/04/2024 | No Class | No Class | No Class | No Class |
| 06/05/2024 | W10 | Sprint 5 | CICD | lecture slides lab folder |
| 13/05/2024 | W11 | Closing sprint | MS 2 presentations | See project section |
| 31/05/2024 | Exam | See exam section |
- Relevant: Focused on core concepts of building ML applications. Tailored choice of current best practices.
- Practical: Concrete Labs, resources, real life examples, time to experiment, support line, …
- Engagin: Interactive class session. Healthy tempo (break out exercises, QA, …). … And lots of memes.
There are 3 points of learnings for students following this course:
- Lectures: Present theoretical concepts and practices. Usually the first part of each class.
- Labs: Labs are there to learn how to use key tools widely used to build ML systems. They've been cherry picked based on usability, performance, popularity and accessibility.
- Project: You will apply the theoretical and technical learnings in one large group project. You will build a ML application in an engaging way - you're in the driving seat.
Here is a list of all topics covered during this course (and links):
| Week & material | Topics |
|---|---|
| Lecture W0 - Course introduction | Key concepts of ML Systems Design Roles & organisation of ML projects |
| Lecture W01 - Use case definition | Deep dive in real world use cases (Real estate valuation assistant, Rug cutting detection & Data driven sales) Project phases & challenges ML Canvas (project definition) |
| Lecture W02 - Project organization | Waterfall, Agile, Scrum & Kanban way of working Data sources types & identification (internal & external) Data labelling techniques Git flow & trunk based code versioning PEP8 |
| Lab W02 - Git code versioning | Introduction to Git and basic commands GitFlow ohshitgit VSCode |
| Lecture W03 - Data preparation | Basic data format and models Databases (OLTP & OLAP) Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) Data cleaning & feature engineering |
| Lab W03 - YData Profiling | Basic EDA using YDataProfiling |
| Lecture W04 - Model experimentation & containerisation | Model testing (offline & online) Virtual environments Virtual machines Docker Kubernetes |
| Lab W04 - Containerisation | Hands-on for Virtual environments Virtual machines Docker Kubernetes |
| Lecture W05 - API Implementation | API, REST & RPC |
| Guest lecture W05 - Connexion (Robbe Sneyders) | Connexion Concurrency, parallelism & async WSGI, ASGI & middleware Working open source |
| Lab W05 - Flask | Build a simple local Flask API |
| Lecture W06 - Model serving & Cloud infrastructure | Batch vs real-time serving Asynchronous vs synchronous serving Cloud vs on-prem deployment |
| Guest lecture W06 - Cloud Infrastructure (Philippe Modard) | Kaggle platform Cloud computing GCP services Vertex AI |
| Lab W06 - Cloud Run | Deploy an API in the Cloud using Cloud Run |
| Lecture W07 - Serving & training optimisation | Model serving optimisation Parallel and distributed training (data, model and pipeline) Triton Inference Server Model complexity optimisation |
| Lab W07 - Triton Inference Server | Deploying a local Triton Inference Server |
| Lecture W08 - Model pipelines | Microservice architecture ML Model pipeline Pipeline orchestrators |
| Lab W08 - Docker compose | Create an ML oriented microservice system with Docker Compose |
| Lecture W09 - Monitoring & dashboarding | Logging vs monitoring Resource vs performance monitoring Model performance monitoring Drift types: data, target and concept |
| Lab W09 - Google Cloud Storage | Download and upload files using Google Cloud storage |
| Lab W09 - Streamlit | Create an ML oriented dashboard using Streamlit and deploy it to Cloud Run |
| Lecture W10 - CICD | Continuous integration, Continuous development & Continuous deployment Code testing (unit, integration, system & acceptance) Pytest & pylint Multi-environment management (dev, tst, acc, prd) Infrastructure as code Terraform AI AI Legislation A guide to Trustworthy |
| Lab W10 - Gihub Actions | Use Gihub Actions for CICD |
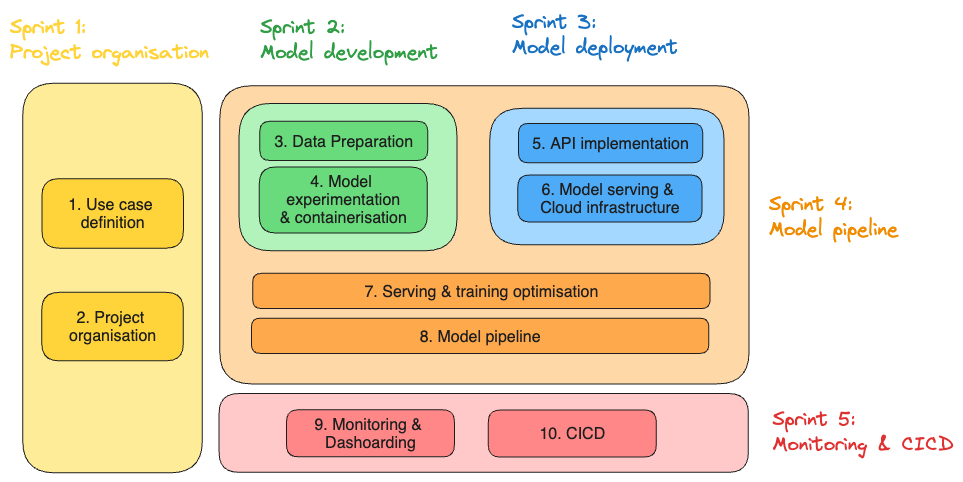
And here is an overview of how the sprints are organised:
All the project info can be found in the project/project_description.pdf document.
