In root folder mp4, run
python3 -m venv .env
source .env/bin/activate
.env/Scripts/activate
pip install -r requirement.txtTest installation
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('we love you'))"Expected output:
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998704791069031}]To compile the project, you need to have Golang installed on your machine. You can download Golang from here. Once you have Golang installed, you need to download dependency gRPC and Protobuf. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
go get -u google.golang.org/grpc
go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
After you have all the dependencies installed, you can compile the project by running the following command in your terminal:
make all
This will generate the executable files in the bin folder.
You can run the executable file by running the following command in your terminal:
cd bin
./dns
cd bin
./idunno
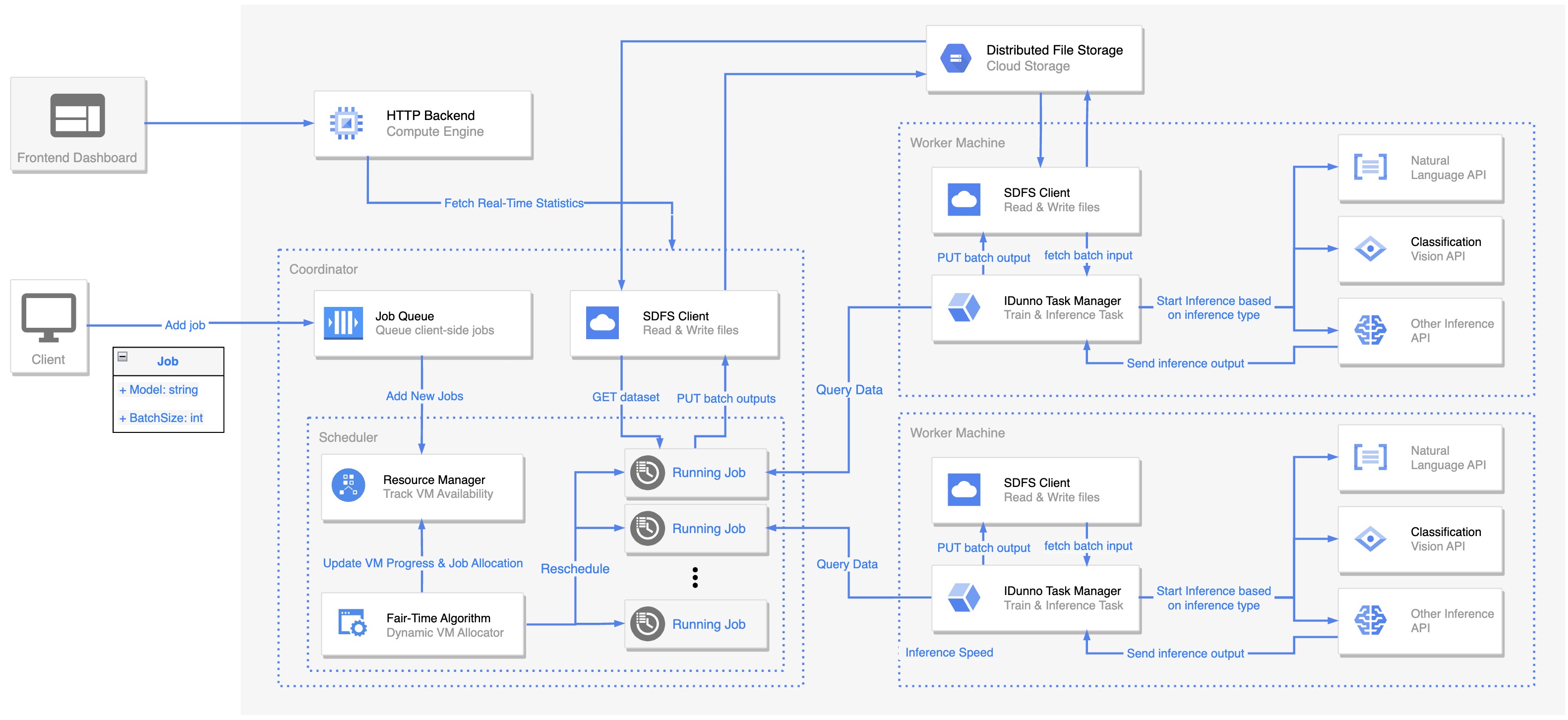
IDunno server automatically starts python gRPC server for inference.
