diffusers-interpret is a model explainability tool built on top of 🤗 Diffusers
Install directly from PyPI:
pip install --upgrade diffusers-interpret
Let's see how we can interpret the new 🎨🎨🎨 Stable Diffusion!
- Explanations for StableDiffusionPipeline
- Explanations for StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
- Explanations for StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
import torch
from contextlib import nullcontext
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
from diffusers_interpret import StableDiffusionPipelineExplainer
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
use_auth_token=True,
# FP16 is not working for 'cpu'
revision='fp16' if device != 'cpu' else None,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device != 'cpu' else None
).to(device)
# optional: reduce memory requirement with a speed trade off
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
# pass pipeline to the explainer class
explainer = StableDiffusionPipelineExplainer(pipe)
# generate an image with `explainer`
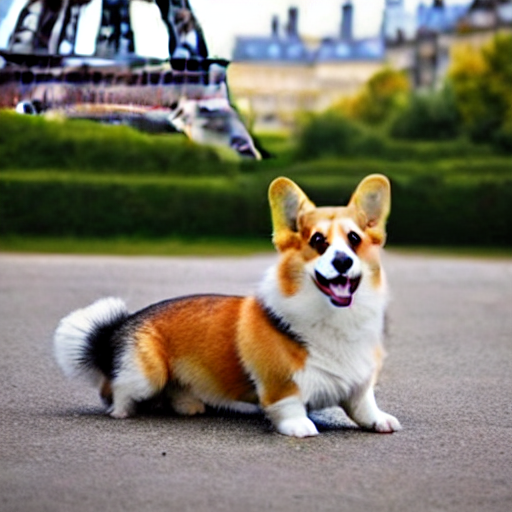
prompt = "A cute corgi with the Eiffel Tower in the background"
with torch.autocast('cuda') if device == 'cuda' else nullcontext():
output = explainer(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=15
)If you are having GPU memory problems, try reducing n_last_diffusion_steps_to_consider_for_attributions, height, width and/or num_inference_steps.
output = explainer(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=15,
height=448,
width=448,
n_last_diffusion_steps_to_consider_for_attributions=5
)
You can completely deactivate token/pixel attributions computation by passing n_last_diffusion_steps_to_consider_for_attributions=0.
Gradient checkpointing also reduces GPU usage, but makes computations a bit slower:
explainer = StableDiffusionPipelineExplainer(pipe, gradient_checkpointing=True)
To see the final generated image:
output.imageYou can also check all the images that the diffusion process generated at the end of each step:
output.all_images_during_generation.show()To analyse how a token in the input prompt influenced the generation, you can study the token attribution scores:
>>> output.token_attributions # (token, attribution)
[('a', 1063.0526),
('cute', 415.62888),
('corgi', 6430.694),
('with', 1874.0208),
('the', 1223.2847),
('eiffel', 4756.4556),
('tower', 4490.699),
('in', 2463.1294),
('the', 655.4624),
('background', 3997.9395)]Or their computed normalized version, in percentage:
>>> output.normalized_token_attributions # (token, attribution_percentage)
[('a', 3.884),
('cute', 1.519),
('corgi', 23.495),
('with', 6.847),
('the', 4.469),
('eiffel', 17.378),
('tower', 16.407),
('in', 8.999),
('the', 2.395),
('background', 14.607)]diffusers-interpret also computes these token/pixel attributions for generating a particular part of the image.
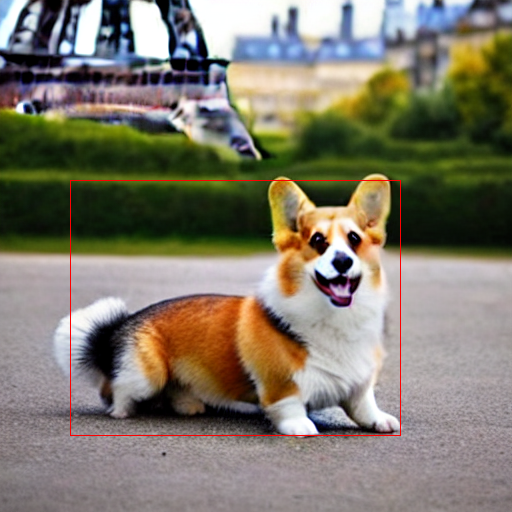
To do that, call explainer with a particular 2D bounding box defined in explanation_2d_bounding_box:
with torch.autocast('cuda') if device == 'cuda' else nullcontext():
output = explainer(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=15,
explanation_2d_bounding_box=((70, 180), (400, 435)), # (upper left corner, bottom right corner)
)
output.imageThe generated image now has a red bounding box to indicate the region of the image that is being explained.
