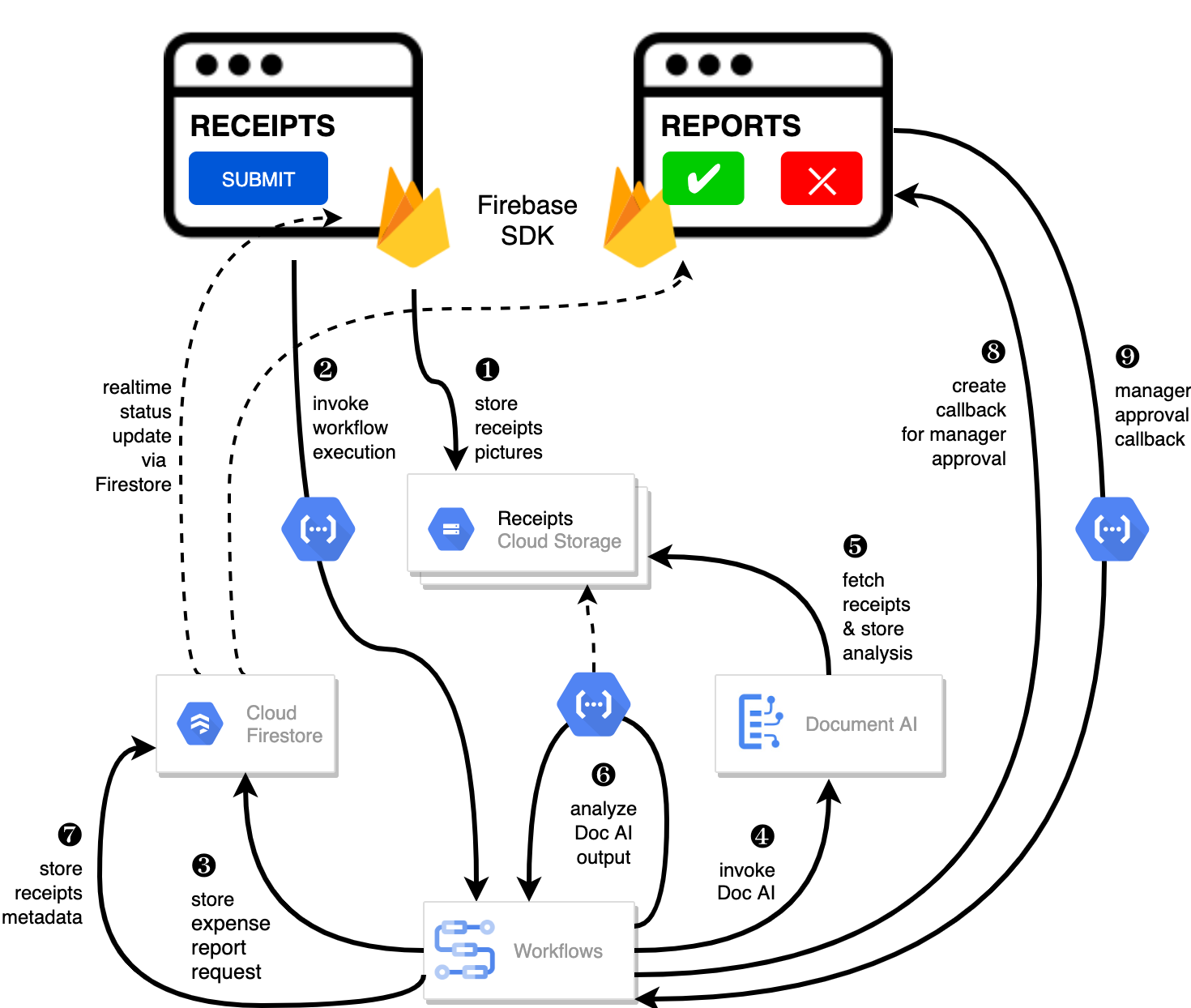
Here is the architecture diagram of the application demonstrated in the Cloud Next 2021 talk "AI-powered applications with Google Cloud" (DEV202).
