ngx-base-state 🐍
Classes have implemented base work with state
Idea
The main idea of this library is remove useless code from class.
Usually state services violate DRY pattern
This library will help to create state in 3 lines.
Wiki
Visit wiki page to get more useful information.
Installation
npm install ngx-base-state --save
OPTIONAL: If you want to use Devtools to explore your state via Chrome Extension:
In your AppModule
import {
NgxBaseStateDevtoolsModule,
NgxBaseStateDevtoolsConfig,
NGX_BASE_STATE_DEVTOOLS_CONFIG
} from 'ngx-base-state';
import { environment } from 'src/environments/environment';
@NgModule({
imports: [NgxBaseStateDevtoolsModule],
providers: [
{
provide: NGX_BASE_STATE_DEVTOOLS_CONFIG,
useValue: new NgxBaseStateDevtoolsConfig({
isEnabled: !environment.production // Devtools will not work in production
})
}
]
})
export class AppModule {}Chrome Extension
This tool allows you to see data in your states based on ngx-base-state.
- Install
ngx-base-stateextension from Chrome WebStore; - Open tab with your Application using ngx-base-state;
- Press F12 to open Devtools;
- Choose ngx-base-state panel in devtools;
Main page will contain list of all your states. Click to some state and will opened "details page" with state changes history.
| List of States | List of Actions | State details |
|---|---|---|
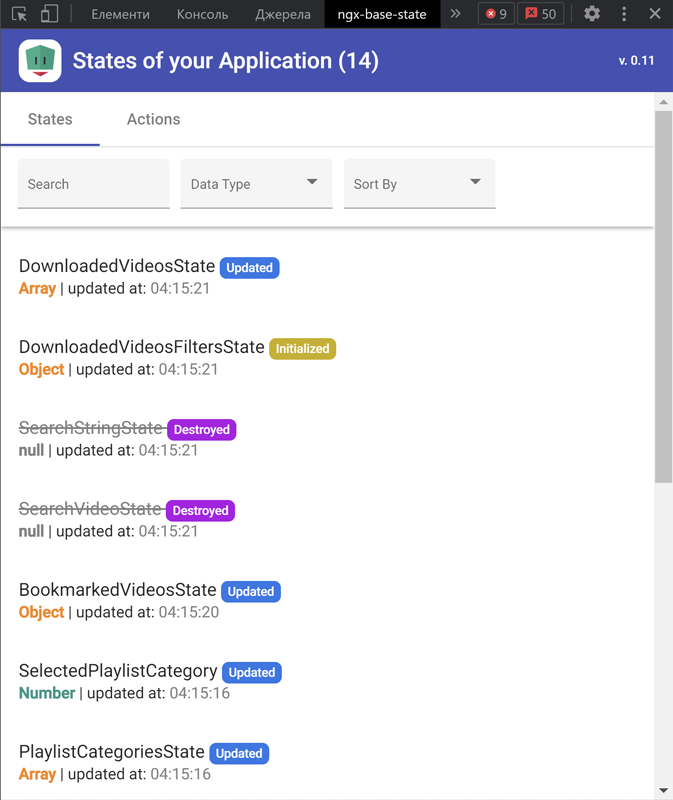 |
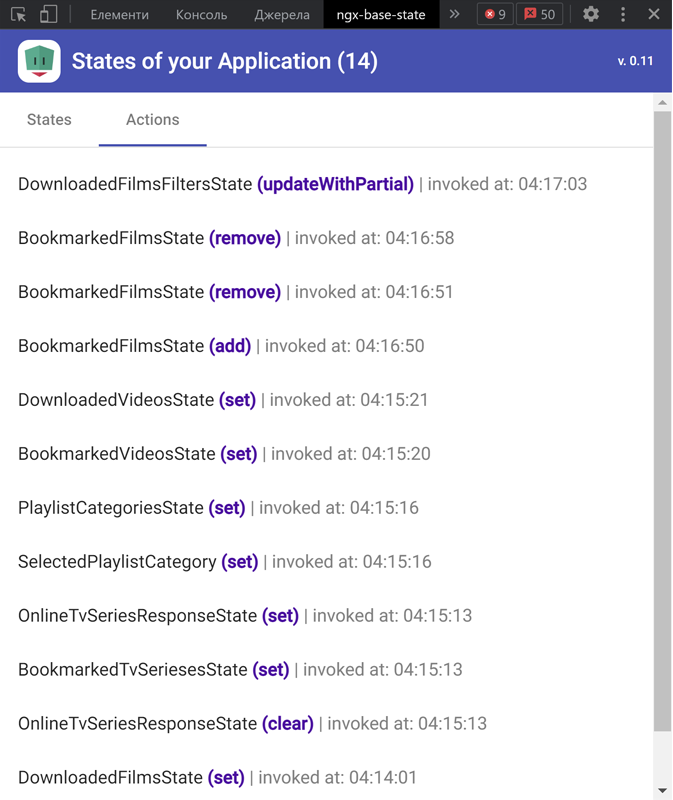 |
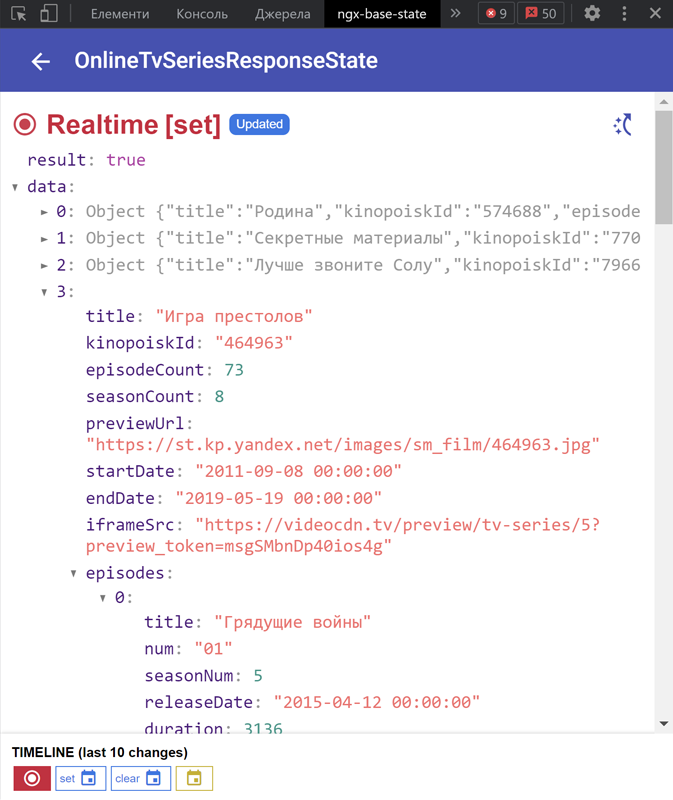 |
Properties & Methods
BaseState
Base class for all kinds of states. You can create your abstract class
based on BaseState to store the necessary custom data.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data$ | Observable<T | null> | state data stream |
| data | T | state data |
| set | value: T (generic type) | set new value for state |
| clear | clear value in the state | |
| restoreInitialData | restore initial data from constructor. |
ObjectState
Extend your class from ObjectState to store the object.
