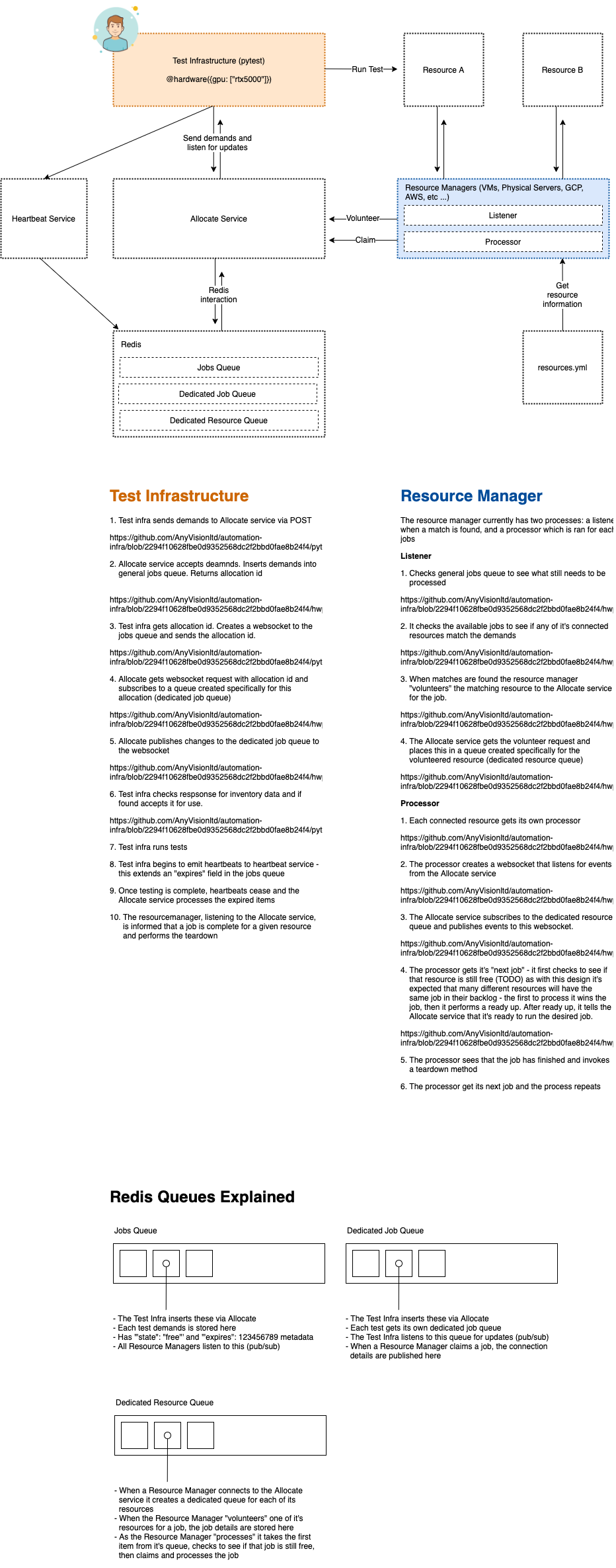
This is a suite of services which manage the provisioning of hardware resources to AnyVision employees for testing purposes.
## Terminology
Test Infrastructure - this is a suite of python scripts which can be invoked with PyTest that allows a user to easily write tests which integrate with the Lab.
Demands - a set of requirements needed for a single test (CPU, Memory, GPUs, OS etc)
Resource - a resource which the Test Infrastructure can run its tests on. Virtual Machines, Physical Servers, Edge Devices, Cloud Resources etc
Resource Manager - is the representative of all resources. Listens to the Allocate service for jobs and volunteers its resources
Allocate Service - handles requests from both the Test Infrastructure and Resourcemanager. Checks for finished jobs. Exposes data from Redis.
Heartbeat Service - very simple service for extending the duration of a resource reservation
- docker (tested on version 19.03.5)
- make (tested on version GNU Make 4.1)
For your convenience, several commands have been added to this directory for you. You can avail of these by running make <command>, e.g. make tests
$ make
run runs the applications in docker-compose
tests run all modules tests sequentially
shell runs pipenv shell
lint run all modules linters sequentially
test-complexity run only python complexity analysis
test-security run only python security analysis
test-lint-docker run only docker linter
test-lint-shellcheck run only shell/bash linter
clean clean up environmentnote: each sub-directory also has it's own set of commands.
## i want to run it manually
If you want to run each container independently you can do so with the following commands:
export MYIP=<INSERT YOUR MACHINES IP HERE>
# run redis in detached mode
docker run --rm -d -e ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD=yes -p 6379:6379 -ti redis:5.0.7
# build and run allocate service
cd ./hwprovisioner/allocate
docker build -t=allocate .
# note: replace $MYIP with the ip of your redis container (your machine ip probably)
docker run --rm -e REDIS_USER=guest -e REDIS_PASSWORD=pAssw0Rd! -e REDIS_HOST=$MYIP -e REDIS_PORT=6379 -e REDIS_DB=0 -v $(pwd):/src -w /src -p 8080:8080 -ti allocate watchmedo auto-restart --recursive -d . -p '*.py' -- python3 -m 'webapp.app' serve
# build and run resource manager (this can be anywhere on the network. works on localhost too ofc)
cd ./hwprovisioner/resourcemanager
vim resources.yml # copy this from example.resources.yml and edit as required
docker build -t=resourcemanager .
# note: replace $MYIP with the ip of your allocate container (your machine ip probably)
docker run --rm -e ALLOCATE_API=http://$MYIP:8080/ -e CONFIG_FILE=./resources.yml -p 9080:8080 -v $(pwd):/src -w /src -ti resourcemanager watchmedo auto-restart --recursive -d . -p '*.py' -- python3 -m 'webapp.app' serve
# build and run heartbeats service
cd ./hwprovisioner/heartbeats
docker build -t=heartbeats .
# note: replace $MYIP with the ip of your allocate container (your machine ip probably)
docker run --rm -e REDIS_HOST=${MYIP} -e REDIS_PORT=6379 -e REDIS_DB=0 -e REDIS_USER=guest -e REDIS_PASSWORD=password -v ${PWD}:/src -w /src -p 7080:8080 -ti heartbeats watchmedo auto-restart --recursive -d . -p '*.py' -- python3 -m 'webapp.app' serve