A PyTorch Implementation for Drop an Octave
This repository contains a PyTorch implementation of the paper Drop an Octave: Reducing Spatial Redundancy in Convolutional Neural Networks with Octave Convolution.
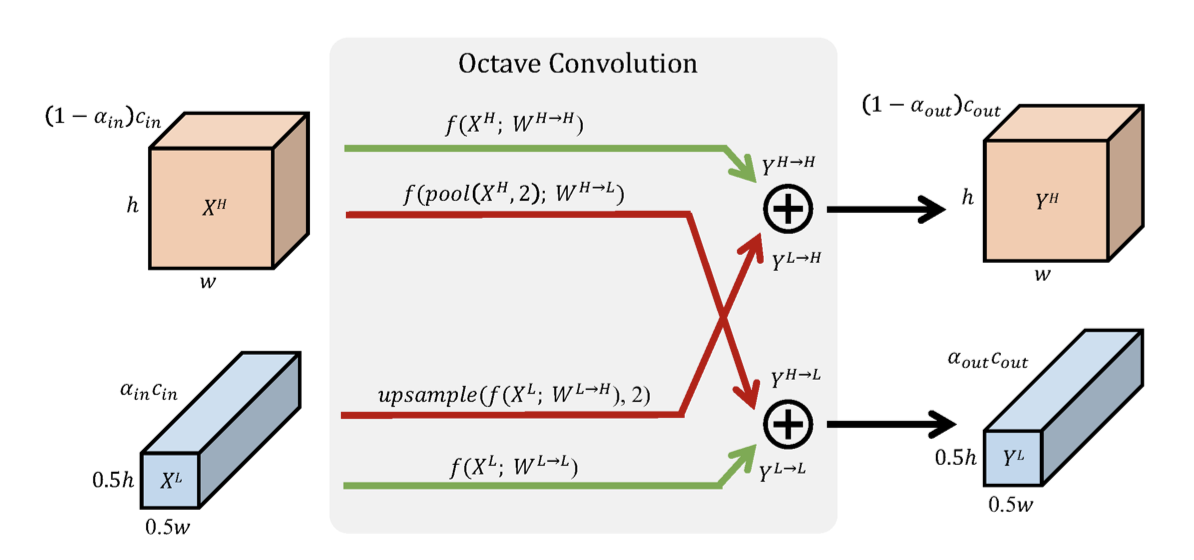
You can pretty much use the OctConv2d layers to replace your normal nn.Conv2d layers, with a small difference. There are three types of Octave Convolutions, 'first', 'regular', and 'last'. The "First" type takes a tensor input and returns a tuple of two tensors. The "Regular" type takes the tuple and outputs the same spec of tuple. The "Last" type takes the tuple and outputs one tensor.
Here's an example:
class OctCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.convs = nn.Sequential(OctConv2d('first', in_channels=1, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3),
OctReLU(),
OctConv2d('regular', in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3),
OctReLU(),
OctConv2d('regular', in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3),
OctReLU(),
OctMaxPool2d(2),
OctConv2d('regular', in_channels=128, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3),
OctReLU(),
OctConv2d('last', in_channels=128, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(6272, 256),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(256, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.convs(x)
x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))
x = self.fc(x)
return x
Note that OctReLU and OctMaxPool2d are wrappers for nn.ReLU and nn.MaxPool2d, so that you can use OctConv2d layer with nn.Sequential.
- group/dilation/padding congruency
- Added ResNets
MXNet implementation by terrychenism here
Another PyTorch implementation by lxtGH here
This repo is MIT licensed.