Contains all fields and methods like at BaseState, and also:
| Name | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
| updateWithPartial | value: Partial<T> | update state by merging current state with new partial object |
RecordState
Extend your class from RecordState to store the object with Record interface.
Store data in key -> value format.
Contains all fields and methods like at BaseState, and also:
| Name | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
| keys$ | stream with all keys of your Record object | |
| keys | all keys of your Record object | |
| values | all values of your Record object | |
| values$ | stream with all values of your Record object | |
| setItem | key: TKey, value: TValue | set item by key into state's object |
| removeItem | key: TKey | remove item by key from state's object |
| removeAllItems | remove all items from state's object |
ArrayState
Extend your class from ArrayState to store the array.
Contains all fields and methods like at BaseState, and also:
| Name | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getItemId | item: T | protected method might be overridden, it used for comparing items in array |
| set | value: T[] | set new array for state |
| pushItem | item: T | push new item to array |
| unshiftItem | item: T | unshift item to array |
| shift | shift array | |
| pop | pop array | |
| insertItemByIndex | index: number, item: T | insert item in array by index. |
| updateItem | itemToUpdate: T | update item in array |
| updateItemByIndex | item: T, index: number | update item in array by index |
| concatWith | array: T[] | concat current state with another array |
| removeItem | item: T | remove item from array |
| removeItemById | itemId: unknown | remove item from array by id (define id by overriding getItemId method) |
| removeItemByIndex | index: number | remove item from array by index |
PrimitiveState
Extend your class from PrimitiveState to store the: number, string, boolean, enum, type etc...
