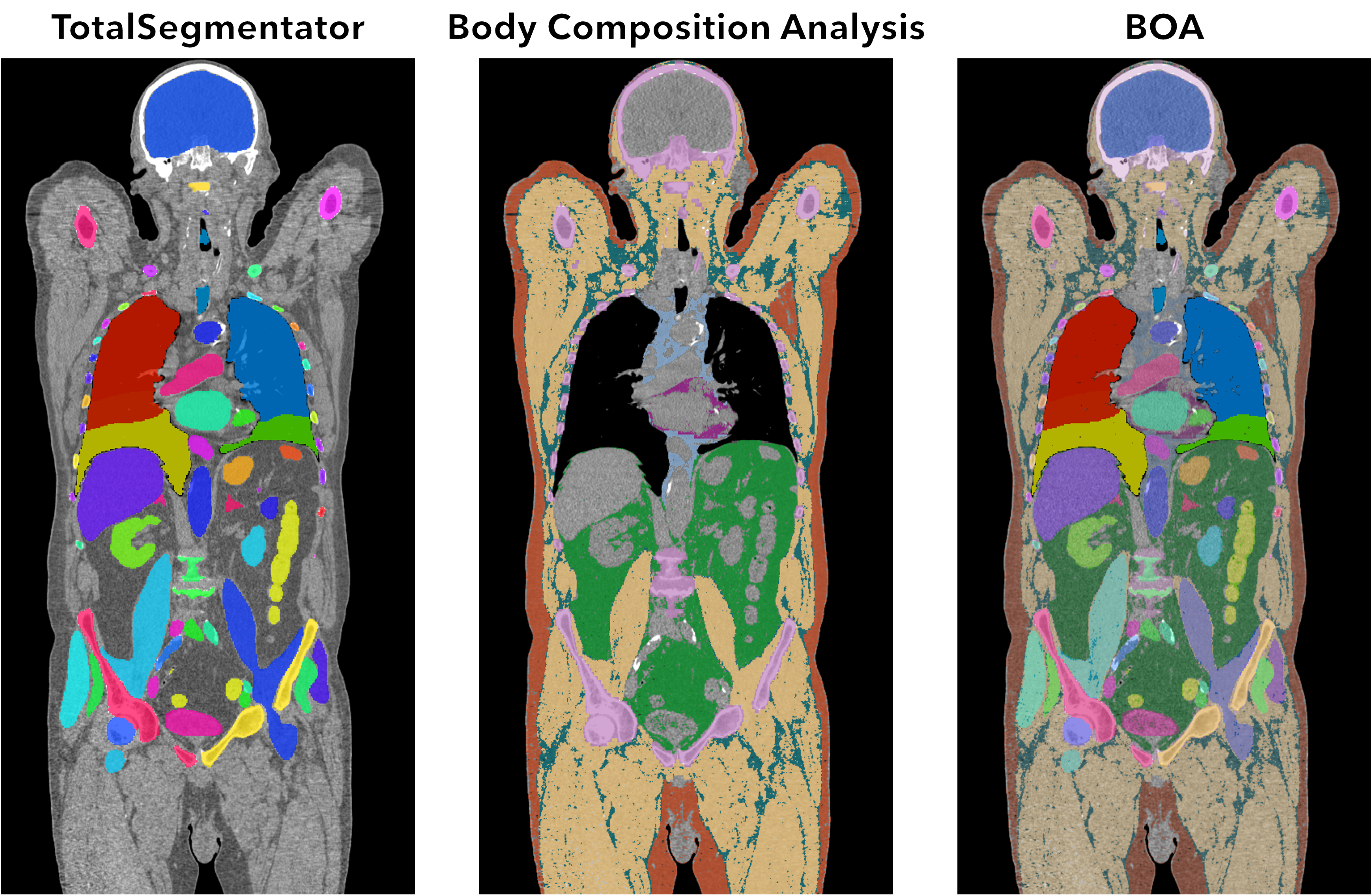
BOA is a tool for segmentation of CT scans developed by the SHIP-AI group at the Institute for Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Combining the TotalSegmentator and the Body Composition Analysis, this tool is capable of analyzing medical images and identifying the different structures within the human body, including bones, muscles, organs, and blood vessels.
The BOA tool can be used to generate full body segmentations of CT scans:
Additionally, the generated segmentations can be used as input to generate realistic images using Siemens' Cinematic Rendering.
If you use this tool, please cite the following papers:
BOA:
Haubold, J., Baldini, G., Parmar, V., Schaarschmidt, B. M., Koitka, S., Kroll, L., van Landeghem, N., Umutlu, L., Forsting, M., Nensa, F., & Hosch, R. (2023). BOA: A CT-Based Body and Organ Analysis for Radiologists at the Point of Care. Investigative radiology, 10.1097/RLI.0000000000001040. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000001040
Wasserthal J, Breit H-C, Meyer MT, et al. TotalSegmentator: Robust Segmentation of 104 Anatomic Structures in CT Images. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2023:e230024. Available at: https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/ryai.230024.
Isensee F, Jaeger PF, Kohl SAA, et al. nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods. 2021;18(2):203–211. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-020-01008-z.
- Set up the environment variables.
- Either use the PACS integration or the command line tool.
To make an estimate on how much power and time is needed to process a study, we used the following table provided by the TotalSegmentator. However, for very large series (e.g. 1600 slices 1mm), the performance may be worse and more CPU power may be needed. According to our tests, 16GB of GPU should be sufficient.