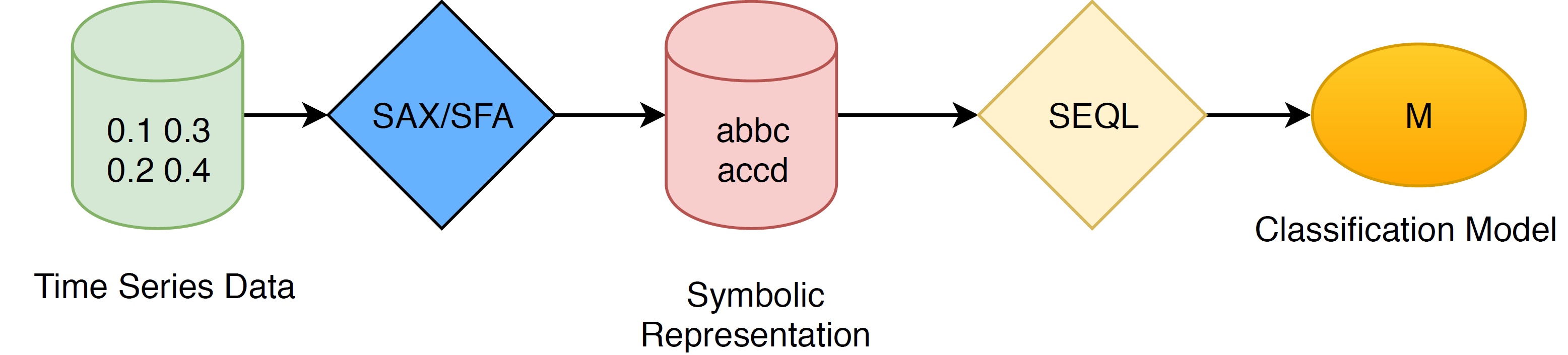
Mr-SEQL is a time series classification software which utilizes linear models (logistic regression) and multiple symbolic representations of time series (SAX, SFA) to deliver an accurate and interpretable time series classifier.
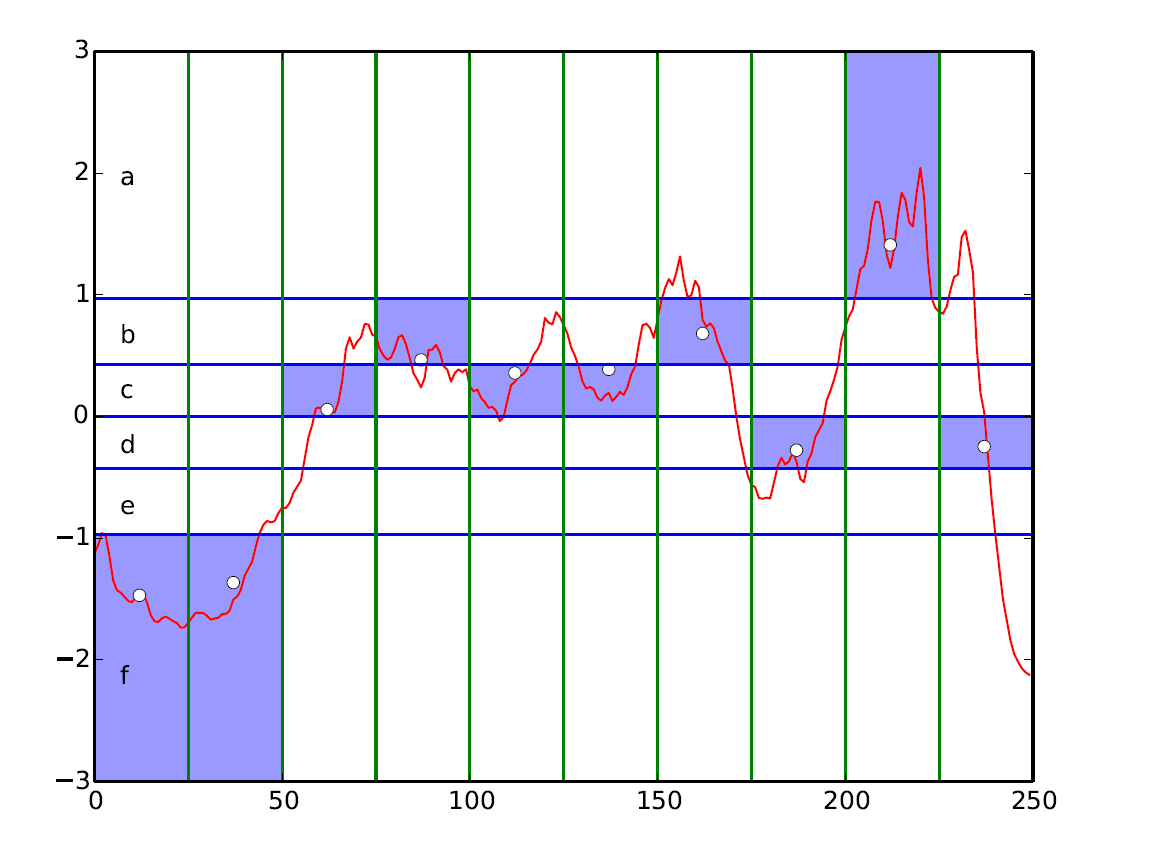
SAX is a transformation method to convert a numeric vector to a symbolic representation, i.e., a sequence of symbols from a predefined alphabet a. SAX first computes the Piecewise Aggregate Approximation (PAA) of a time series in the time domain, then transforms this approximation to a symbolic representation.
PAA reduces a time series of length L to a vector of length l (l < L is also the length of the symbolic sequence) by dividing the time series into equal segments. Each segment is then replaced with its mean value.
PAA is then followed by a discretisation step which replaces each value of the PAA with a corresponding symbol. The symbol is selected from the alphabet based on the interval in which the value falls. There are a intervals, as many as the size of the alphabet. Each interval is associated with a symbol from the alphabet. Assuming that the time series is normal distributed, the intervals are divided under the normal distribution (i.e. N(0,1)) with equal probability.
SFA also transforms a time series to a symbolic representation, but this time using the frequency domain for the discretisation. The core differences between SAX and SFA are the choices of approximation and discretisation techniques. SFA uses a Discreet Fourier Transform (DFT) method to approximate a time series.
More information on SFA can be found here: https://github.com/patrickzib/SFA
SEQL is a symbolic sequence learning algorithm (e.g., it can take as input sequences "abcd aabc ...") that efficiently traverses a large feature space and selects the most discriminative subsequences for a linear model, based on a training dataset.
The original SEQL software and its description can be found here: https://github.com/heerme/seql-sequence-learner
SEQL learns a linear classification model from the symbolic representation of time series (either SAX or SFA).
