Mlxtend (machine learning extensions) is a Python library of useful tools for the day-to-day data science tasks.
- This open source project is released under a permissive new BSD open source license and commercially usable
Sebastian Raschka 2014-2016
- Documentation:
- PyPI: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/mlxtend
- Changelog: http://rasbt.github.io/mlxtend/changelog
- Contributing: http://rasbt.github.io/mlxtend/contributing
- Questions? Check out the Google Groups mailing list
## Recent changes
- Sequential Feature Selection algorithms: SFS, SFFS, and SFBS
- Neural Network / Multilayer Perceptron classifier
- Ordinary least square regression using different solvers (gradient and stochastic gradient descent, and the closed form solution)
To install mlxtend, just execute
pip install mlxtend Alternatively, you download the package manually from the Python Package Index https://pypi.python.org/pypi/mlxtend, unzip it, navigate into the package, and use the command:
python setup.py installThe mlxtend version on PyPI may always one step behind; you can install the latest development version from the GitHub repository by executing
pip install git+git://github.com/rasbt/mlxtend.git#egg=mlxtendOr, you can fork the GitHub repository from https://github.com/rasbt/mlxtend and install mlxtend from your local drive via
python setup.py installConda packages are now available for Mac, Windows, and Linux. You can install mlxtend using conda by executing
conda install -c rasbt mlxtendimport numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import itertools
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from mlxtend.classifier import EnsembleVoteClassifier
from mlxtend.data import iris_data
from mlxtend.evaluate import plot_decision_regions
# Initializing Classifiers
clf1 = LogisticRegression(random_state=0)
clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=0)
clf3 = SVC(random_state=0, probability=True)
eclf = EnsembleVoteClassifier(clfs=[clf1, clf2, clf3], weights=[2, 1, 1], voting='soft')
# Loading some example data
X, y = iris_data()
X = X[:,[0, 2]]
# Plotting Decision Regions
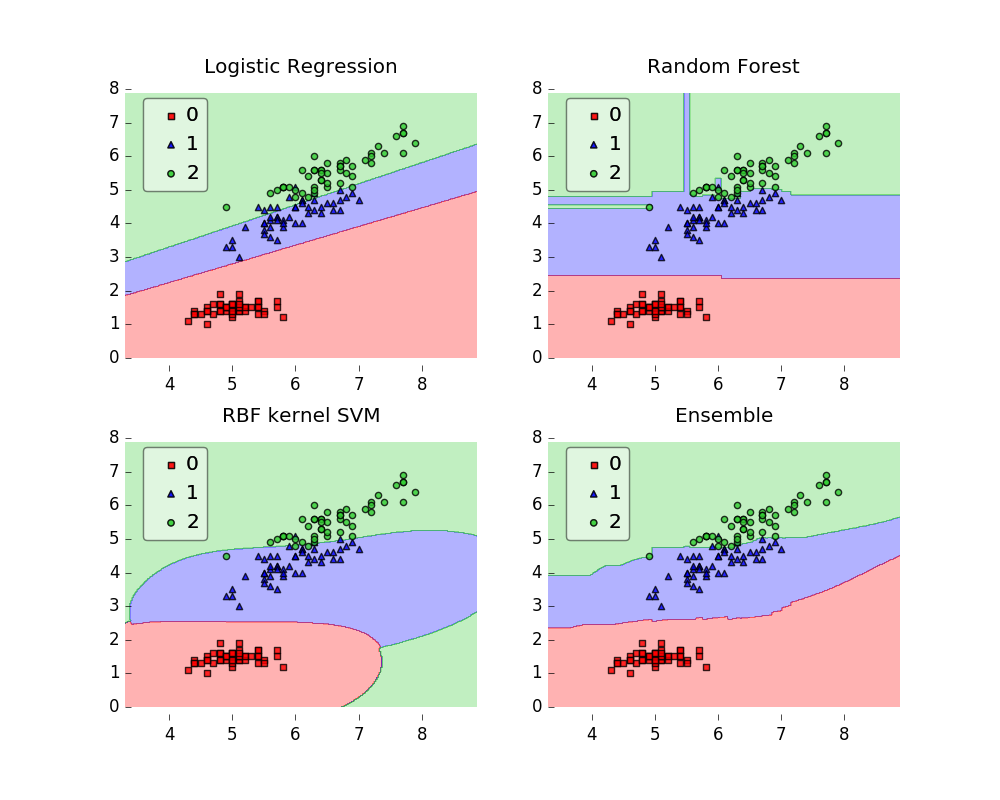
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 2)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
for clf, lab, grd in zip([clf1, clf2, clf3, eclf],
['Logistic Regression', 'Random Forest', 'RBF kernel SVM', 'Ensemble'],
itertools.product([0, 1], repeat=2)):
clf.fit(X, y)
ax = plt.subplot(gs[grd[0], grd[1]])
fig = plot_decision_regions(X=X, y=y, clf=clf, legend=2)
plt.title(lab)
plt.show()If you use mlxtend as part of your workflow in a scientific publication, please consider citing the mlxtend repository with the following DOI:
@misc{raschkas_2016_49235,
author = {Raschka, Sebastian},
title = {Mlxtend},
month = apr,
year = 2016,
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.49235},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.49235}
}
I received a lot of feedback and questions about mlxtend recently, and I thought that it would be worthwhile to set up a public communication channel. Before you write an email with a question about mlxtend, please consider posting it here since it can also be useful to others! Please join the Google Groups Mailing List!
If Google Groups is not for you, please feel free to write me an email or consider filing an issue on GitHub's issue tracker for new feature requests or bug reports. In addition, I setup a Gitter channel for live discussions.