High-Resolution 3D EBSD Map Generation Using An Efficient Quaternion Transformer Network
Devendra K. Jangid, Neal R. Brodnik, McLean P. Echlin, Chandrakanth Gudavalli, Connor Levenson, Tresa M. Pollock, Samantha H. Daly, B.S. Manjunath
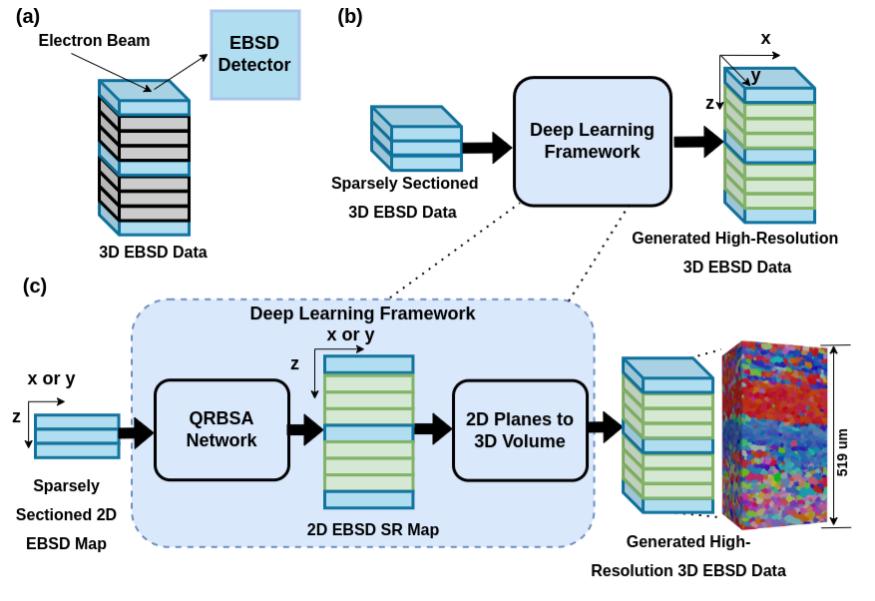
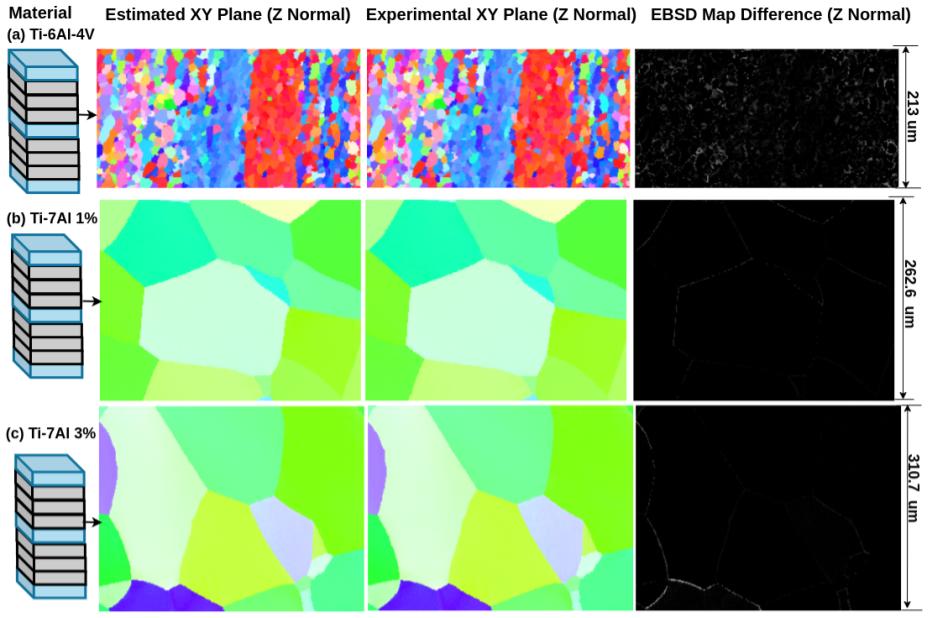
Abstract: Gathering 3D material microstructural information is time-consuming, expensive, and energy-intensive. Acquisition of 3D data has been accelerated by developments in serial sectioning instrument capabilities; however, for crystallographic information, the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) imaging modality remains rate limiting. We propose a physics-based efficient deep learning framework to reduce the time and cost of collecting 3D EBSD maps. Our framework uses a quaternion residual block self-attention network (QRBSA) to generate high-resolution 3D EBSD maps from sparsely sectioned EBSD maps. In QRBSA, quaternion-valued convolution effectively learns local relations in orientation space, while self-attention in the quaternion domain captures long-range correlations. We apply our framework to 3D data collected from commercially relevant titanium alloys, showing both qualitatively and quantitatively that our method can predict missing samples (EBSD information between sparsely sectioned mapping points) as compared to high-resolution ground truth 3D EBSD maps.
