Effortlessly add natural, intuitive interactions with tracked controller, touch, or mouse input in A-Frame.
The goal of super-hands is to make it easy to handle user input in
Web VR by providing a high-level API that is consistent across all devices.
Instead of dealing directly with controller button events, raycasters, and
collision detection components, you setup your scene and components instead
to respond to 'gestures' like hovering and grabbing.
The currently implemented gestures are:
- Hover: Holding a controller in the collision space of an entity or pointing at an entity with a cursor or laser pointer
- Grab: Pressing a button while hovering an entity, potentially also moving it
- Stretch: Grabbing an entity with two hands and resizing
- Drag-drop: Activating one entity and then gesturing to another entity to interact with it
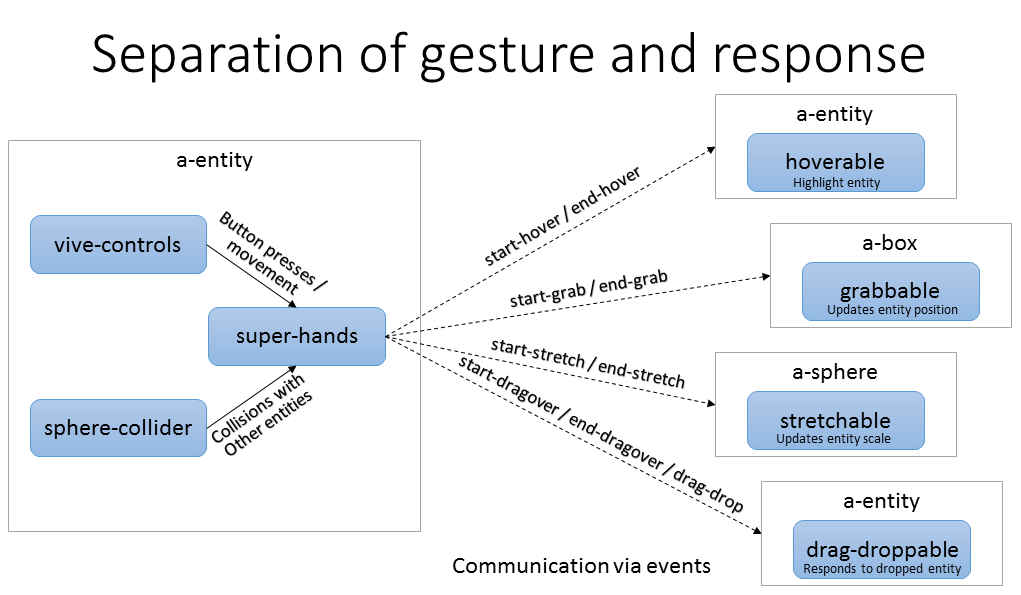
The family of components in this library fall into two categories:
Core: The super-hands component itself does the work of gathering
events from user input devices and collision detection components to
interpret them into gestures that it communicates out to the targeted
entities via custom events. This component is placed on the same entities
as your tracked controllers and/or your cursor raycaster.
Reaction Components: The super-hands core component alone only
communicates user intent via gesture events to the entities users want to
interact with; reaction components
enable the interactivity on those entities. This package includes components for
common reactions, hoverable, clickable, grabbable, stretchable,
draggable, and droppable, and it is also designed to be easily
extended with your own custom reaction components.
Install and use by directly by including the browser files:
<head>
<title>Most Basic Super-Hands Example</title>
<script src="https://aframe.io/releases/1.0.4/aframe.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.rawgit.com/donmccurdy/aframe-extras/v4.1.2/dist/aframe-extras.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/super-hands@^3.0.1/dist/super-hands.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<a-scene>
<a-assets></a-assets>
<a-entity>
<a-camera></a-camera>
<a-entity sphere-collider="objects: a-box" super-hands hand-controls="hand: left"></a-entity>
<a-entity sphere-collider="objects: a-box" super-hands hand-controls="hand: right"></a-entity>
</a-entity>
<!-- hover & drag-drop won't have any obvious effect without some additional event handlers or components. See the examples page for more -->
<a-box hoverable grabbable stretchable draggable dropppable color="blue" position="0 0 -1"></a-box>
</a-scene>
</body>Install via npm:
npm install super-handsThen require and use.
require('aframe');
require('super-hands');- Examples
- News
- Compatibility
- Super Hands Core Component
- Reaction components
- Customizing interactivity
The examples page showcases a variety of configurations and use cases for super-hands.