The attributions are now computed only for the area specified in the image.
>>> output.normalized_token_attributions # (token, attribution_percentage)
[('a', 1.891),
('cute', 1.344),
('corgi', 23.115),
('with', 11.995),
('the', 7.981),
('eiffel', 5.162),
('tower', 11.603),
('in', 11.99),
('the', 1.87),
('background', 23.05)]import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
from diffusers_interpret import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipelineExplainer
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
use_auth_token=True,
).to('cuda')
explainer = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipelineExplainer(pipe)
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation"
# let's download an initial image
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
response = requests.get(url)
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
init_image = init_image.resize((448, 448))
with torch.autocast('cuda'):
output = explainer(
prompt=prompt, init_image=init_image, strength=0.75
)output will have all the properties that were presented for StableDiffusionPipeline.
Additionally, it is also possible to visualize pixel attributions of the input image as a saliency map:
output.input_saliency_map.show()or access their values directly:
>>> output.pixel_attributions
array([[ 1.2714844 , 4.15625 , 7.8203125 , ..., 2.7753906 ,
2.1308594 , 0.66552734],
[ 5.5078125 , 11.1953125 , 4.8125 , ..., 5.6367188 ,
6.8828125 , 3.0136719 ],
...,
[ 0.21386719, 1.8867188 , 2.2109375 , ..., 3.0859375 ,
2.7421875 , 0.7871094 ],
[ 0.85791016, 0.6694336 , 1.71875 , ..., 3.8496094 ,
1.4589844 , 0.5727539 ]], dtype=float32)or the normalized version:
>>> output.normalized_pixel_attributions
array([[7.16054201e-05, 2.34065039e-04, 4.40411852e-04, ...,
1.56300011e-04, 1.20002325e-04, 3.74801020e-05],
[3.10180156e-04, 6.30479713e-04, 2.71022669e-04, ...,
3.17439699e-04, 3.87615233e-04, 1.69719147e-04],
...,
[1.20442292e-05, 1.06253210e-04, 1.24512037e-04, ...,
1.73788882e-04, 1.54430119e-04, 4.43271674e-05],
[4.83144104e-05, 3.77000870e-05, 9.67938031e-05, ...,
2.16796136e-04, 8.21647482e-05, 3.22554370e-05]], dtype=float32)Note: Passing explanation_2d_bounding_box to the explainer will also change these values to explain a specific part of the output image.
The attributions are always calculated for the model's input (image and text) with respect to the output image.
Same as StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline, but now we also pass a mask_image argument to explainer.
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
from diffusers_interpret import StableDiffusionInpaintPipelineExplainer
def download_image(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
pipe = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
use_auth_token=True,
).to('cuda')
explainer = StableDiffusionInpaintPipelineExplainer(pipe)
prompt = "a cat sitting on a bench"
img_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png"
mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png"
init_image = download_image(img_url).resize((448, 448))
mask_image = download_image(mask_url).resize((448, 448))
with torch.autocast('cuda'):
output = explainer(
prompt=prompt, init_image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, strength=0.75
)output will have all the properties that were presented for StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline and StableDiffusionPipeline.
The only difference is that we can now see the masked part of the image:
output.input_saliency_map.show()Check other functionalities and more implementation examples in here.
-
Add interactive display of all the images that were generated in the diffusion process -
Add explainer for StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline -
Add explainer for StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline - Add attentions visualization
- Add unit tests
- Website for documentation
- Do not require another generation every time the
explanation_2d_bounding_boxargument is changed - Add interactive bounding-box and token attributions visualization
- Add more explainability methods
Feel free to open an Issue or create a Pull Request and let's get started 🚀
A special thanks to:
- @andrewizbatista for creating a great image slider to show all the generated images during diffusion! 💪
- @TomPham97 for README improvements and the GIF visualization 😁