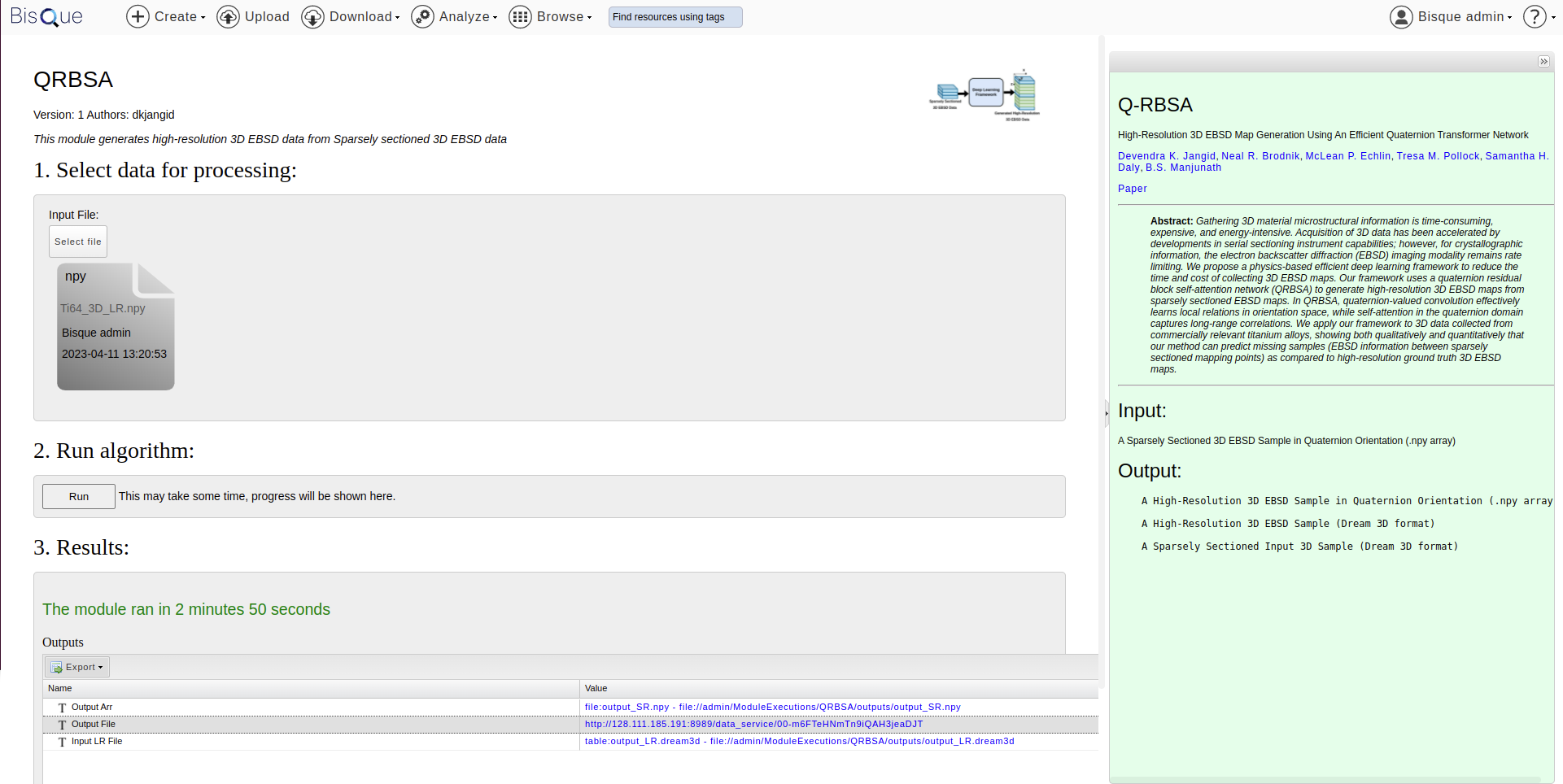
We have provided inference model on BisQue. Users would need to create an account on BisQue to use QRBSA inference module. Below are the guidelines with images to use module on BisQue.
