Images are the largest source of data in healthcare and, at the same time, one of the most difficult sources to analyze. Clinicians today must rely largely on medical image analysis performed by overworked radiologists and sometimes analyze scans themselves. Computer vision software based on the latest deep learning algorithms is already enabling the automated analysis to provide accurate results that are delivered immeasurably faster than the manual process can achieve. Multimodal medical imaging can provide us with separate yet complementary structure and function information of a patient study and hence has transformed the way we study living bodies. The motivation for multimodal imaging is to obtain a superior exquisite image that will provide accurate and reliable statistics than any single image while retaining the best functions for the snapshots software program for medically testing, diagnosing and curing diseases.
Diagnostic tools include Computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and thus these are the two modalities that we will consider for Image Fusion Process.
We aim to approach a three step process:
- Image Registeration
- Image Fusion
- Image Segmentation
Image registration is the process of transforming images into a common coordinate system so corresponding pixels represent homologous biological points. Registration can be used to obtain an anatomically normalized reference frame in which brain regions from different patients can be compared.
Image landmark registration is a simple process where a number of points (landmarks) are defined on the same locations in two volumes. The landmarks are then matched by an algorithm, and the volumes are thus registered. The CT scan image is taken as the reference (fixed) image and the MRI scan image is aligned as per the points selected by the user.
- Python Notebook -
Navigate to
python scripts/Image Registration Process.ipynband select the CT and MRI Images. - GUI -
Setup Flask and install dependencies and run:
python app.pySelect the appropriate CT and MRI Images. The registered MRI Image gets saved instatic/mri_registered.jpg
Transfer learning is an optimization that allows rapid progress or improved performance when modeling the second task. We aim to use the VGG-19 CNN architecture with its pre-trained parameters which would help us to achieve our target. Visual Geometry Group (VGG-19) is a convolutional neural network that is trained on more than a million images from the ImageNet database. The network is 19 layers deep and can classify images into 1000 object categories.
We convert our images to YCbCr color format because it preserves detailed information of luminance component.
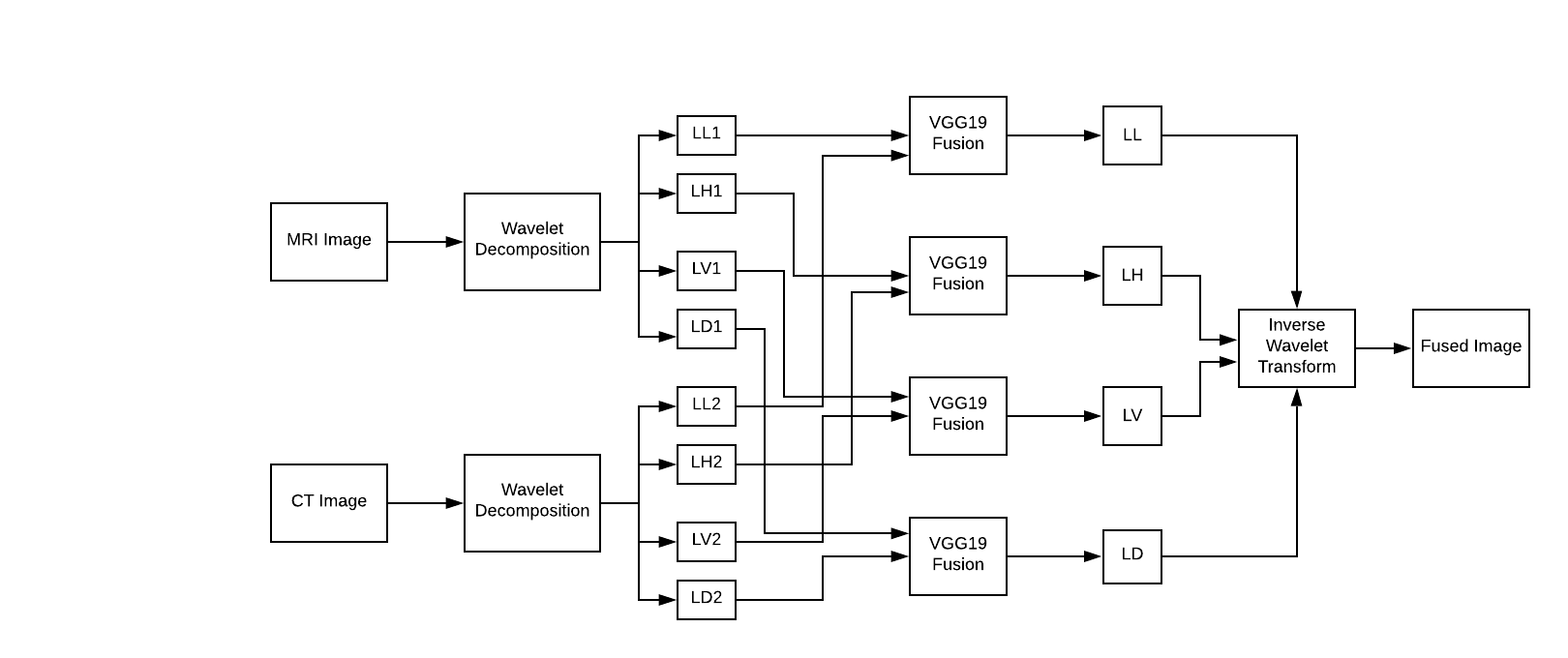
Wavelet transform provides high frequency resolution at low frequencies and high time resolution at high frequencies. A discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is a wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. It captures both frequency and location information (location in time).
- Apply wavelet decomposition on CT image to generate approximate coefficient LL1 and three detail coefficients: LH1(horizontal), LV1(vertical), LD1(diagonal)
- Apply wavelet decomposition on MR image to generate approximate coefficient LL2 and three detail coefficients: LH2(horizontal), LV2(vertical), LD2(diagonal)
- Apply fusion based on VGG-19 network on four pairs: (LL1 and LL2), (LH1 and LH2), (LV1 and LV2) and (LD1 and LD2), to generate LL band, LH band, LV band and LD band.
- Apply inverse wavelet transform on the four bands generated in step 3 to obtain fused image.
- Python Notebook -
Navigate to
python scripts/Transfer_Learning.ipynband provide paths to registered set of MRI and CT Images. - GUI -
Setup Flask and install dependencies and run:
python app.pyIn continuation to the above GUI approach the fused image gets saved instatic/fusion.jpg
Watershed segmentation is a region-based technique that utilizes image morphology. It requires selection of at least one marker (“seed” point) interior to each object of the image, including the background as a separate object. The markers are chosen by an operator or are provided by an automatic procedure that takes into account the application-specific knowledge of the objects. Once the objects are marked, they can be grown using a morphological watershed transformation
- Python Notebook -
Navigate to
python scripts/Image Segmentation.ipynband provide paths to registered set of MRI and CT Images. - GUI -
Setup Flask and install dependencies and run:
python app.pyIn continuation to the above GUI approach the fused image gets saved instatic/segmented.jpg
All the above functionalities have also been implemented on a Desktop Application using Tkinter.