You need to run only one dns executable file. You can run multiple idunno executable files. Each idunno executable file will be a host server.
Here is a list of commands you can use in the idunno executable file:
join # Join the ring
leave # Leave the ring
list_mem # List all members in the ring
clear # clear all content from log file
stat # print statistics of Bps read/write, #pings, #failures, system elapsed time
low_droprate # Set the drop rate to low (0.03)
mid_droprate # Set the drop rate to medium (0.3)
high_droprate # Set the drop rate to high (0.9)
Here are more commands for the SDFS:
get <sdfsfilename> <local_filename> # Get a file from the SDFS
put <local_filename> <sdfsfilename> # Put a local file to the SDFS
putdir <local_directory> <sdfs_directory> # Put a local directory with all files inside to the SDFS
delete <sdfsfilename> # Delete a file from the SDFS
deldir <sdfs_directory> # Delete a directory with all files inside from the SDFS
ls <sdfsfilename> # List the servers storing the file
store # List all files stored in the current server
get-versions <sdfsfilename> <num versions> <localfilename> # Retrieve the last num versions of the file
Here are more commands for the IDunno Learning Cluster:
train <model> <dataset> # train a model on specified dataset
serve <model> <batch_size> # start inference on model with a batch size
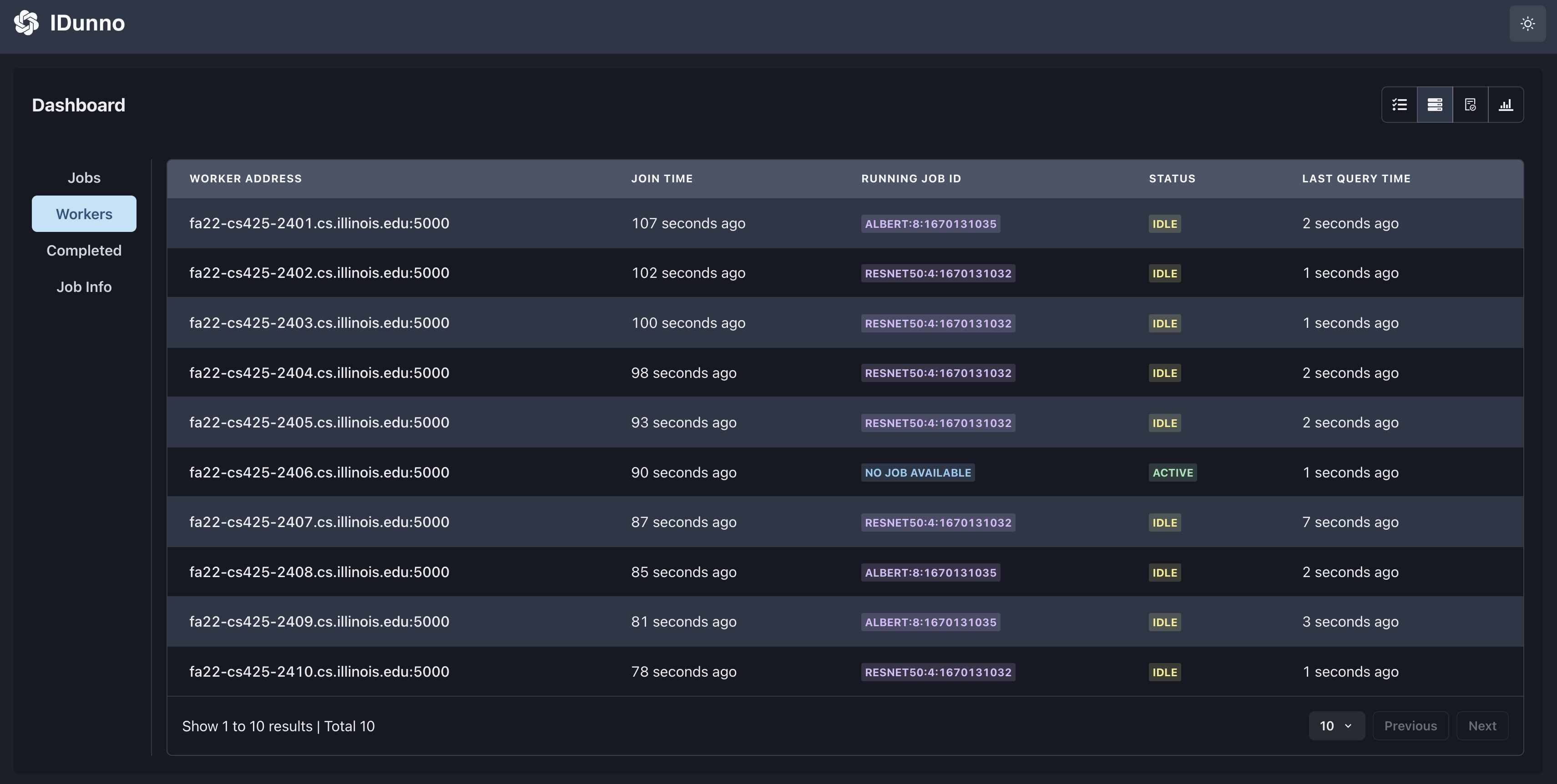
w # display all workers
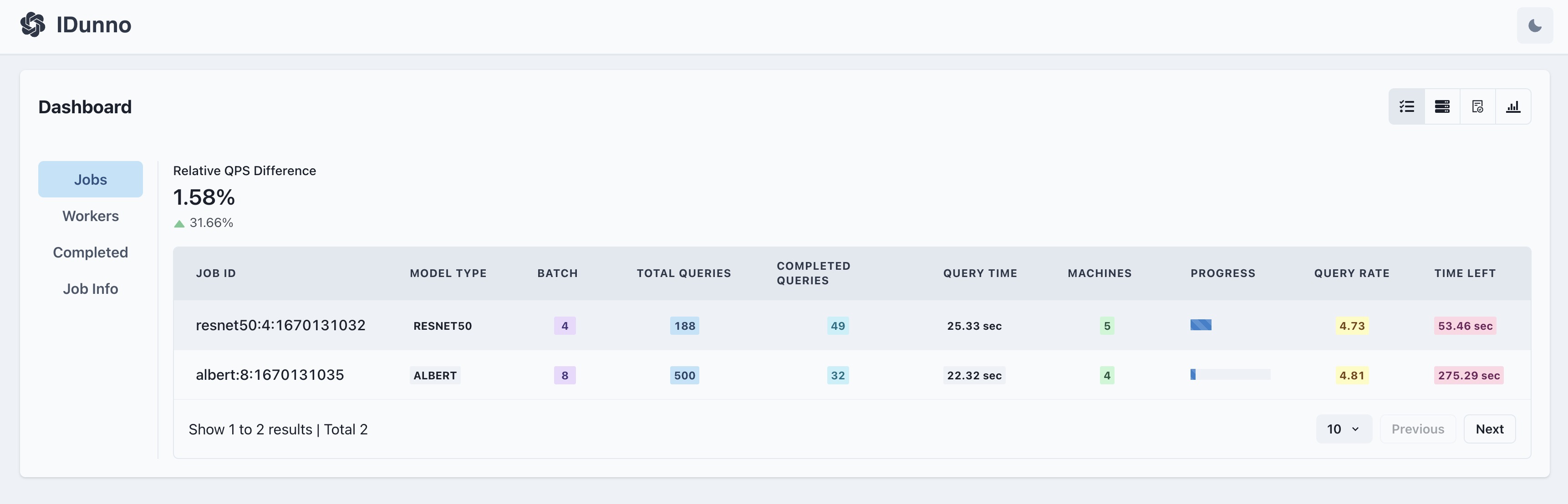
j # display all running jobs & their current states
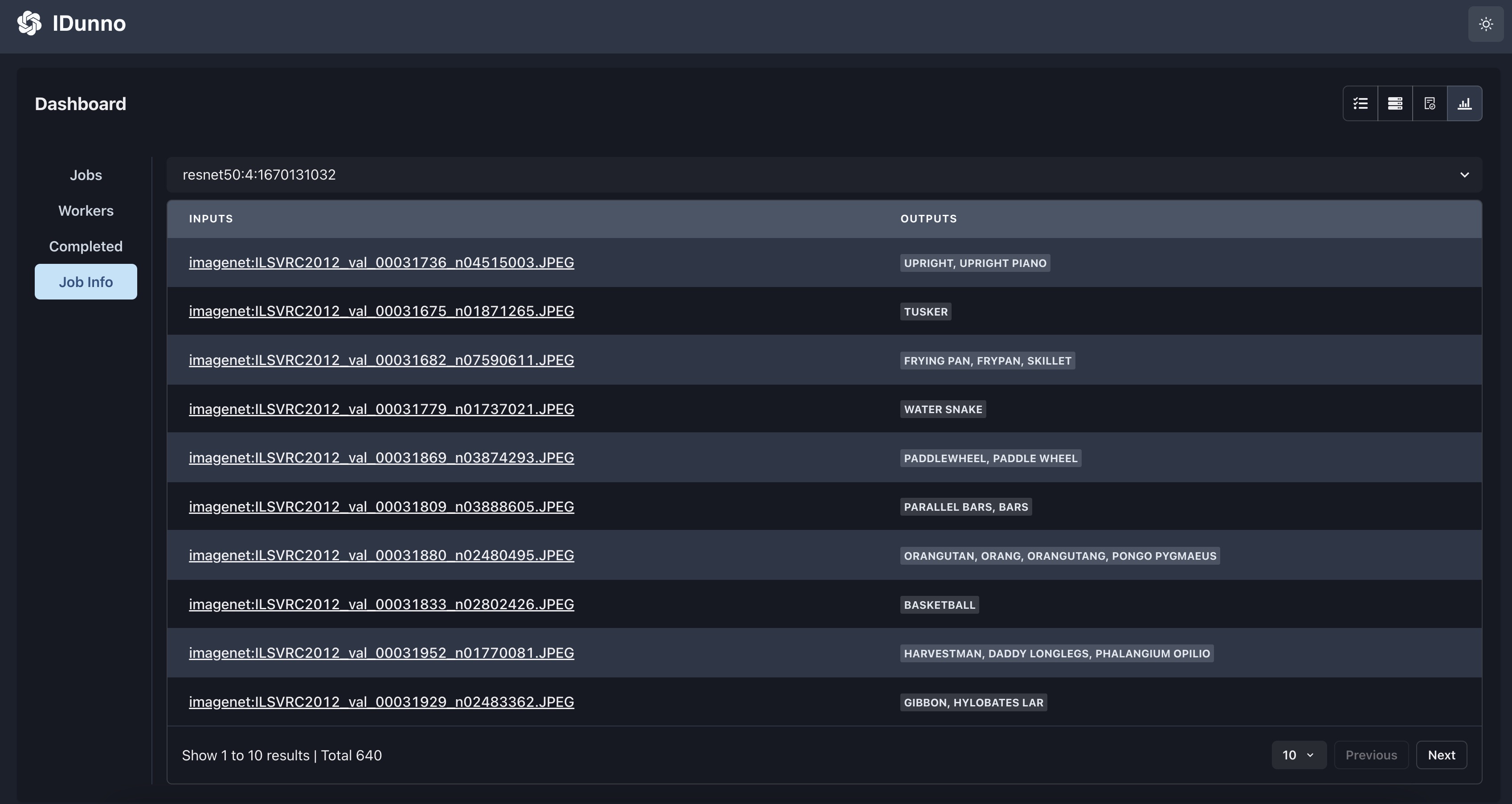
ij <job_id> # display a particular job's current inference output and accuracy
