This repo contains a python implementation of the algorithm detailed in this paper. It handles second order linear differential equations of the form
Example usage:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from Solver import Solver
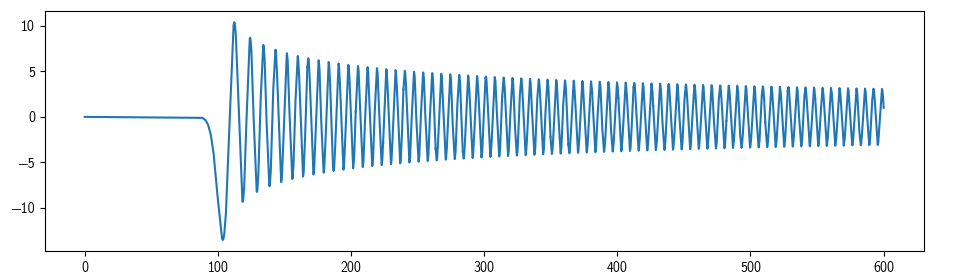
Solver.Local.initialize(16,4,1e-5)
solver = Solver.Solver(0, 600,
lambda x: 1/x,
lambda x: 1 - (100/x)**2,
lambda x: np.zeros_like(x),
1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1)
x, u, du = solver.solve()
plt.plot(x, u)
plt.show()For more detail read the docstring of Solver.Solver.
There is additionally a simple Newton's iteration algorithm implemented on top of the linear solver. It solves equations of the form
from Solver import Nonlinear
Solver.Local.initialize(16,4,3e-5)
# sn(x), m=0.5
EllipticK = 1.8540746773013719184338503471952600462175988235217669055859
xs, u, du, ddu = Nonlinear.newton(0, EllipticK,
lambda x, y, dy: y**3 - 1.5*y,
lambda x, y, dy: 3*y**2 - 1.5,
lambda x, y, dy: np.zeros_like(x),
1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1)
plt.plot(xs, u)
plt.show()