Important to highlight that you are the decision makers for the design of your project 👐 Design it in a coherent way. Spend time on features that make sense. Don't see the workpackages as a long checklist, rather on possible points to implement.
For example, if you implement a computer vision model you might spend more time on the model serving rather than the data exploration. Or conversely, if you need to get tabular data from external APIs you might want to spend more time on the data construction rather than on model serving optimisation. Those are design choices you need to make depending on your project - and as always make sure to ask questions to the teaching staff if you have any (ideally at the end of lectures).
The main way to handover the results of your projects will be during the 2 milestones.
The first Milestone will be used to present the work you did during sprint 1 & 2. The main purpose of the first Milestone is to provide feedback and guidance on the project. The final project grade will be determined at the end of the project. If there are any issues highlighted during the milestone there is room for fixing it in the later development of the project.
The second and final Milestone will be used to present the overall project once completed. It will be held during the last class of the semester, in the classroom, instead of a lecture. Teams are welcomed to attend other project presentations.
Make it your own! Focus on what is relevant and interesting. You are free to decide which material (if any) you will use to present your results (short slide deck, demo, show codes, ...).
The project counts for 70% of the final grade, while the exam counts for the remaining 30%.
- At each milestone, you will show your results through a 10 minutes presentation followed by a 5 minutes QA from the teaching staff.
- Next to that, you will submit the codes you implemented so far by creating a pull requests in Github and asking the teaching staff to review it. Make sure to clearly document what is important in the code base for the teaching staff to look at. By default, the teaching staff will focus on the README and the pull request description. Send your codes before the milestone meeting and by an email with a link to the pull request to the teaching staff (t.vrancken@uliege.be and Matthias.Pirlet@uliege.be)
Make sure to send an email with a link to the pull request to the teaching staff when it is ready. Just tagging the teaching staff on Github is not enough.
Milestone 1 presentations will happen between the 11/03/2024 and the 18/03/2024.
- You can book an online meeting via a Google Meets between 13:00 and 17:00 in the days available for each specific milestone (for exact days see calendar invite and timing section)
- You can present it in the classroom from 11:30 to 12:30 right after the lectures in the two weeks following the closing sprint of a milestone (for exact days see calendar invite and timing section). As the class will be busy with presentations after the course those weeks, it means that other teams can still use the time to work on their projects but from another location. Support on the project will then be more ad-hoc those weeks. You can still raise questions by email, Discord or during the open office hours every Monday till 18:00 in office 77B in building B28.
The schedule for the presentations can be found in this sheet. If your group is not in there or if the time does not work for your group please let the teaching staff know.
Attendace: Note that it is fine if one of your team member can really not attend the presentation. If it is not possible for a more people of your team to present that day you can also request to do it another day in an online meeting presentation.
The exam will take the form of an oral exam in whih you will have to answer a series of 4-5 questions based on a case study. You will have 30 minutes to prepare your answer and then 20 minutes to present them. The questions will be based on the course material and tools you used during the project. You can see what you need to know and what is not needed at the end of each lecture. You can also find a practice exam in the exams/practice_exam_june_2024.pdf document.
The PhD students are exempt from the exam. They will be graded on the project only.
You will receive an email with a Doodle link to select your preferred exam slot. It will be first come first serve. The exam will take place on 31/05/2024.
You can first go to the "preparation room" (B28 R.18 (0/18) [Liège Sart-Tilman - Polytech]), where you will be handed your exam page and some paper to take notes. You will have 30 minutes to prepare it, before going to the room where you will actually take the exame (office 77B in B28).
The exam counts for 30% of the final grade, while the project counts for the remaining 70%.
- University of Bari.
- Paper: "Teaching MLOps in Higher Education through Project-Based Learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.01048 (2023) (link)
- Lanubile Filippo, Silverio Martínez-Fernández and Luigi Quaranta
- Stanford University
- CS 329S: Machine Learning Systems Design (link)
- Chip Huyen
- Carnegie-Mellon University
- Machine Learning in Production / AI Engineering (link)
- Christian Kästner
- Machine Learning Engineering for Production (MLOps) Specialization (Coursera, Andrew Ng) (link)
- Made with ML (link)
- Marvelous MLOps (link)
- Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning System - Google (link)
- Building Machine Learning Powered Applications: Going from Idea to Product (Emmanuel Ameisen)
- Introducing MLOps (Mark Treveil, Nicolas Omont, Clément Stenac et al.)
- Machine Learning Design Patterns (Valliappa Lakshmanan, Sara Robinson, Michael Munn)
Many people helped and supported through the preparation of this course. Special thanks to:
- Gilles Louppe
- Filippo Lanubile
- Luigi Quaranta
- Robbe Sneyders
- Philippe Modard
- Sebastian Wehkamp
- Ruwan Lambrichts
- Jason Li
- Thomas Janssens