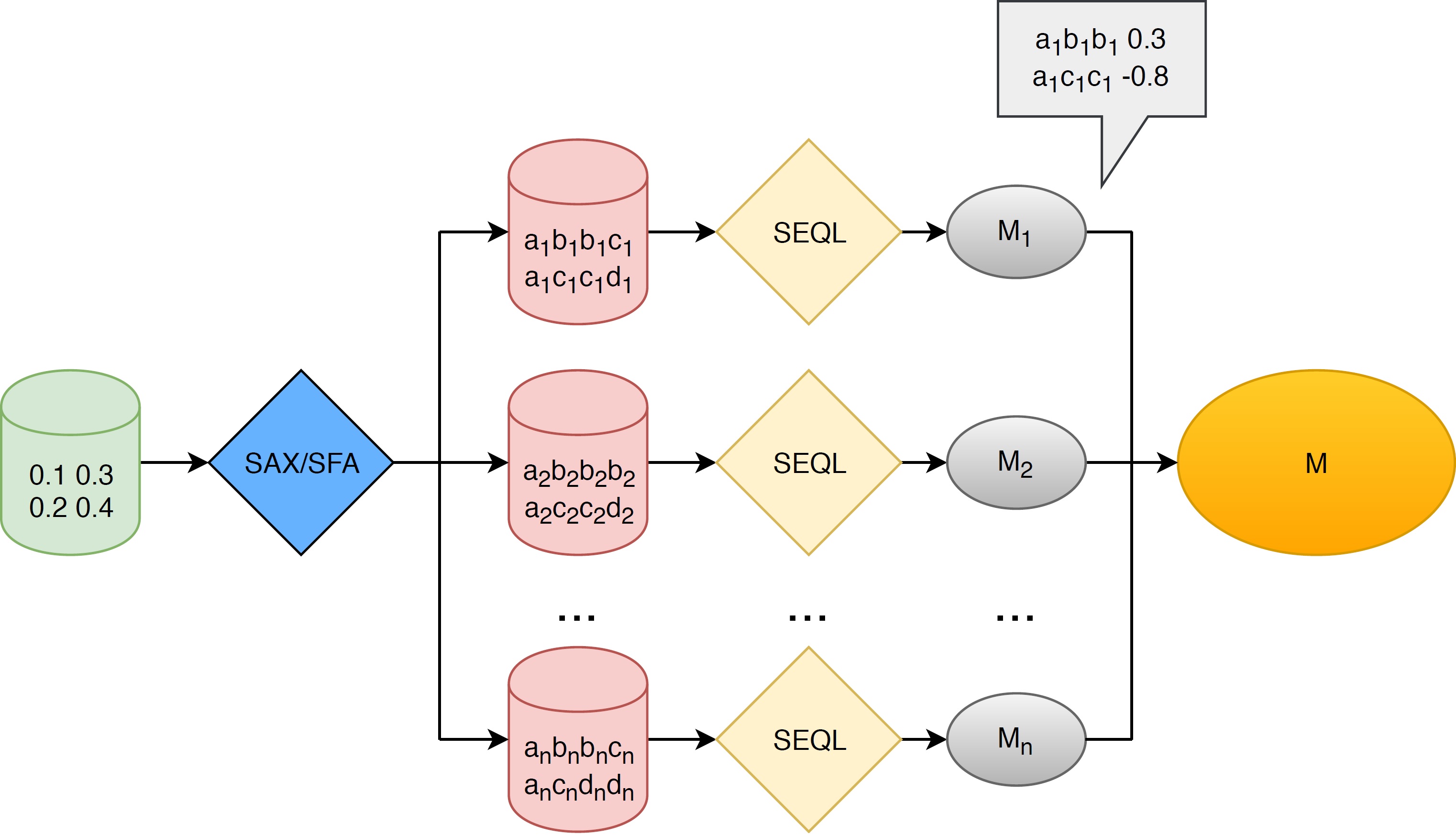
SEQL can be combined with symbolic representations of multiple resolutions and multiple domains.
As the resulting time series classifier is linear, the model itself is interpretable. We can visualize the SAX features selected by SEQL by mapping them back to the raw time series domain.
Requires: cmake for compiling the C source code. To compile execute following commands in the src directory:
mkdir -p build
cd build
mkdir -p Release
cd Release
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ../../src/
make
cd bin
Copy data to the working directory. Create a new directory to store output:
cp ../../../data/Coffee/Coffee_* .
mkdir saxdir
Prepare the SAX representations for Coffee_TRAIN and output results in "saxdir/sax.train". Parameter configurations are saved in "saxdir/config". In the config file, on each row is the description of a fixed SAX representation, e.g., for a line "0 16 16 4" the first number (0) is the index of the representation, the second number (16) is the window length, the third number (16) is the word length and the fourth number (4) is the alphabet size.