Learn how you can harness the power of serverless computing with AI services like Document AI. Build applications with speed, ease, and intelligence. See how AI-powered use cases, combined with Workflows and Cloud Functions, can help automate use cases at your enterprise. We’ll show you how to leverage pretrained models for form types like including receipts, invoice processing, and more. Developers will be able to increase productivity by spending less time worrying about infrastructure, and dedicate more time building applications for their businesses.
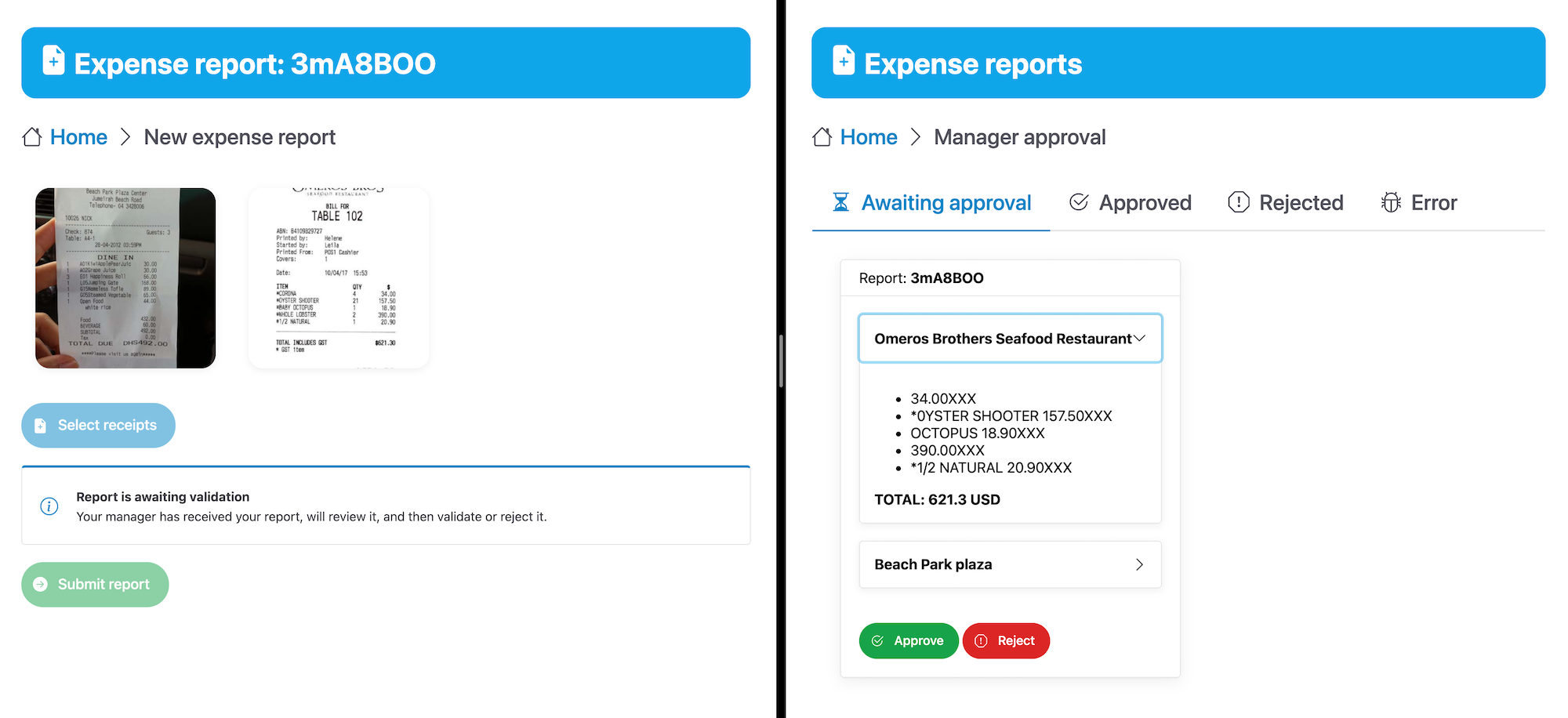
This demo application is a smart expense report application, consisting of two main screens:
- a page for employees where they can select receipts and submit their expense reports,
- a page for manager to review, then approve or reject submitted expense reports.