| Example Scene | Description | Target VR Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Hand controllers with physics | Grab, stretch, and drag-drop cubes with simulated physical behavior in roomscale VR | Vive, Rift, Windows MR |
| Gaze and laser pointer controls without physics | Showcase fallback controls used for simpler VR devices and fallback interactivity without physics simulation | Desktop, mobile, cardboard, Gear VR, Daydream, Vive, Rift, Windows MR |
v3.0.1
- A-Frame 1.0.4 support confirmation
- Updated dependencies and fixed tests
- No notable changes
v3.0.0
- The 'Less is More' update. This package has scope has been narrowed to keep
it maintainable, increase the frequency of updates, and allow for focus on
implementing new gestures instead of peripheral components.
progressive-controlsanda-locomotorremoved from this repo. I understandprogressive-controlswas fairly popular, but is has a compatibility issue with the latest A-Frame which was holding up releases for the entire package. I intend to refactor it and release it in another library, but you can still use the last version by including its source file in your project.
- Smarter raycasting support: chooses nearest intersected entity first, reordering stack as distances change (* if the raycaster in use updates intersection objects' distances)
- Improved nested entity handling: only one component can react to each gesture event.
- Improved stretching of complex physics bodies: all shapes, child entity shapes, and offsets are updated
- Added support for
'worker'and otheraframe-physics-systemdrivers ingrabbable - v2.x deprecations removed:
drag-droppablecomponent andsuper-hands.colliderStateproperty.
- Two-handed physics grabs don't feel great
- Help wanted with configuring ideal constraints for this situation
too much recursionerrors when using two raycasting controllers: When using raycasters, always set theirobjectsproperty to prevent the raycasters from colliding with each other's lines.
With the right configuration, super-hands can provide interactive controls
for any device: desktop, mobile ("magic window"), cardboard viewer + button,
3DOF (Daydream, GearVR) and full 6DOF tracked controls (Vive, Oculus Touch, Valve Index, et c).
super-hands dependency version compatibility:
| super-hands Version | A-Frame Version | aframe-extras Version | aframe-physics-system Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| ^v3.0.1 | ^v1.0.4 | ^v6.1.1 | ^v4.0.1 |
| v3.0.0 | ^v0.8.2 | ^v4.1.2 | ^v3.1.2 |
| ^v2.0.0 | v0.6.x | ^v3.11.4 | ^v2.0.0 |
The super-hands component is the core of the library.
It communicates gesture events to entities based on
user-input and entity collisions. The component is generally placed on
the controller entities (or the camera for gaze interaction) and depends on
a collision detection component (e.g. raycaster, aframe-extras sphere-collider,
of aframe-physics-extras physics-collider)
which needs to be placed on the same entity or a child entity of super-hands.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| colliderEvent | Event that your chosen collider emits when identifying a new collision | 'hit' |
| colliderEventProperty | Name of property in event detail object which contains the collided entity |
'el' |
| colliderEndEvent | Event that your chosen collider emits when a collision ends | 'hitEnd' |
| colliderEndEventProperty | Name of property in event detail object which contains the un-collided entity |
'el' |
| grabStartButtons | Array of button event types that can initiate grab | Button press, touch start, and mouse down events |
| grabEndButtons | Array of button event types that can terminate grab | Button release, touch end, and mouse up events |
| stretchStartButtons | Array of button event types that can initiate stretch | Button press, touch start, and mouse down events |
| stretchEndButtons | Array of button event types that can terminate stretch | Button release, touch end, and mouse up events |
| dragDropStartButtons | Array of button event types that can initiate dragging/hovering | Button press, touch start, and mouse down events |
| dragDropEndButtons | Array of button event types that can execute drag-drop | Button release, touch end, and mouse up events |
Collider-related property defaults are set to work with sphere-collider.
Default button events include specific events for vive-controls,
hand-controls, oculus-touch-controls, daydream-controls,
gearvr-controls, windows-motion-controls, oculus-go-controls, mouse, and touch.
Events will be emitted by the entity being interacted with.
