This plugin adds Vector Base Amplitude Panning (VBAP) to Unreal Engine. It's intended as a proof of concept and a lot of work can still be done. Because UE restricts the number of speakers, and soundfield submixes are also generally designed to be used with ambisoncis or HRTF, there are a couple of hacks that needed to be employed to get this to work.
I found the lack of support for larger speaker systems than 7.1 (8 channels) quite restricting. UE is a very powerful tool to create virtual worlds and it's nice to experience those on powerful speaker systems.
This plugin implements a Spatializer that is used to attach spatial information to the audio buffer, which will then be used to encode the audio to a VBAP-SoundfieldPacket. The plugin uses a SoundfieldEndpointSubmix to create a custom audio output to the hardware, to use an arbitrary number of speakers.
Well, you probably don't... But maybe you have a lot of speakers laying around and you want to spatialize your awesome sounds using all of them.
Clone the repository (or download as a .zip file.)
git clone https://github.com/TobiasGrothmann/Spatial-Audio-Plugin-for-Unreal-Engine.gitCopy the folder SpatialAudio into your project's Plugins directory. It is installed like any other UE plugin. (If it does not exist, create a folder called Plugins next to your .uproject file.)
Open the .upoject file and Unreal Engine will ask you to let it compile:
Right-click the .uproject and select generate project files. This will create the Visual Studio project file. Open the Visual Studio (2019) project and select Build > Rebuild Solution. Afterwards, you can either start with a debugger attached by hitting F5 or just close VS open the .uproj file.
Create the .xcworkspace by running:
<path/to/engine>Engine/Build/BatchFiles/Mac/GenerateProjectFiles.sh -projectfiles -project=<path/to/project> -game -engineopen the xcode workspace and hit cmd + r to compile and run.
- UE_4.25 on MacOS or Windows
- audio device that supports lots of speakers
- lots of speakers, well you really don't need a lot lot; a couple are enough, but you need to place them in a three-dimensional layout.
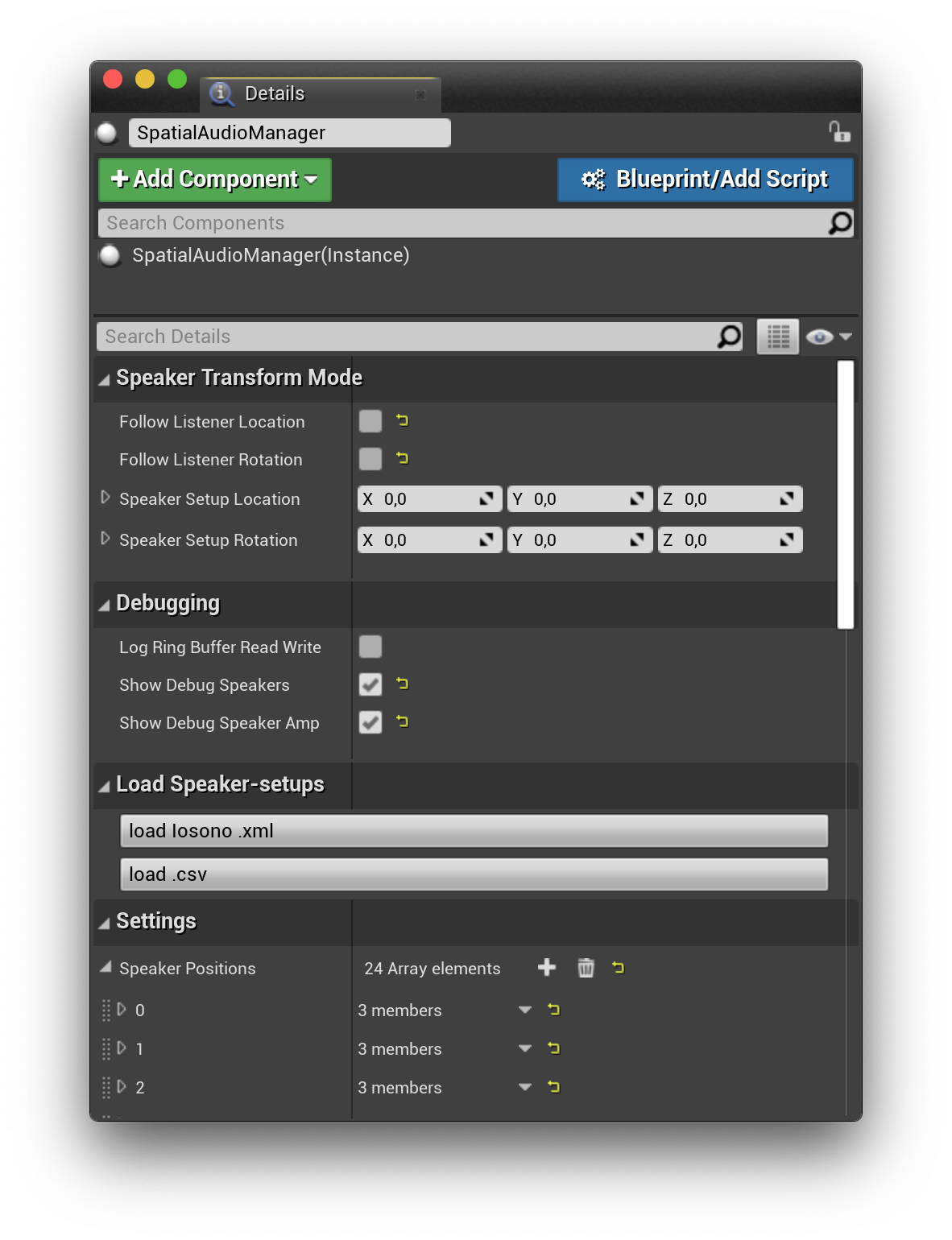
- coordinates for all of your speakers, you can either enter them manually or load them as a .csv file directly from the Spatial Audio Manager
- RtAudio in UE (which is used to output sound) only supports the Direct Audio API on windows. This means that it might not detect the number of channels correctly.
