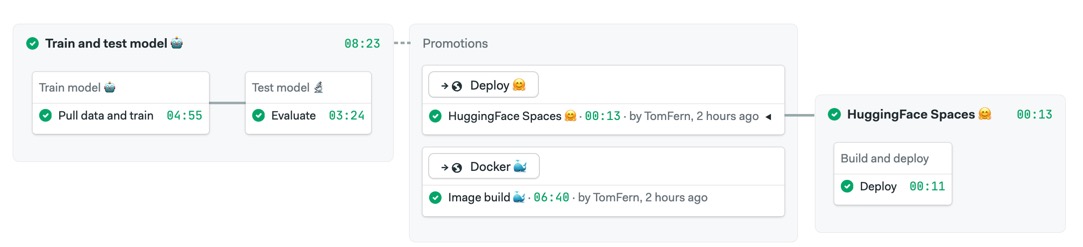
This repository contains everything needed to automate training, testing and deployment of an example ML model with DevOps tools and CI/CD.
The original code can be found in Kaggle.com. Feel free to copy the notebook and run it on the cloud to get familiar with the demo:
https://www.kaggle.com/code/tomasfern/cats-or-dogs-classifier
The base model is resnet34, a 34-layer Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. This repository fine-tunes the base model to classify images as dogs or cats.
For fine-tuning, we'll usethe Oxfort IIIT Pets dataset. It consists of 7393 labeled images of dogs and cats. The labels are taken from the name of the file. For example:
yorkshire_terrier_85.jpg
- The filename begins with lowercase, indicating it's a dog.
- The words indicate the breed of the dog.
- The number indicates the sample item.
Russian_Blue_111.jpg
- The filename begins with uppercase, indicating it's a cat.
- The words indicate the breed of the cat.
- The number indicates the sample item.
We use streamlit to run a web application on top of the model.
main: final version of the repo with DVC and Semaphore CI/CD initialized.initial: this branch only contains the code. Good starting point to learn how to setup MLOps.
Before starting, you'll need the folliwing tools:
- DVC
- Python 3 and pip
- Docker Desktop or Docker Engine
- Git and Git-LFS
- AWS CLI
It is also recommended to sign up for free accounts on the following websites:
- Fork and clone this repository
- Create a virtualenv:
python -m venv .venv - Activate it:
source .venv/bin/activate - Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Initialize the DVC repository:
dvc init - Download the sample dataset:
dvc get https://thor.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/pets/images.tar.gz data/images.tar.gz(alternative link: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/tomasfern/oxford-iit-pets) - Ensure the downloaded tarball is located in
data/images.tar.gz
To train the model manually:
- Run data prepare script (unpack tarball):
python src/prepare.py - Run training script:
python src/train.py - Run test script:
python src/test.py
You should now have the models files in the models/ directory.
You can now run the application with:
$ streamlit run src/app.pyStreamlit should open a browser window, you can upload pictures and get the model to classify them.
To run the application in a container:
$ docker build -t cats-and-dogs .
$ docker run -d -it -p 8501:8501 cats-and-dogsOpen your browser to https://localhost:8501 to use the application.
To deploy the application to HugginFace Spaces:
- Create a HuggingFace account.
- Create a SSH keypair and upload the public key to HugginFace.
- Create a Streamlit Space on HuggingFace
- Run the deployment script:
# eg ./deploy.sh https://huggingface.co/spaces/tomfern/cats-and-dogs /home/semaphore/.ssh/id_ed25519 ./deploy <huggingface_https_git_repo> <path_to_priv_key>
- After a few minutes the application should be running in your HuggingFace Space.
We'll use DVC to track datasets and automate the whole process.
First, download
To setup a DVC ML Pipeline, use dvc stage add like this:
# prepare stage
$ dvc stage add -n prepare \
-d src/prepare.py -d data/images.tar.gz \
-o data/images \
python src/prepare.py
# train stsage
$ dvc stage add -n train \
-d src/train.py -d data/images \
-o models/model.pkl -o models/model.pth \
--plots metrics/confusion_matrix.png \
--plots metrics/top_losses.png \
--plots metrics/finetune_results.png \
python src/train.py
# test stage
$ dvc stage add -n test \
-d src/test.py -d models/model.pkl -d models/model.pth \
python src/test.pyThis will create dvc.yaml. You can see the dependecy graph with:
$ dvc dag
+---------+
| prepare |
+---------+
*
*
*
+-------+
| train |
+-------+
*
*
*
+------+
| test |
+------+To run the pipeline:
$ dvc reproThis will execute the required steps (ala Makefile) only. After each execution you should commit dvc.yaml and dvc.lock to preserve the state of the training in Git.
As of now, only the hashes of the trained model is stored in the GitHub. The actual model files are automatically added to .gitignore when the DVC stages are created, so they only exist in your machine. This makes sense because both the data and the model might turn up being too large and unwieldy for a GitHub repository.
To push the to the cloud you need to add remote storage. DVC supports multiple storage providers including Google Cloud and AWS S3 Buckets.
In the following example, we use an S3 Bucket for remote storage:
- Go to your AWS Console and create an S3 Bucket (eg.
mybucket-dvc) - Check you have access to the buckets from your machine:
aws s3 ls - Add the AWS remote to DVC:
dvc remote add mybucket-dvc s3://mybucket/main - Set the bucket as default:
dvc remote default mybucket-dvc - Push the files to the bucket:
dvc push
Now each time you make change you should both commit the changes to GitHub and then do a dvc push. You can get the latest files from the remote storage with dvc pull
You can reproduce the training in another machine by leveraging Git and the remote storage. Once you configure the AWS CLI to access your S3 bucket you can:
- Pull from dvc remote repo:
dvc pull - Run workflow:
dvc repro - Push data and artifacts to remote repo:
dvc push - Commit changes:
git add -A && git commit
To setup a CI/CD pipeline you'll need a few things:
- A token with access to the remote storage. For example, an IAM account with restricted access to the S3 bucket (read/write).
- For containers, a token to access the Docker registry. For example, the user/password for a hub.docker.com account.
- For running the app in HuggingFace Spaces, you'll need to upload your SSH pubkey and install GIT LFS.
Example configuration with Semaphore CI/CD:
- Create secrets for:
- AWS:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYwith S3 bucket access. - hub.docker.com:
DOCKER_USERNAMEandDOCKER_PASSWORD - huggingface: upload private SSH key to
/home/semaphore/.ssh/(e.gid_ed25519)
- AWS:
- Add your project to Semaphore
- Ensure the secrets names are correct and change the paths in the deploy pipeline to match your HuggingFace repository HTTPS URL.
- Push changes and see your pipeline flow.
The main branch includes an example pipeline to train, test, containerize and deploy your application.
Copyright 2024 RenderedText
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.