The entity that super-hands is attached to is sent in the event detail as the property hand.
| Type | Description | Target | detail object |
|---|---|---|---|
| hover-start | Collided with entity | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| hover-end | No longer collided with entity | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| grab-start | Button pressed while collided with entity and hand is empty | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| grab-end | Button released after grab-start | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| stretch-start | Both controllers have button pressed while collided with entity | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity, secondHand: second controller entity |
| stretch-end | Release of button after stretch-start | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| drag-start | Drag-drop button pressed while collided with entity and hand is empty | collided entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| drag-end | Drag-drop button released while dragging an entity | dragged entity | hand: super-hands entity |
| dragover-start | Collision with entity while dragging another entity | collided entity & held entity | hand: super-hands entity, hovered: collided entity, carried: held entity |
| dragover-end | No longer collided with entity from dragover-start | collided entity & held entity | hand: super-hands entity, hovered: collided entity, carried: held entity |
| drag-drop | Button released while holding an entity and collided with another | collided entity & held entity | hand: super-hands entity, dropped: carried entity, on (carried entity only): receiving entity |
Notes:
- References to buttons being "released" and "pressed" are dependent on the schema settings.
- Only one entity at a time will be targeted for each event type,
even if multiple overlapping collision zones exist.
super-handstracks a LIFO stack of collided entities and a nearest-first queue of raycasted Entities to determine which will be affected. - drag-drop: For the receiving entity,
onentry in the detail isnull. If needed, useevent.targetinstead. - For events triggered by buttons, the triggering button event is passed
along in
detail.buttonEvent - When entities are nested, gesture events will bubble to the closest parent
with a related reaction component. This makes it easy to make specific
hotspots on larger objects by making the child collidable
but placing the reaction component on the parent
(e.g., a door with the handle as a collidable child and a
grabableparent door so the whole door moves only when the handle is grabbed). To prevent a gesture from bubbling, trap it on the child by giving it reaction components or listening-for and cancelling the gesture events (see Gesture acceptance and rejection)
In addition to the A-Frame style gesture events,
super-hands also causes standard HTML events analogous to VR
interactions to be emitted by the target entities. This allows the use of these
common Global Event Handler properties on entities to add reaction directly
in the HTML. View the
related example
to see this in use.
| entity HTML attribute | conditions | event.relatedTarget |
|---|---|---|
| onmouseover | hovering in an entity's collision zone | super-hands entity |
| onmouseout | leaving an entity's collision zone | super-hands entity |
| onmousedown | grab started while collided with entity | super-hands entity |
| onmouseup | grab ended while collided with entity | controller entity |
| onclick | grab started and then ended while collided with entity | controller entity |
| ondragstart | drag-drop started while collided with entity | controller entity |
| ondragend | drag-drop started while collided with entity | controller entity |
| ondragenter | hovering in an entity's collision zone while drag-dropping another entity | the other entity* |
| ondragleave | leaving an entity's collision zone while drag-dropping another entity | the other entity* |
| ondrop | drag-drop ended while holding an entity over a target | the other entity* |
The event passed to the handler will be a MouseEvent. At present the only property implemented
is relatedTarget, which is set as
listed in the table. Drag-dropping events will be dispatched on both the entity being dragged and the drop target, and the relatedTarget property for each will point to the other entity in the interaction.
Add these components to entities in your scene to make them react to super-hands gestures.
Used to indicate when the controller is within range to interact with an entity by adding the 'hovered' state.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hovered | Added to entity while it is collided with the controller |
Makes and entity move along with the controller's movement and rotation
while it is grabbed. grabbable works with
up-close grabbing (6DOF controllers like Vive and Oculus Touch
with hand-controls and sphere-collider)
and with pointing at a distance (3DOF controllers like GearVR and Daydream
with laser-controls).
This works best with aframe-physics-system
to manage grabbed entity movement including position and rotation,
but it will fallback to manual position updates
if physics is not available
or is disabled with usePhysics = never.