cj # display all completed jobs
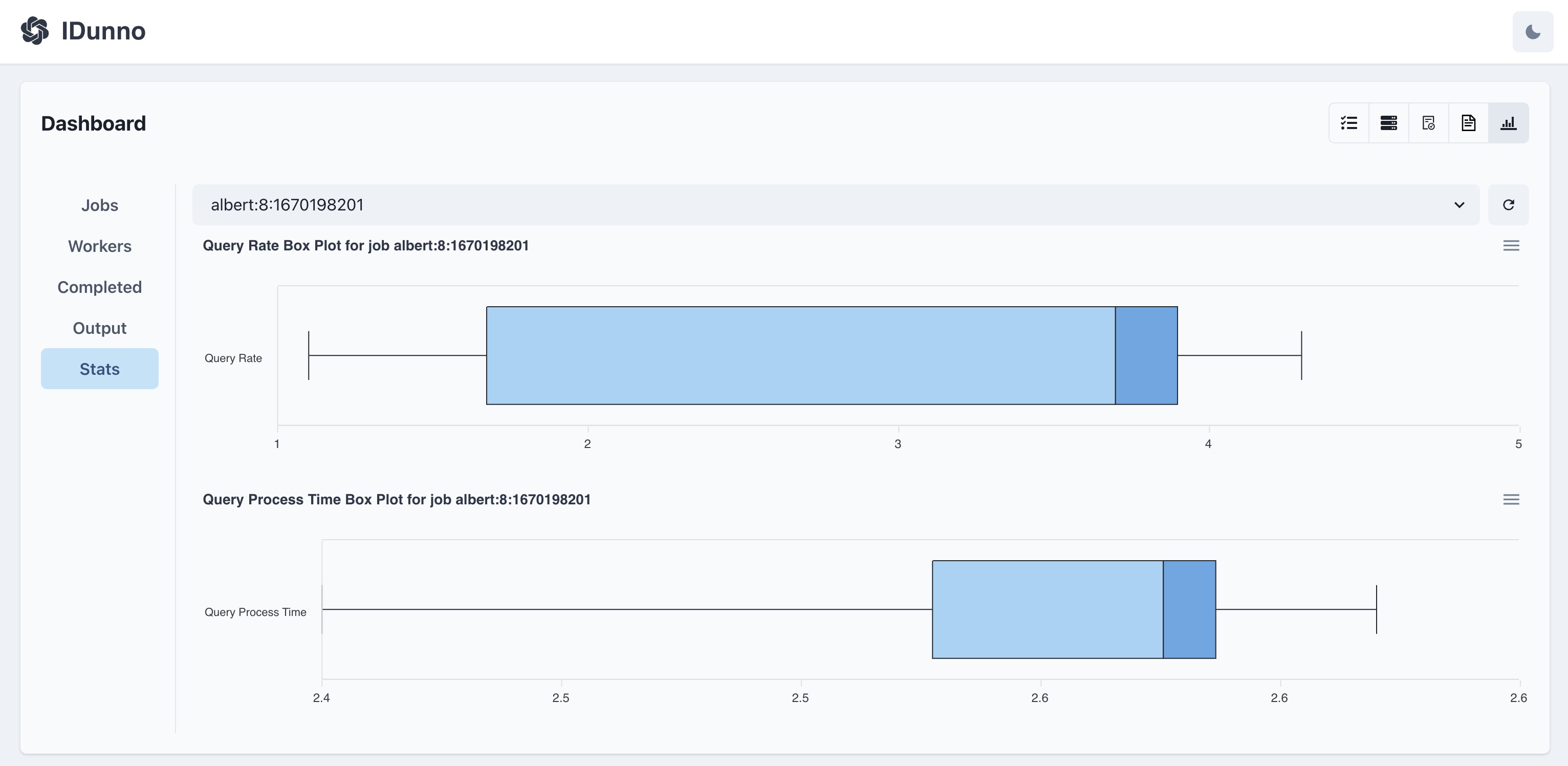
ijs <job_id> # displat a particular job's query rate and query processing time statistics
qps [global|local] # change scheduling mode to be local or global
To provide a better user experience in viewing real-time updates of IDunno system, we built a frontend dashboard using React and TypeScript. Here are steps to start frontend dashboard:
Backend server automatically starts after executing ./dns.
Go to ./frontend. Run
pnpm install
pnpm run dev