Contains all fields and methods like at BaseState and currently nothing else.
Example with ObjectState
user.state.ts
import { ObjectState, NgxState } from 'ngx-base-state';
// So easy to create new State :)
@NgxState()
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
class UserState extends ObjectState<User> {}user.service.ts
import { User } from '../interfaces';
import { UserApi } from '../api';
import { UserState } from '../states';
// IMPORTANT: Work with states only via "Service" layer.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
class UserService {
// Share data for components.
public readonly data$ = this.userState.data$;
constructor(
private readonly userApi: UserApi,
private readonly userState: UserState
) {}
// Make your methods with business logic, which might affect states.
// Return Observable. Components can process result by subscribing (complete/next/error).
public update(): Observable<User> {
return this.userApi.getCurrent()
.pipe(
tap((user) => this.userState.set(user))
);
}
}user.component.ts
import { ToastService } from '@my-library';
import { UserService } from '@features/user';
// IMPORTANT: Don't inject States directly to components!
// Only services with business logic should know how to affect your states.
@Component({
selector: 'smart-user',
template: '{{ user$ | async | json }}'
})
class UserComponent implements OnInit {
// Here is data from our state.
public readonly user$ = this.userService.data$;
constructor(
private readonly userService: UserService,
private readonly toastService: ToastService
) {}
public ngOnInit(): void {
this.updateUser();
}
// Run some services business logic from the smart component
private updateUser(): void {
this.userService.update()
.pipe(
catchError(() => this.showErrorToastAboutUserUpdatingError())
)
.subscribe();
}
// This is task of specific smart components to show UI staff, like: toasts, dialogs, bottomSheets etc...
private showErrorToastAboutUserUpdatingError(): Observable<unknown> {
return this.toastService.createError(`Can't update user!`);
}
}Example with ArrayState
users.state.ts
import { ArrayState, NgxState } from 'ngx-base-state';
import { UserFilters } from '../interfaces';
@NgxState()
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
class UsersState extends ArrayState<User> {
constructor() {
super([]); // Here you can set initial data.
}
// Example of "custom action"
public filter(filters: UserFilters): void {
const newUsers = this.data!.filter((user) => user.name.includes(filters.searchString));
this.set(newUsers);
}
// ArrayState have base methods to work with array, like: removeItem, updateItem
// and these methods might compare items in array using some unique value.
// You can override method `getItemId` if you want operate with items via specific unique value like `id`.
protected override getItemId(user: User): number {
return user.id;
}
}users.service.ts
import { UsersState } from './users.state';
// This service demonstrates examples of work with methods of ArrayState.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class UsersService implements OnInit {
// Async data for components.
public readonly data$ = this.usersState.data$;
// Sync data for components.
public get data(): User {
return this.usersState.data;
}
constructor(
private readonly usersState: UsersState
) {
this.usersState.data$
.subscribe(console.log);
this.setUserArray(); // [{ name: 'Nillcon', id: 248 }, { name: 'noname', id: 1 }]
this.updateUser() // [{ name: 'New name', id: 248 }, { name: 'noname', id: 1 }]
this.removeUser(); // [{ name: 'New name', id: 248 }]
this.addUser(); // [{ name: 'New name', id: 248 }, { name: 'John Doe', id: 2 }]
}
private setUserArray(): void {
this.usersState.set([
{
name: 'Nillcon',
id: 248
},
{
name: 'noname',
id: 1
}
]);
}
private updateUser(): void {
let user = this.usersState.data[0]; // { name: 'Nillcon', id: 248 }
user.name = 'New name';
// ngx-base-state will create new instance of user to avoid possible object mutations
this.usersState.updateItem(user);
}
private removeUser(): void {
const user = this.usersState.data[1]; // { name: 'noname', id: 1 }
this.usersState.removeItem(user);
}
private addUser(): void {
this.usersState.pushItem({
name: 'John Doe',
id: 2
});
}
}
