SiteLocalization
Binding site localization on non-homogeneous cell surfaces using topological image averaging
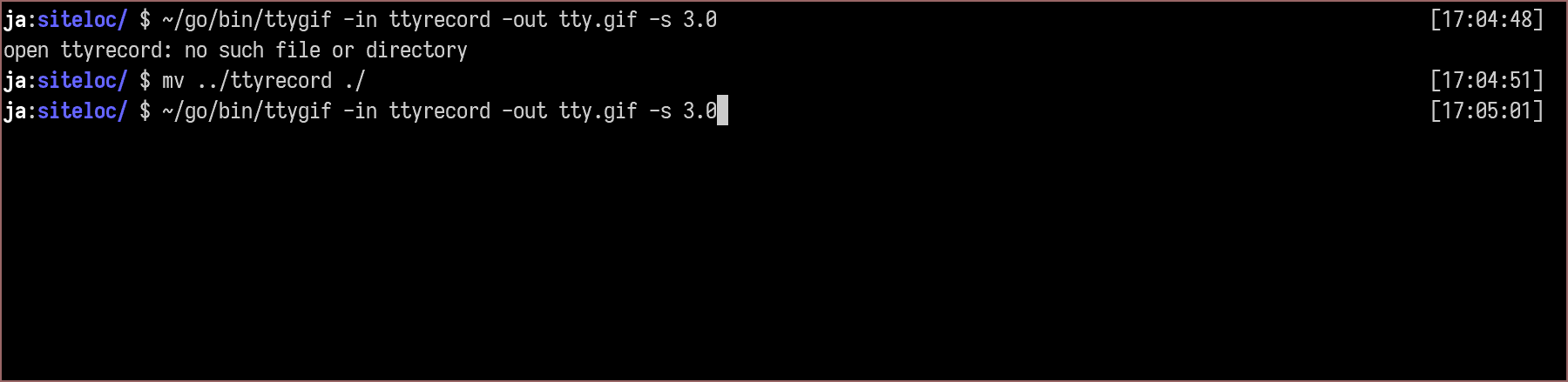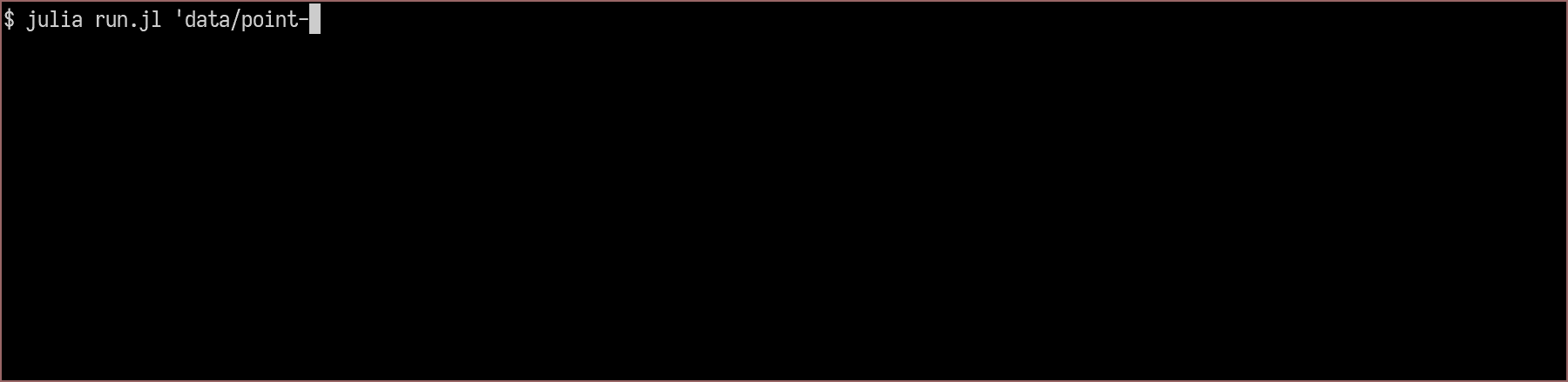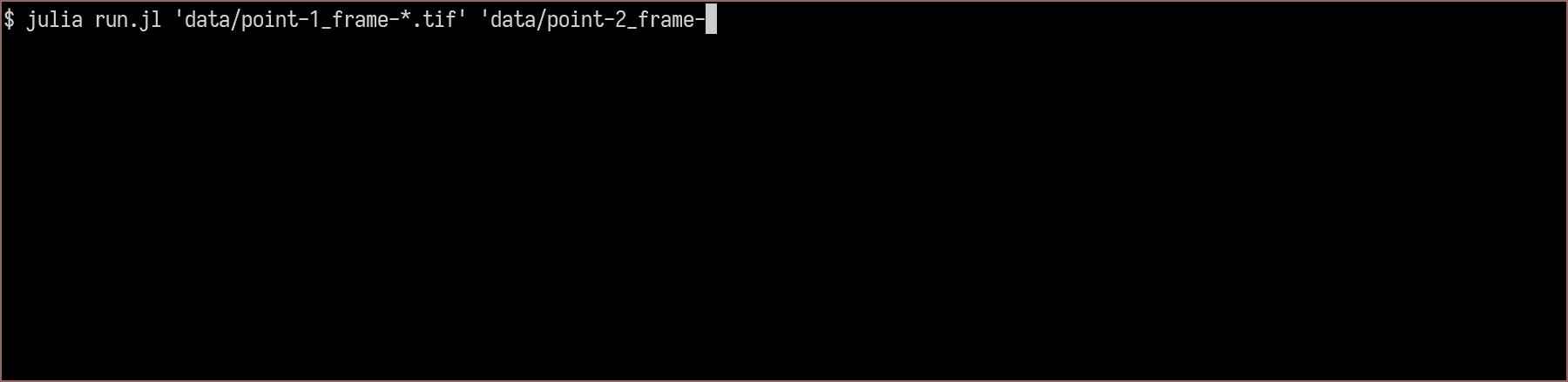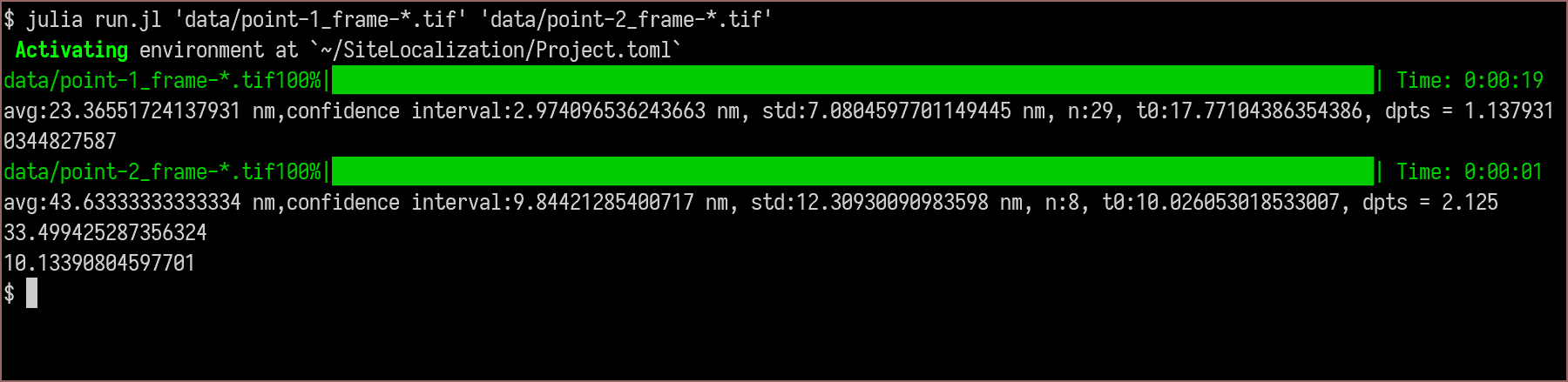
Usage
usage: run.jl [--pixelsize PIXELSIZE] [--shiftwindow SHIFTWINDOW]
[--maxpeakswindow MAXPEAKSWINDOW]
[--iterations ITERATIONS] [--psf_sigma PSF_SIGMA]
[--highp HIGHP] [--lowp LOWP] [--blur BLUR]
[--mindistance MINDISTANCE] [--margin MARGIN]
[--votingthreshold VOTINGTHRESHOLD] [--rmin RMIN]
[--rmax RMAX] [--pxmult PXMULT] [--al-shifty AL-SHIFTY]
[--al-shiftx AL-SHIFTX]
[--first-snr-limit FIRST-SNR-LIMIT]
[--snr-ratio-limit SNR-RATIO-LIMIT] [--limit-outside]
[--maxdist MAXDIST] [--debug-plots]
[--enable-sigma-norm] [--name NAME] [-h] images...
positional arguments:
images images to analyze
optional arguments:
--pixelsize PIXELSIZE
image pixel size in nanometers (type: Float64,
default: 20.5333)
--shiftwindow SHIFTWINDOW
for sliding average of peak alignment, 0 if
only aligning max of peaks (type: Int64,
default: 7)
--maxpeakswindow MAXPEAKSWINDOW
sliding average for sum of several circles
(type: Int64, default: 0)
--iterations ITERATIONS
