py-spy: Sampling profiler for Python programs
py-spy is a sampling profiler for Python programs. It lets you visualize what your Python program is spending time on without restarting the program or modifying the code in any way. py-spy is extremely low overhead: it is written in Rust for speed and doesn't run in the same process as the profiled Python program. This means py-spy is safe to use against production Python code.
py-spy works on Linux, OSX, Windows and FreeBSD, and supports profiling all recent versions of the CPython interpreter (versions 2.3-2.7 and 3.3-3.7).
Installation
Prebuilt binary wheels can be installed from PyPI with:
pip install py-spy
If you're a Rust user, py-spy can also be installed with:
cargo install py-spy
On Arch Linux, py-spy is in AUR and can be installed by using your favorite AUR helper, for example:
yay -S py-spy
Usage
There are some sub-commands for using py-spy.
Record
py-spy works from the command line and takes either the PID of the program you want to sample from or the command line of the python program you want to run:
py-spy record --pid 12345
# OR
py-spy record -- python myprogram.pyThat sub-command will generate a file containing raw data representing stack traces.
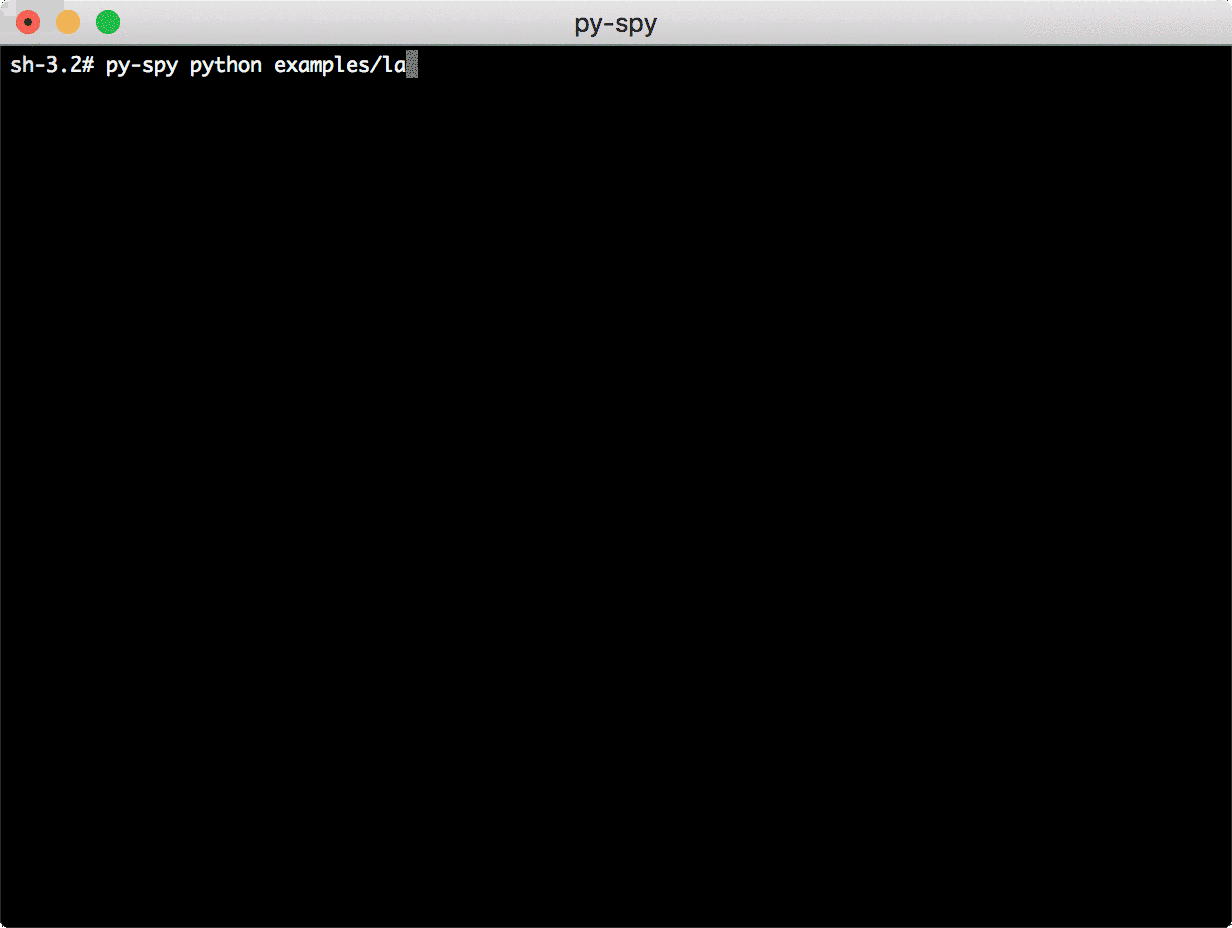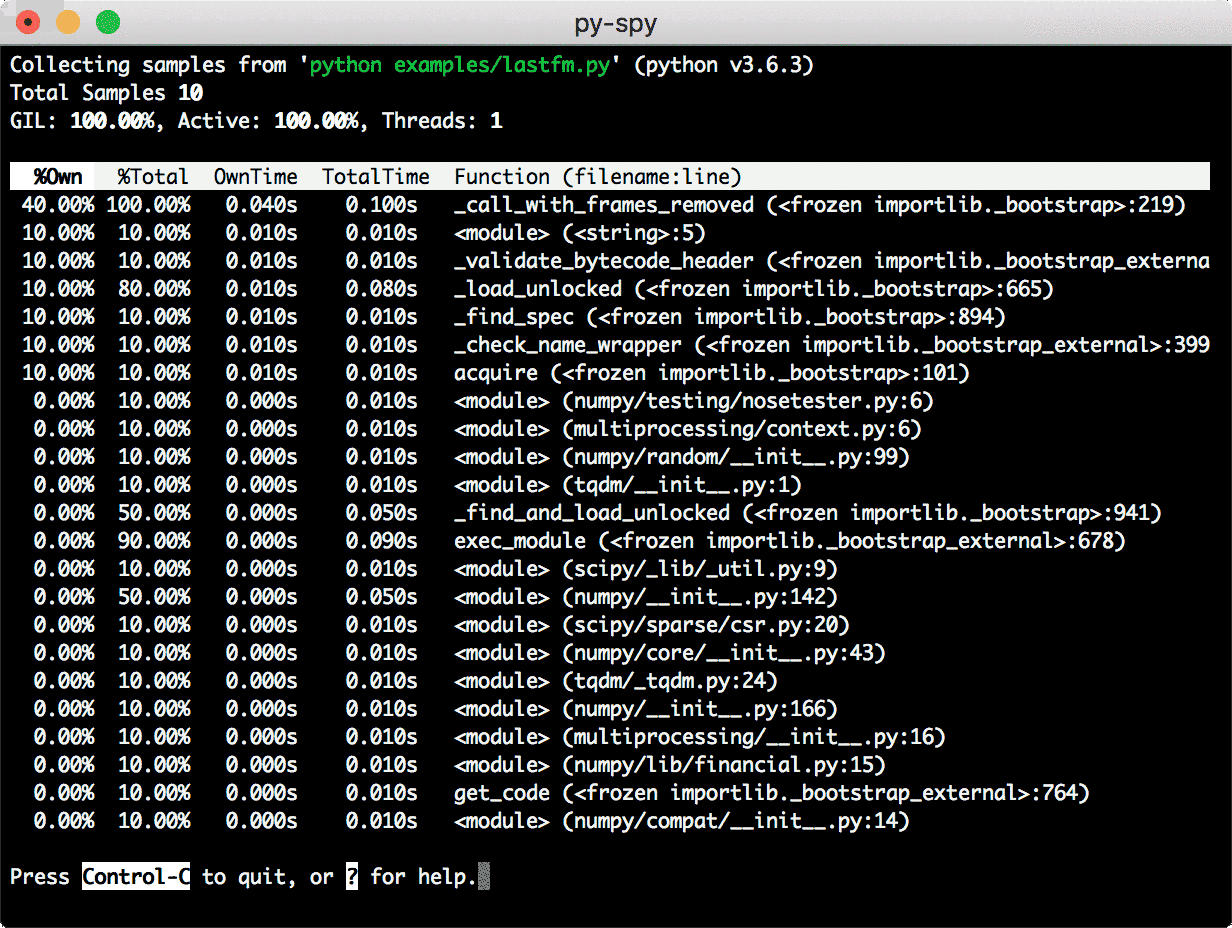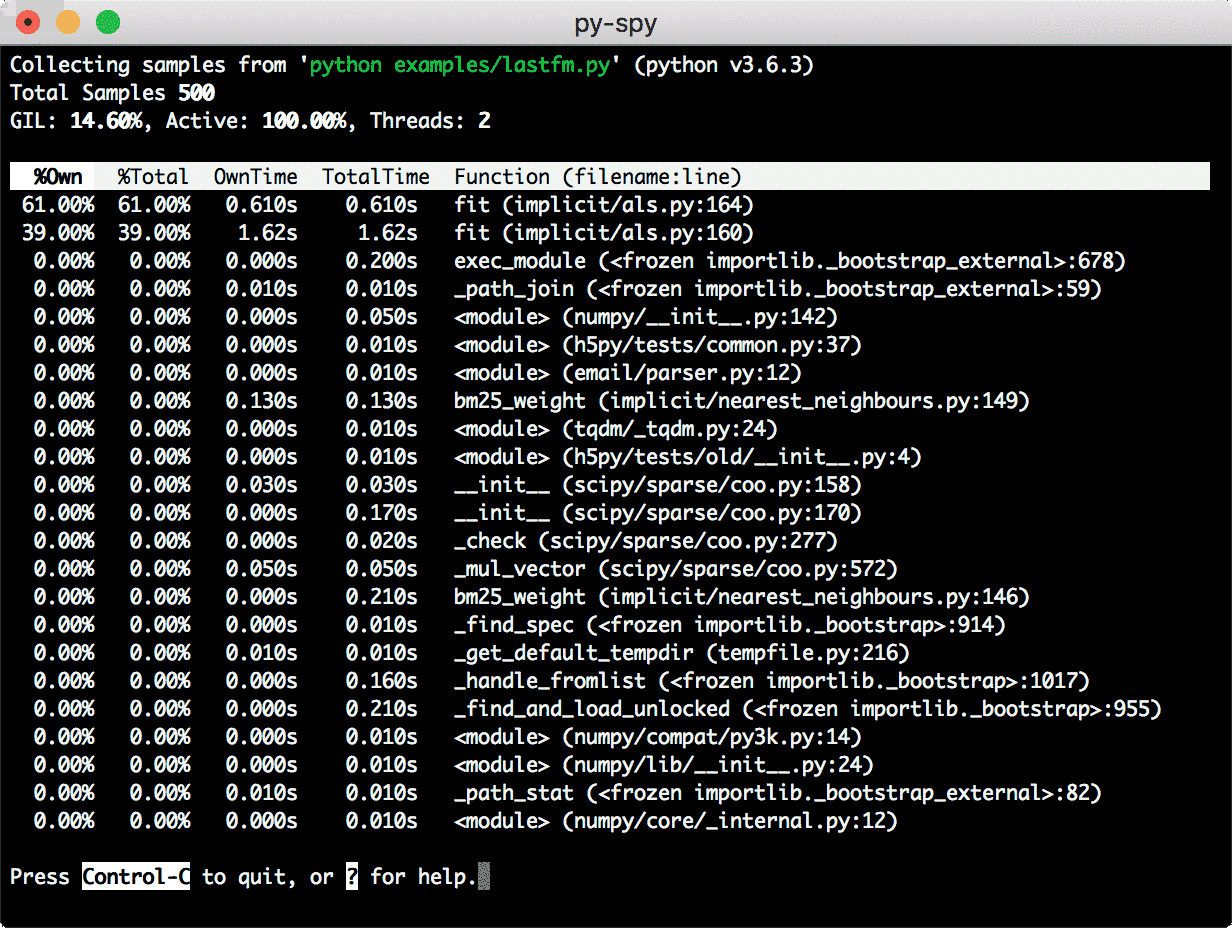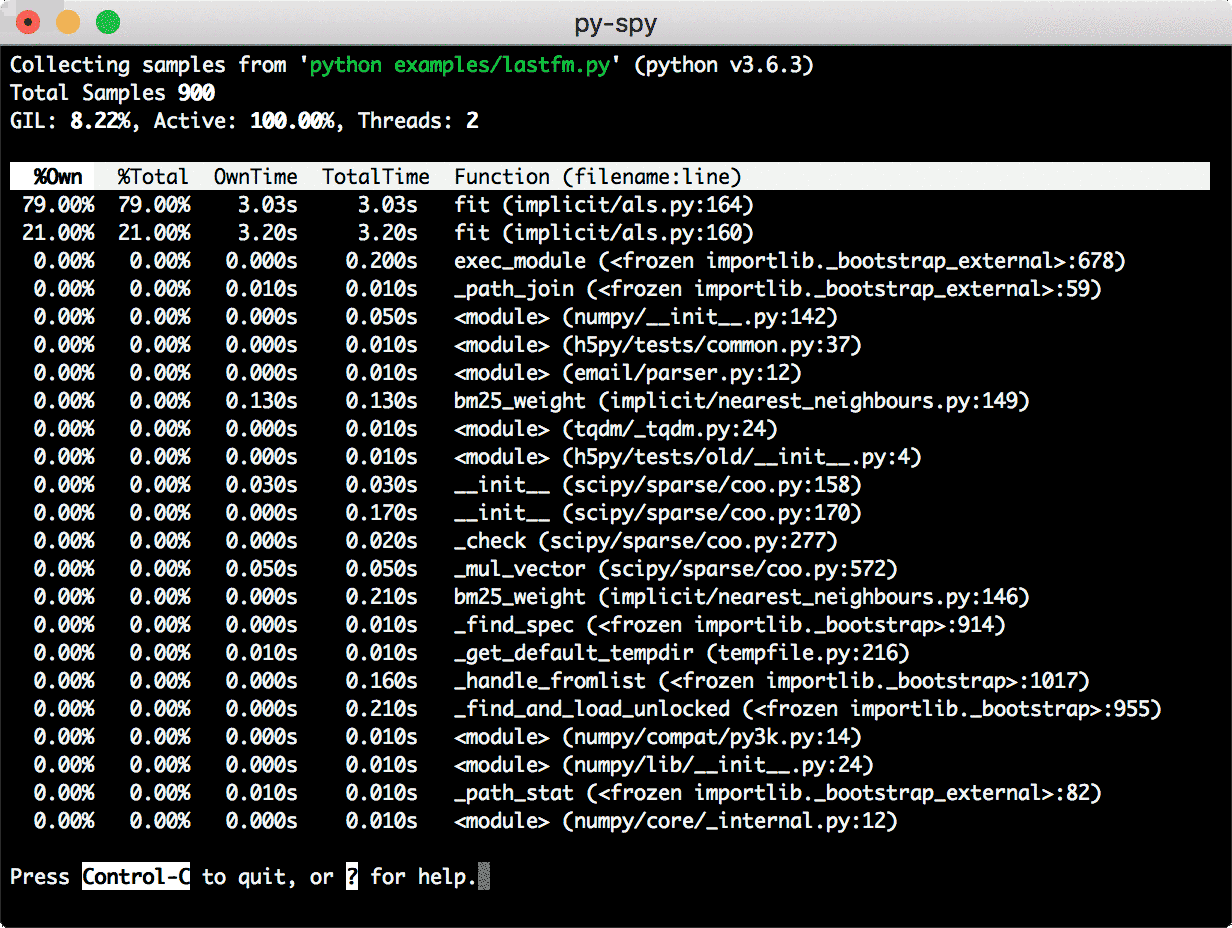
Top
It will generate a top-like live view of your python program:
Display
There is also support for generating flame graphs from the running process:
py-spy display -g RAW_DATA_FILE -s START_TIME_OFFSET -e END_TIME_OFFSETWhich will generate a SVG file looking like:
Dump
It also possible to dump out the current call stack for each thread by passing --dump to the command line.