The project makes use of the following Google Cloud products:
- Document AI to parse and analyse receipts to find meaningful information (supplier, line items, amounts, currency),
- Workflows to organize the overall business process, invoking Document AI and data analysis function, to update status in Firestore, to create a callback waiting for the manager's approval,
- Cloud Functions to make the link between frontend and backend, and to extract data from Document AI's JSON output,
- Firestore to store all the data about the expense reports and receipts
- Cloud Stroage to store pictures of receipts,
- Firebase on the frontend to upload receipt pictures and to keep UI up-to-date with the realtime status of the expense report processing.
The project is using:
- Vue.js as its frontend progressive JavaScript framework,
- Shoelace as its library of web components,
- Node.js for the code of the few cloud functions.
Certain URLs pointing at cloud storage buckets or function locations are hard-coded. To deploy the sample application in your own Google Cloud Project, you should update:
In workflow.yaml:
- The
bucket_inputandbucket_outputvariables to point at globally unique GCS buckets. - In
invoke_document_aistep, point at your location and at the right Document AI processor ID. - In
process_annotationsstep, point at the URL of your cloud function analysing Document AI's JSON output.
In public/js/common.js:
- Update the Firebase project configuration to point at your project (see Firebase documentation)
In public/js/admin.js:
- Change the
callbackFunctionUrlURL to point at the URL of your approval callback function.
In public/js/request.js:
- Change the
fnUrlURL to point at the URL of your workflow invocation function.
gcloud workflows deploy batch-process-receipts \
--location=europe-west4 \
--source=workflow.yaml
Login with Firebase (use --no-localhost flag if running in Cloud Shell):
firebase login
Deploy static assets to Firebase hosting
firebase deploy --only hosting
Run local server:
firebase serve
Environment variables
export FUNCTION_REGION=europe-west1
export WORKFLOW_REGION=europe-west4
export WORKFLOW_NAME=batch-process-receipts
Function invoking the workflow from the web frontend:
gcloud functions deploy invoke-workflow \
--region=${FUNCTION_REGION} \
--source=./services/invoke-workflow \
--runtime nodejs14 \
--entry-point=invokeWorkflow \
--set-env-vars PROJECT_ID=${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT},WORKFLOW_REGION=${WORKFLOW_REGION},WORKFLOW_NAME=${WORKFLOW_NAME} \
--trigger-http \
--allow-unauthenticated
Function calling the workflow callback from the web frontend:
gcloud functions deploy approval-callback \
--region=${FUNCTION_REGION} \
--source=./services/approval-callback \
--runtime nodejs14 \
--entry-point=approvalCallbackCall \
--trigger-http \
--allow-unauthenticated
Note: The service account used by the function calling the callback URL should have the Workflows Editor (or Workflows Admin) and Service Account Token Creator permissions.
Function analysing the Doc AI output
gcloud functions deploy process-annotations \
--region=${FUNCTION_REGION} \
--source=./services/process-annotations \
--runtime nodejs14 \
--entry-point=processAnnotations \
--trigger-http
To allow the web pages to access the data (in read-only mode) in Firestore, the security rules for Firestore should be updated with:
rules_version = '2';
service cloud.firestore {
match /databases/{database}/documents {
match /{document=**} {
allow read, write: if false;
}
}
}
All solutions within this repository are provided under the Apache 2.0 license. Please see the LICENSE file for more detailed terms and conditions.
This repository and its contents are not an official Google Product.