To open up the Spatial Audio Setup-tab click the icon in the toolbar:
Make sure that the Spatial Audio Spatializer is used as the spatializer plugin in the project settings for your platform. Also make sure that there is exactly one SpatialAudioManager in the persistent level.
To spatialize sounds using VBAP, the checkbox spatialized has to be checked for the actor and the checkbox Endpoint has to be checked for the used sound asset. This makes sure that spatialization is used and set to "binaural" (not really the case, but UE uses this term to show that a spatializer plugin is used). It also makes sure that the audio asset is routed to the SASoundfieldEndpoint (Located in "SpatialAudio Content -> Sound -> SASoundfieldEndpoint"; select ViewOptions -> Show Plugin Content" first).
Select the SpatialAudioManager in the scene and change the settings in its details panel. Select the right Audio Output Device. As you can see, I am using Loopback Audio, because the output device needs to support as many speakers as you have set up in your speaker layout in the Speaker Positions array:
If anything doesn't work check the OutputLog (Window -> DeveloperTools -> Output Log) and feel free to ask. Remember, this is just a proof of concept.
Select Show Debug Speaker and Show Debug Speaker Amp from the Spatial Audio Manager's details panel. This will spawn a speaker actor for every speaker you have setup. If you start a play session, the size of the speaker will visualize the currently used VBAP gain coeffient.
Make sure you selected the correct audio device in the SpatialAudioManager.
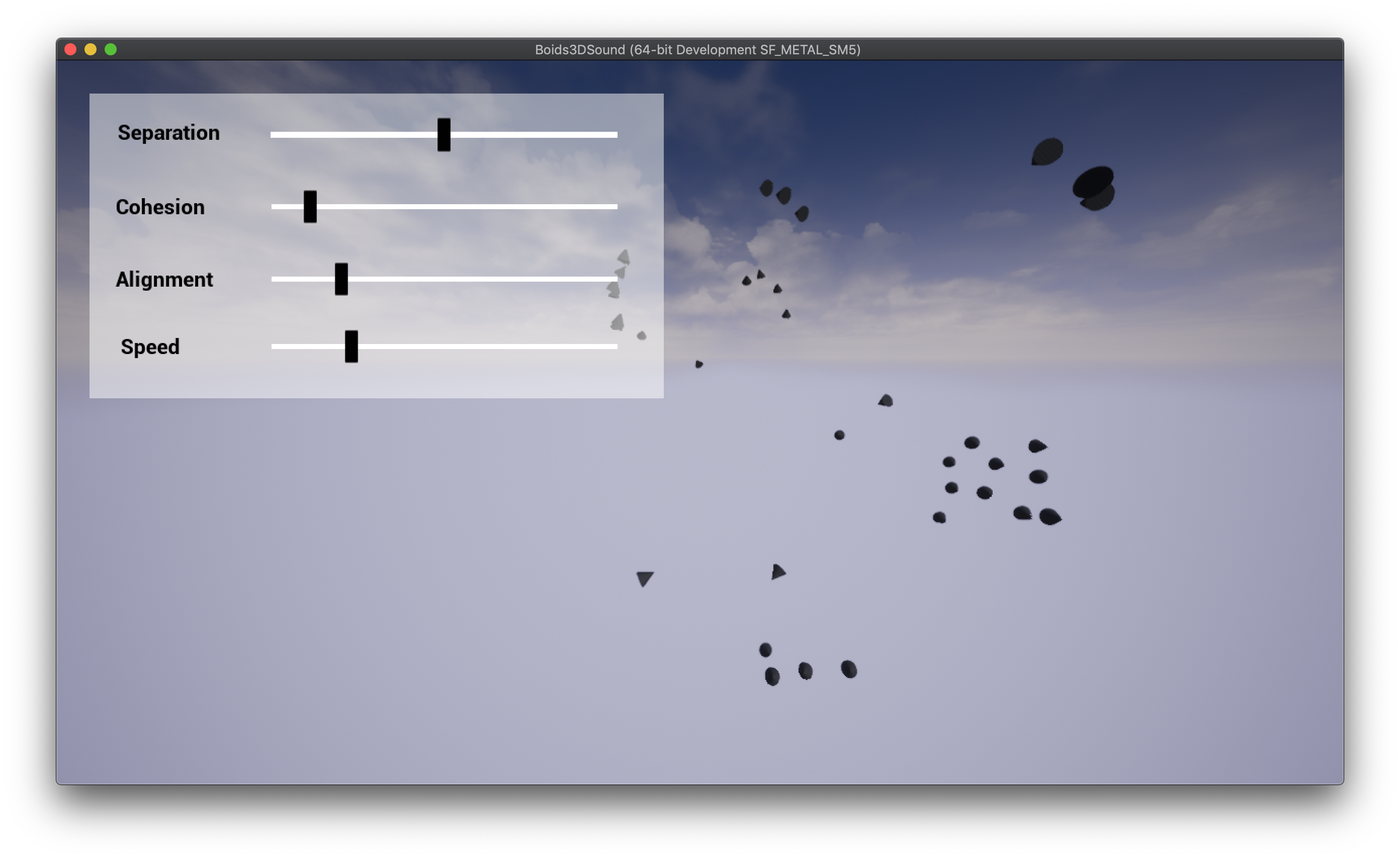
To get started, try the example project which uses the Boids flocking algorithm to spatialize sounds around the listener.