Sub-interval Analysis Support
Py-spy is capable of filtering existing results to generate sub-interval results within the time period of preivous results. It is convenient for users to have a detailed obversation on some specific intervals with the large time interval when they spot some performance issues.
To use this feature, users should first profile a large time period and after that they can use the following command.
py-spy display -g RAW_DATA_FILE -s START_TIME_OFFSET -e END_TIME_OFFSETUsers need to specify the raw data file which is generated by the record sub-command and two time stamps offset to the starting point of previous profiling
to represent the target interval. Then a flame graph named ${RAW_DATA_FILE}.svg will be generated.
Black List Support
Sometimes, users does not want some functions to show in the results e.g. some functions make the thread idle. They can specify a black list and let the profiler
load that list and filter the result. Users can use -i option in the command to specify the black list file. Within that file, users can use following line format
function_name program_name(module_name) check_modeNote that the function_name and program_name(module_name) are informantion in the deepest stack frame. The check mode includes that
- X: Exact the same program
- E: End with the program_name
- C: Contain the program_name
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do we need another Python profiler?
This project aims to let you profile and debug any running Python program, even if the program is serving production traffic.
While there are many other python profiling projects, almost all of them require modifying the profiled program in some way. Usually, the profiling code runs inside of the target python process, which will slow down and change how the program operates. This means it's not generally safe to use these profilers for debugging issues in production services since they will usually have a noticeable impact on performance. The only other Python profiler that runs totally in a separate process is pyflame, which profiles remote python processes by using the ptrace system call. While pyflame is a great project, it doesn't support Python 3.7 yet and doesn't work on OSX, Windows or FreeBSD.
How does py-spy work?
py-spy works by directly reading the memory of the python program using the process_vm_readv system call on Linux, the vm_read call on OSX or the ReadProcessMemory call on Windows.
Figuring out the call stack of the Python program is done by looking at the global PyInterpreterState variable to get all the Python threads running in the interpreter, and then iterating over each PyFrameObject in each thread to get the call stack. Since the Python ABI changes between versions, we use rust's bindgen to generate different rust structures for each Python interpreter class we care about and use these generated structs to figure out the memory layout in the Python program.
Getting the memory address of the Python Interpreter can be a little tricky due to Address Space Layout Randomization. If the target python interpreter ships
with symbols it is pretty easy to figure out the memory address of the interpreter by dereferencing the
interp_head or _PyRuntime variables depending on the Python version. However, many Python
versions are shipped with either stripped binaries or shipped without the corresponding PDB symbol files on Windows. In
these cases we scan through the BSS section for addresses that look like they may point to a valid PyInterpreterState
and check if the layout of that address is what we expect.
Can py-spy profile native extensions?
Since we're getting the call stacks of the python program by looking at the PyInterpreterState we don't yet get information about non-python threads and can't profile native extensions like those written in languages like Cython or C++. Native code will instead show up as spending time in the line of Python that calls the native function, rather than as its own entry in the current stable release.
However, there is a pre-release at pip install py-spy==0.2.0.dev3 that will let you profile
native C/C++ or Cython extensions on 64-bit Linux and Windows machines. Any feedback on this feature is appreciated,
and you can follow progress or leave comments on this issue.