Step 1: Upload Input 3D EBSD File. This file has information about EBSD orientation in Quaternion domain (numpy array). A test sample is provided on BisQue with name Ti64_3D_LR.npy.
Step 2: Click on Run. The module takes around 3 minutes for a file size (30 X 142 X 270) on CPU. We will work on optimization of code to reduce inference time.
Step 3: QRBSA module will generate three files:
-
Output Arr: High-Resolution 3D EBSD orientation in quaternion domain (numpy array)
-
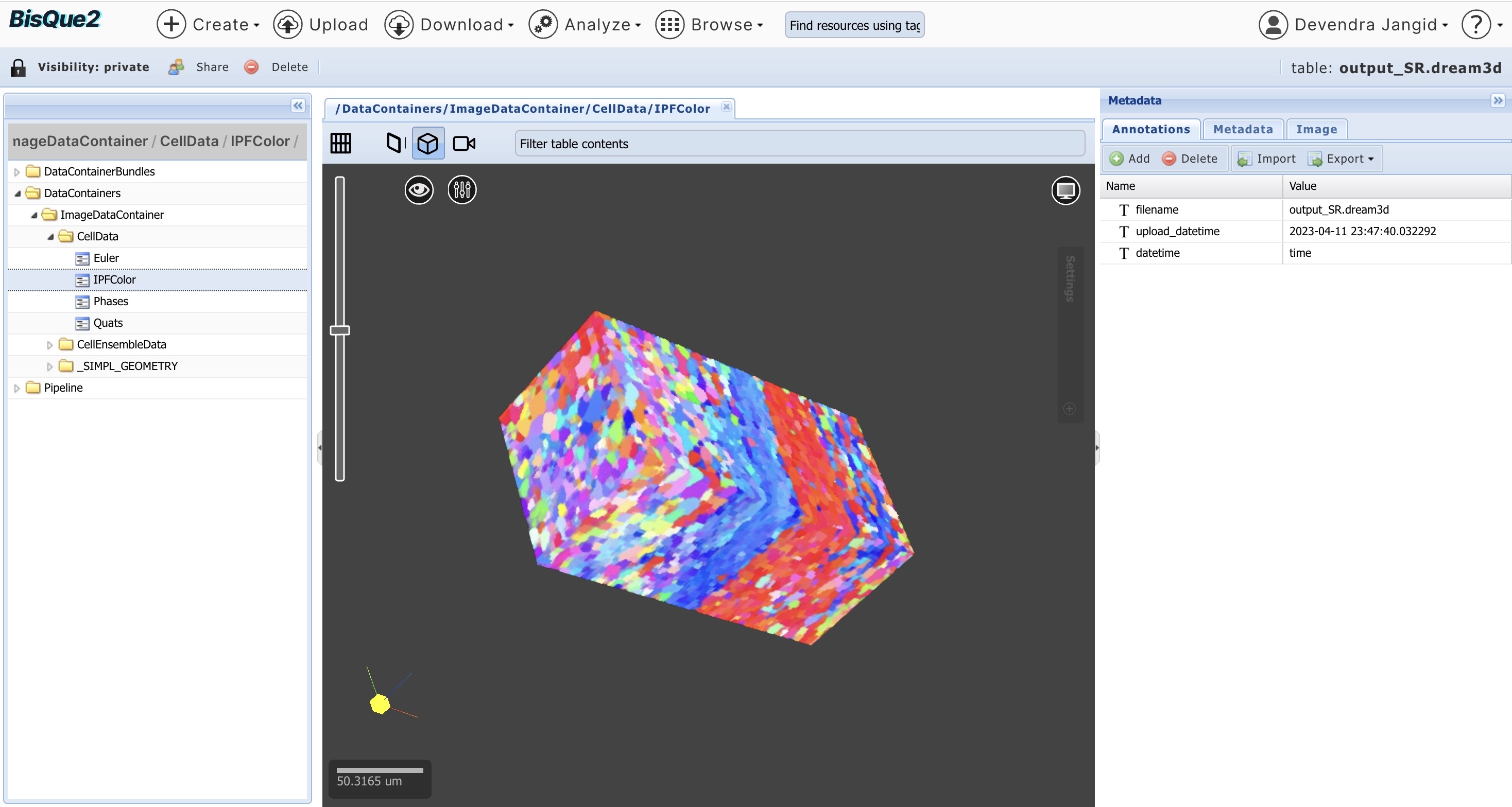
Output File: High-Resolution 3D EBSD file in dream 3d format. Users can click on file and go to (DataContianers/ImageDataContainer/CellData/IPFColor) to visualize in 3D as shown in image below
-
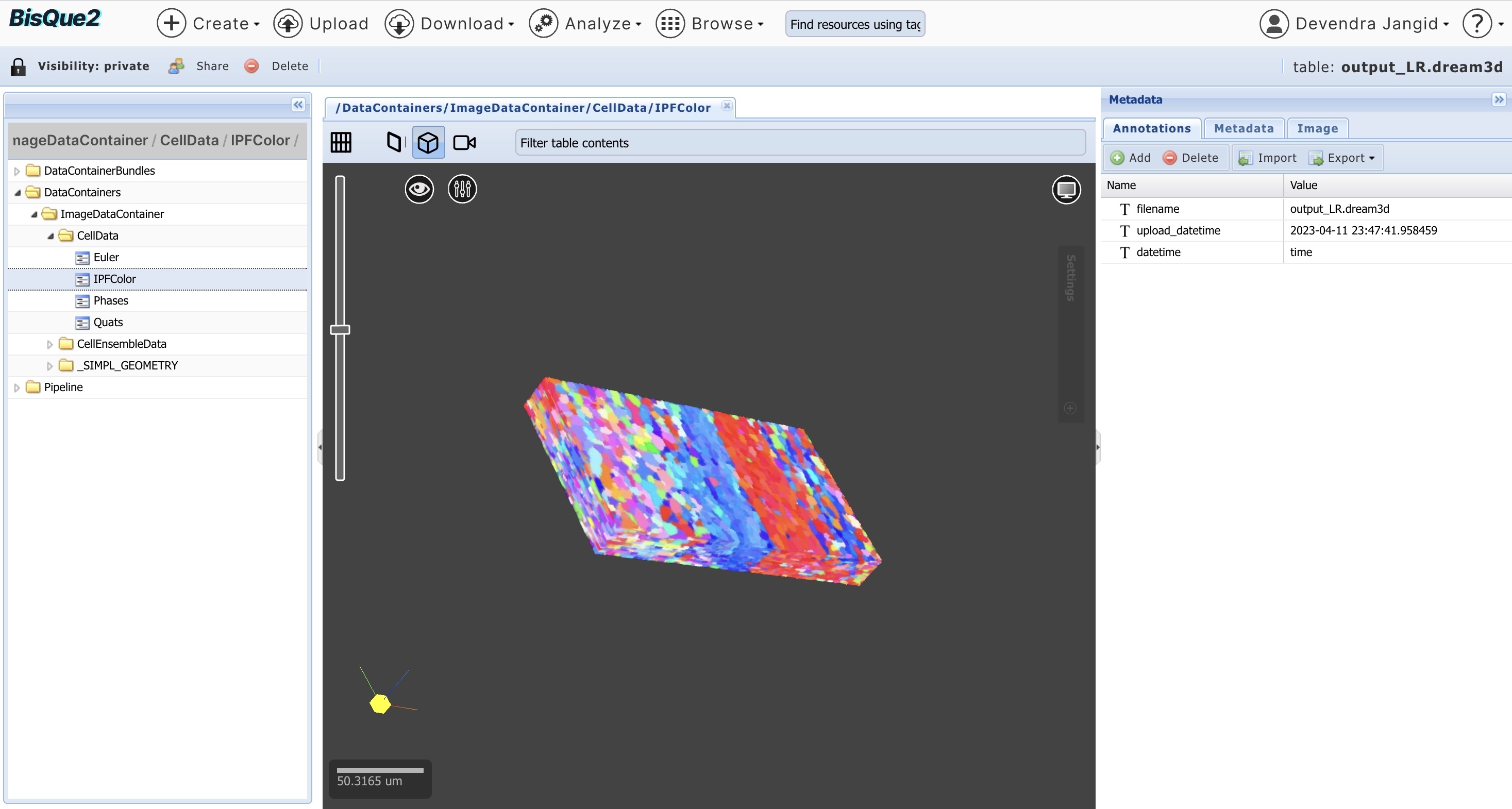
Input LR FIle: Low-Resolution 3D EBSD File in dream3D format. For visualization, Users can click on file and go to (DataContianers/ImageDataContainer/CellData/IPFColor)
Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS
All other required dependencies are in requirement.txt
Step 1: Clone repo
git clone "https://github.com/UCSB-VRL/Q-RBSA.git"