./sax_convert -i Coffee_TRAIN -o saxdir/sax.train > saxdir/config
Prepare the SAX representations for Coffee_TEST and output results in "saxdir/sax.test"
./sax_convert -i Coffee_TEST -o saxdir/sax.test
Classify with Ensemble SEQL by running the binary "mr_seql". This outputs several files in folder saxdir: "feature" includes the features selected by SEQL from each representation; "train.x and test.x" contain the vector space representation for the train and test time series and "train.y and test.y" contain the class labels. These files can subsequently be used for training another classifier such as logistic regression (or any other classifier).
./mr_seql -t saxdir/sax.train -T saxdir/sax.test -o saxdir
Classify with features selected by SEQL and linear models (or any other classifier). The following example uses sklearn Logistic Regression for classification with the selected features. In this scenario, SEQL is used for feature selection. Data is transformed in a feature vector space and fed to a logistic regression classifier. To run the logistic regression classifier execute:
python ../../../src/python/mf_logreg.py saxdir
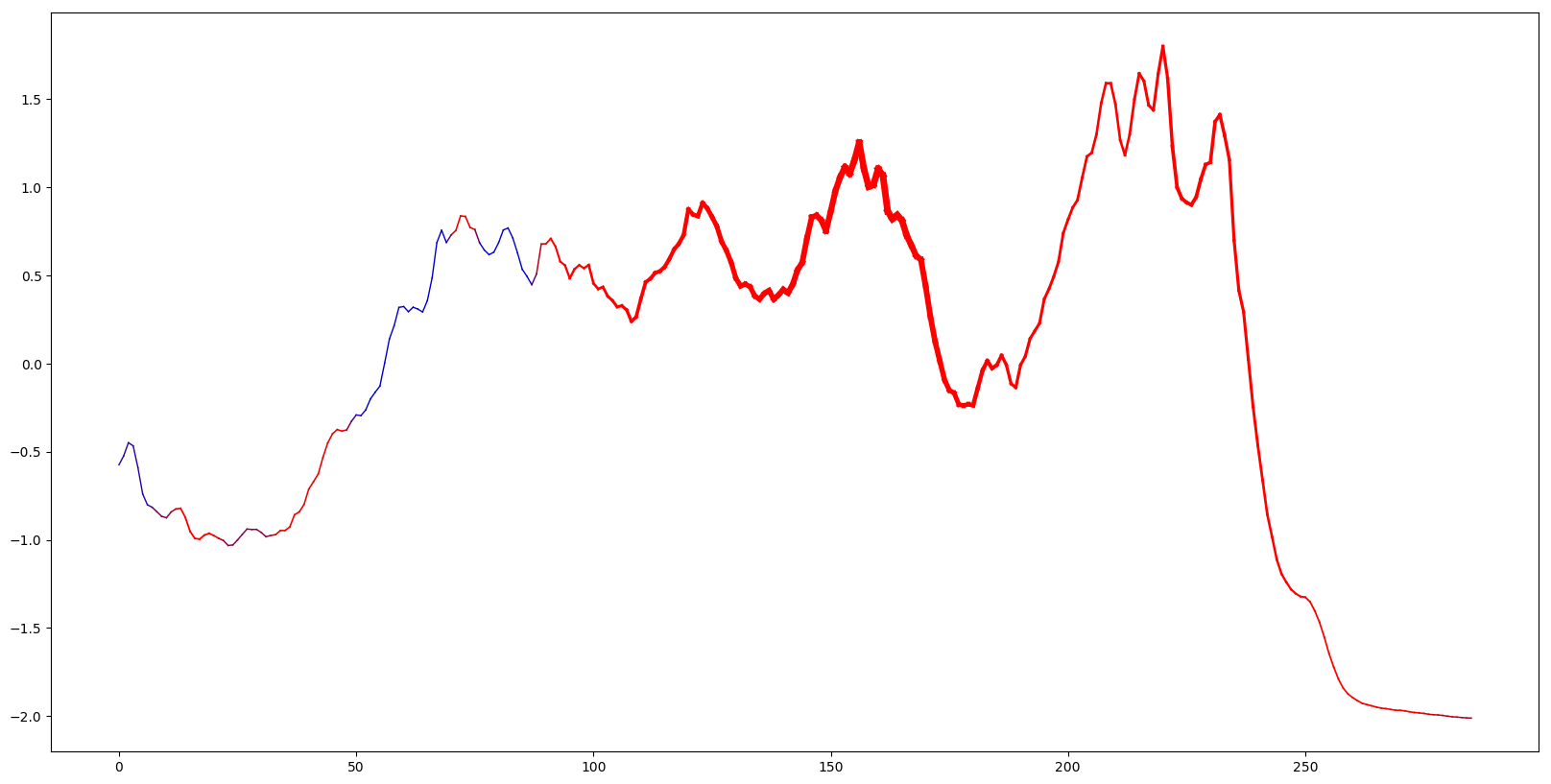
Below we give the code and steps for plotting the SAX features learned with logistic regression, by mapping them back to the raw time series and highlighting the relevant parts of the time series. First we compute the classification score for each point in the time series, by mapping the discriminative SAX subsequence back to the raw time series. These computed scores for each test time series are stored in saxdir/test_scores.
./compute_metats -c saxdir/config -p saxdir/features -i Coffee_TEST -o saxdir/test_scores
Using file saxdir/test_scores, we can now plot the highlighted time series (assumes Python 3.x + matplotlib). The input parameter (1) at the end gives the index of the time series to be plotted. The code below plots the first time series in the test set.
python ../../../src/python/visual_timeseries.py Coffee_TEST saxdir/test_scores 1
The steps to use the SFA representation are similar. We provide in the src folder the python script that can work with the Python port of SFA. To combine SFA features and SAX features for classification, simply add both directories to the above command:
python ../../../src/python/mf_logreg.py saxdir sfadir
Our papers:
Our recent work describing the use of sequence learning models (SEQL) and multiple symbolic representations (SAX, SFA) to produce accurate and interpretable time series classifiers:
T. L. Nguyen, S. Gsponer, I. Ilie, M. O'reilly and G. Ifrim Interpretable Time Series Classification using Linear Models and Multi-resolution Multi-domain Symbolic Representations in Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery (DMKD), May 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-019-00633-3
T. L. Nguyen, S. Gsponer, I. Ilie, and G. Ifrim, Interpretable Time Series Classification using All-Subsequence Learning and Symbolic Representations in Time and Frequency Domains. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.04022
Our prior work on adapting sequence learning for working with symbolic representation of time series (one fixed SAX representation and variable-length SAX words): T. L. Nguyen, S. Gsponer, and G. Ifrim, "Time Series Classification by Sequence Learning in All-Subsequence Space" in 2017 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), April 2017, pp. 947–958.
Other SEQL-based projects:
https://github.com/heerme/seql-sequence-learner
https://github.com/lnthach/SAX-SEQL
https://github.com/svgsponer/SqLoss
Read more about SAX and other time series techniques here. The site also hosts the popular UCR Time Series Classification Archive.
SFA implementation by the author.
The UEA & UCR Time Series Classification Repository. Datasets and implementations of most state-of-the-art time series classifiers can be found here.
This work was funded by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) under grant number 12/RC/2289 (Insight Centre).
We want to thank the many researchers that made available datasets and open source code for time series classification. In particular, we want to thank Eamonn Keogh and his team for preparing the UCR Time Series Classification Archive, and Tony Bagnall and his team for preparing the UEA Time Series Classification Benchmark.
Many thanks also go to Martin for his contribution to the case study on the Jump data.
These software distributions are open source, licensed under the GNU General Public License (v3 or later). Note that this is the full GPL, which allows many free uses, but does not allow its incorporation (even in part or in translation) into any type of proprietary software which you distribute. Commercial licensing is also available; please contact us if you are interested.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.