When do you need to run as sudo?
py-spy works by reading memory from a different python process, and this might not be allowed for security reasons depending on your OS and system settings. In many cases, running as a root user (with sudo or similar) gets around these security restrictions. OSX always requires running as root, but on Linux it depends on how you are launching py-spy and the system security settings.
On Linux the default configuration is to require root permissions when attaching to a process that isn't a child.
For py-spy this means you can profile without root access by getting py-spy to create the process (py-spy -- python myprogram.py) but attaching to an existing process by specifying a PID will usually require root (sudo py-spy --pid 123456).
You can remove this restriction on linux by setting the ptrace_scope sysctl variable.
Why am I having issues profiling /usr/bin/python on OSX?
OSX has a feature called System Integrity Protection that prevents even the root user from reading memory from any binary located in /usr/bin. Unfortunately, this includes the python interpreter that ships with OSX.
There are a couple of different ways to deal with this:
- You can install a different Python distribution (you probably want to migrate away from python2 anyways =)
- You can use virtualenv to run the system python in an environment where SIP doesn't apply.
- You can disable System Integrity Protection.
How do I run py-spy in Docker?
Running py-spy inside of a docker container will also usually bring up a permissions denied error even when running as root.
This error is caused by docker restricting the process_vm_readv system call we are using. This can
be overridden by setting
--cap-add SYS_PTRACE when starting the docker container.
Alternatively you can edit the docker-compose yaml file
your_service:
cap_add:
- SYS_PTRACE
Note that you'll need to restart the docker container in order for this setting to take effect.
How do I run py-spy in Kubernetes?
py-spy needs SYS_PTRACE to be able to read process memory. Kubernetes drops that capability by default, resulting in the error
Permission Denied: Try running again with elevated permissions by going 'sudo env "PATH=$PATH" !!'
The recommended way to deal with this is to edit the spec and add that capability. For a deployment, this is done by adding this to Deployment.spec.template.spec.containers
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- SYS_PTRACE
More details on this here: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/#set-capabilities-for-a-container Note that this will remove the existing pods and create those again.
How do I install py-spy on Alpine Linux?
Alpine python opts out of the manylinux wheels: pypa/pip#3969 (comment).
You can override this behaviour to use pip to install py-spy on Alpine by going:
echo 'manylinux1_compatible = True' > /usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/_manylinux.py
How can you avoid pausing the Python program?
By setting the --nonblocking option, py-spy won't pause the target python you are profiling from. While
the performance impact of sampling from a process with py-spy is usually extremely low, setting this option
will totally avoid interrupting your running python program.
With this option set, py-spy will instead read the interpreter state from the python process as it is running. Since the calls we use to read memory from are not atomic, and we have to issue multiple calls to get a stack trace this means that occasionally we get errors when sampling. This can show up as an increased error rate when sampling, or as partial stack frames being included in the output.
How are you distributing Rust executable binaries over PyPI?
Ok, so no-one has ever actually asked me this - but I wanted to share since it's a pretty terrible hack that might be useful to other people.
I really wanted to distribute this package over PyPI, since installing with pip will make this much easier for most Python programmers to get installed on their system. Unfortunately, installing executables as python scripts isn't something that setuptools supports.
To get around this I'm using setuptools_rust package to build the py-spy binary, and then overriding the distutils install command to copy the built binary into the python scripts folder. By doing this with prebuilt wheels for supported platforms means that we can install py-spy with pip, and not require a Rust compiler on the machine that this is being installed onto.
Does py-spy support 32-bit Windows? Integrate with PyPy? Work with USC2 versions of Python2?
Not yet =).
Credits
py-spy is heavily inspired by Julia Evans excellent work on rbspy. In particular, the code to generate flamegraph and speedscope files is taken directly from rbspy, and this project uses the read-process-memory and proc-maps crates that were spun off from rbspy.
License
py-spy is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0, see the LICENSE file for the full text.