Allows for multiple hands to register a grab on an entity. In a non-physics setup, this has no effect other than allowing smooth passing of entities between hands. With physics enabled, additional grabbing hands register their own physics constraints to allow for two-handed wielding of entities. Limit or disable this by setting the maxGrabbers schema property.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| startButtons | Which button events to accept to start grab | [] |
| endButtons | Which button events to accept to end grab | [] |
| usePhysics | Whether to use physics system constraints to handle movement, 'ifavailable', 'only', or 'never' | 'ifavailable' |
| maxGrabbers | Limit number of hands that can grab entity simultaneously | NaN (no limit) |
| invert | Reverse direction of entity movement compared to grabbing hand | false |
| suppressY | Allow movement only in the horizontal plane | false |
The default for startButtons and endButtons is to accept any button
recognized by super-hands grabStartButtons and grabDropEndButtons.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| grabbed | Added to entity while it is being carried |
An alternative version of grabbable that registers that a button was pressed, but does not
move the entity. Do not use clickable and grabbable on the same entity
(just use grabbable and watch the "grabbed" state instead of "clicked")
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| startButtons | Which button events to accept to start grab | [] |
| endButtons | Which button events to accept to end grab | [] |
The default for startButtons and endButtons is to accept any button
recognized by super-hands grabStartButtons and grabDropEndButtons.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| clicked | Added to entity while a button is held down |
Makes and entity rescale while grabbed by both controllers as they are moved closer together or further apart.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| startButtons | Which button events to accept to start stretch | [] |
| endButtons | Which button events to accept to end stretch | [] |
| usePhysics | Whether to update physics body shapes with scale changes, 'ifavailable' or 'never' | 'ifavailable' |
| invert | Reverse the direction of scaling in relation to controller movement | false |
| phyicsUpdateRate | Milliseconds between each update to the physics bodies of a stretched entity | 100 |
The default for startButtons and endButtons is to accept any button
recognized by super-hands stretchStartButtons and stretchEndButtons.
There is no CANNON API method for updating physics body scale, but stretchable
will manually rescale shapes and offsets for stretched entity body and
all descendent entity bodies.
This update is throttled and will occur no more than once every
physicsUpdateRate milliseconds to improve performance. Set this to a smaller
number to increase the physics simulation fidelity.
Currently rescalable shapes are: box and sphere. At present, this rescaling
is only possible on when using the 'local' physics driver. If using another
driver, setting usePhysics: never will avoid errors but also cause
loss of sync between stretched entities' appearance and behavior.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| stretched | Added to entity while it is grabbed with two hands |
draggable makes an entity able to participate in a drag and drop
gesture with a droppable entity. This does not move an entity
(also add grabbable for that functionality), but instead tracks whether
a gesture has been made that involves pressing a button down with the controller
pointed at this entity, and then moving the controller to point at another
entity with the droppable component before releasing.
For interactivity, use the global event handler integration,
the event-set from kframe
with the drag-drop event, or create your own component.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| startButtons | Which button events to accept to start drag | [] |
| endButtons | Which button events to accept to end drag | [] |
The default for startButtons and endButtons is to accept any button
recognized by super-hands dragDropStartButtons and dragDropEndButtons.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dragged | Added to entity from button press until button release |
The droppable component sets an entity up as a target to respond to
dragged entities. Optionally, it can be configured to accept only
specific entities and to emit custom events on acceptance or rejection.
Combining the accepts and acceptEvent property of droppable with
event-set from kframe, you can
create rich interactivity without any additional JavaScript or
custom components.
| Property | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| accepts | CSS query string to specify which entities to respond to | '' (accept all entities) |
| autoUpdate | Should it watch for newly added entities that match accepts? May impact performance. |
true |
| acceptEvent | String. Name of custom event to emit upon successful drag-drop interaction | '' (don't emit event) |
| rejectEvent | String. Name of custom event to emit upon rejecting attempted drag-drop that contained an entity not included in accepts |
'' (don't emit event) |
Accept and reject events will contain the dragged entity that was accepted/rejected
in the el property of detail.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dragover | Added to the entity while a controller is holding an acceptable draggable entity in the collision space of the droppable entity |
Separating the reaction to be the responsibility of the entity affected allows for extensibility.
In response to a grab, you may want some entities to lock to the controller and move,
others to rotate around a fixed point, and others still to spawn a new entity but remain unchanged.
With this API schema, these options can be handled by adding or creating different reaction
components to the entities in your scene, and super-hands can work with all of them.
There are two pathways to adding additional interactivity.
- A-Frame style: Each component's API documentation describes the A-Frame custom events and states it uses. These can be used on conjunction with other community A-Frame components or by creating custom components for your project that register event listeners and react accordingly.
- HTML style: The
super-handscomponent also integrates with the Global Event Handlers Web API to trigger standard mouse events analogous to the VR interactions that can easily be handled through properties likeonclick.
Entities which are the target of gestures communicate back to super-hands
that they have accepted the attempted interaction by 'cancelling' the
gesture event (i.e. calling .preventDefault() on the event). This allows
super-hands to penetrate overlapping and nested entities in order to find
the desired target and for reaction components to be discriminating about
their conditions for interaction
(e.g., droppable). All of the provided
reaction components handle this signaling automatically, but, if you
create your own reaction components, it is important to cancel the events when
responding to a gesture so that super-hands knows the gesture has been
accepted and stops searching for a viable target.