A Python library for offline reverse geocoding. It improves on an existing library called reverse_geocode developed by Richard Penman.
Update: v1.1 released! Python 3 not supported still.
Ajay Thampi | @thampiman | opensignal.com | ajaythampi.com
- Besides city/town and country code, this library also returns the nearest latitude and longitude and also administrative regions 1 and 2.
- This library also uses a parallelised implementation of K-D trees which promises an improved performance especially for large inputs.
The K-D tree is populated with cities that have a population > 1000. The source of the data is GeoNames.
$ pip install reverse_geocoder
Package can be found on PyPI.
Update: v1.1 released containing Brandon's and David's fixes
The library supports two modes:
- Mode 1: Single-threaded K-D Tree (similar to reverse_geocode)
- Mode 2: Multi-threaded K-D Tree (default)
import reverse_geocoder as rg
coordinates = (51.5214588,-0.1729636),(13.9280531,100.3735803)
results = rg.search(coordinates) # default mode = 2
print resultsThe above code will output the following:
[{'admin1': 'England',
'admin2': 'Greater London',
'cc': 'GB',
'lat': '51.51116',
'lon': '-0.18426',
'name': 'Bayswater'},
{'admin1': 'Nonthaburi',
'admin2': '',
'cc': 'TH',
'lat': '13.91783',
'lon': '100.42403',
'name': 'Bang Bua Thong'}]
If you'd like to use the single-threaded K-D tree, set mode = 1 as follows:
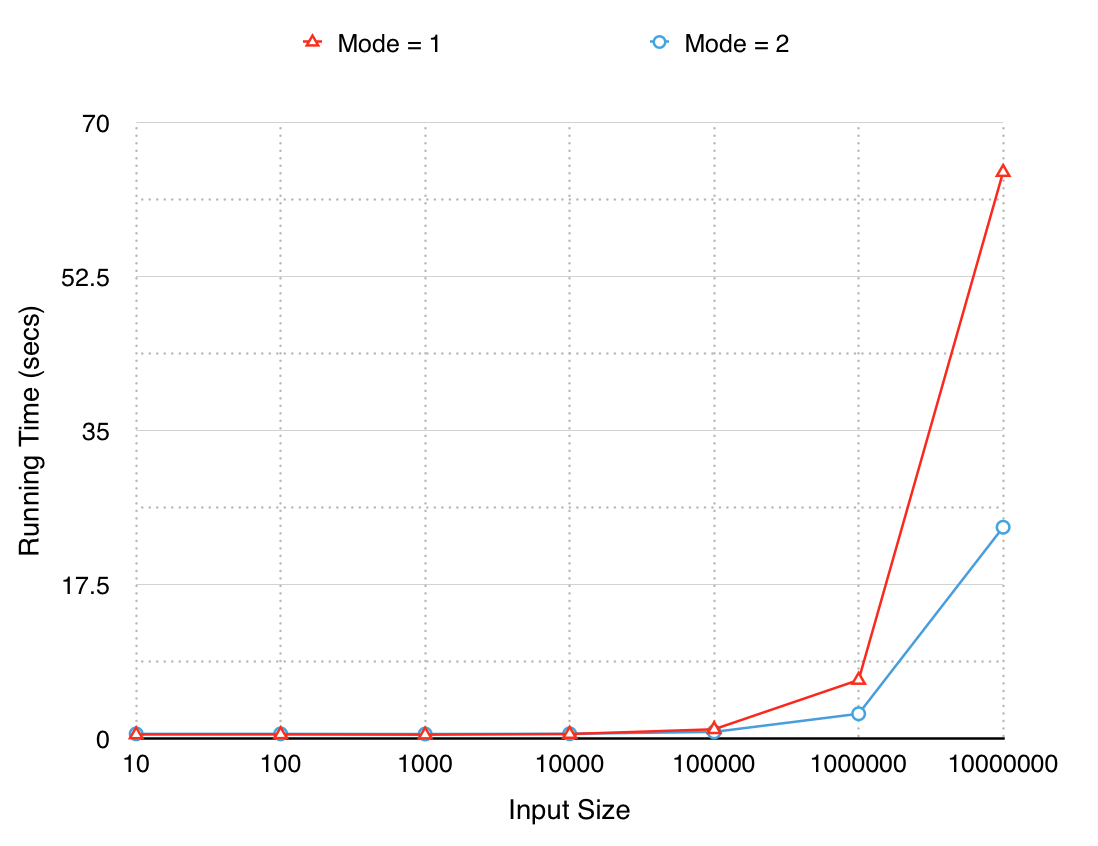
results = rg.search(coordinates,mode=1)The performance of modes 1 and 2 are plotted below for various input sizes.
Mode 2 runs ~2x faster for very large inputs (10M coordinates).
- Major inspiration is from Richard Penman's reverse_geocode library
- Parallelised implementation of K-D Trees is extended from this article by Sturla Molden
- Geocoded data is from GeoNames
The MIT License (MIT)