Step 2: Create Virtual environment
virtualenv -p /usr/bin/python3.10 qrbsa_venv(name of virtual environment)
Step 3: Activate Virtual environment
source qrbsa_venv/bin/activate
Step 4: Download Dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Step 5: Install gradual warmup scheduler. Go to pytorch-gradual-warmup-lr folder and run:
python setup.py install
Run
./train.sh
| Loss | dist_type | syms_req |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | L1 | False |
| L1 with symmetry | L1 | True |
| Rotational distance approximation with symmetry | rot_dist_approx | True |
Define the following parameters to train network
--input_dir: "Directory Path to Datasets"--hr_data_dir: "Path to High Resolution EBSD Maps relative to input_dir"--val_lr_data_dir: "Path to Low Resolution EBSD Val Datasets"--val_hr_data_dir: "Path to High Resolution EBSD Val Datasets"--model: "Choose one of network architectures from edsr, rfdn, san, han"--save: "Folder name to save weights, loss curves and logs"
Important parameters in argparser.py
--syms_req: "It tells whether you want to use symmetry or not during Loss calculation"--patch_size: "Max Size of Patch During Training"--act: "Activation Function in Network"--save_model_freq: "How frequently do you want to save models"
You do not need to use following steps if you are using Bisque infrastructure for inference.
Download trained weights for QRBSA network here
Put it in ./experiment/saved_weights/{name_of_file}/model/{name_of_file}.pt
If you use qrbsa 1D with rotational distance approximation loss:
./experiment/saved_weights/edsr_l1_ti64/model/edsr_l1_ti64.pt
--model: qrbsa_1d
--save: 'qrbsa_1d_rotdist'
--model_to_load: 'model_best'
--dist_type: 'rot_dist_approx'
--test_only
Run
./test.sh
The generated results will be saved at experiments/saved_weights/qrbsa_1d_rotdist/results/Test_model_best in npy format. It will also generate images (.png) for each quaternion channel.
The model will generate superresolved EBSD map in npy format. To convert into IPF maps from npy files, please see IPF Mapping
Material datasets will be available by request at discretion of authors.
This code is built on Q-CNN, Restormer, HAN, and EDSR. We thank the authors for sharing their codes.