RL iterations (type: Int64, default: 0)
--psf_sigma PSF_SIGMA
Measured sigma of psf, for Richardsson Lucy
deconvolution (type: Int64, default: 4)
--highp HIGHP For canny edge detection and circle hough
transform, in percentile (type: Float64,
default: 99.8)
--lowp LOWP For canny edge detection and circle hough
transform, in percentile (type: Float64,
default: 95.0)
--blur BLUR blur for segmentation (type: Float64, default:
3.5)
--mindistance MINDISTANCE
in pixels, the minimum distance between two
circle centers (type: Int64, default: 50)
--margin MARGIN fitted circle radius margin (type: Int64,
default: 20)
--votingthreshold VOTINGTHRESHOLD
sensitivity of circle detection in pixels
(type: Int64, default: 20)
--rmin RMIN fitted circle minimum radius (type: Int64,
default: 36)
--rmax RMAX fitted circle maximum radius (type: Int64,
default: 44)
--pxmult PXMULT pixel interpolation (type: Float64, default:
2.0)
--al-shifty AL-SHIFTY
adjust for measured chromatic aberration
(type: Float64, default: -0.63)
--al-shiftx AL-SHIFTX
adjust for measured chromatic aberration
(type: Float64, default: -1.35)
--first-snr-limit FIRST-SNR-LIMIT
SNR limit for first frame for analyzing a time
sequence (type: Float64, default: 0.0)
--snr-ratio-limit SNR-RATIO-LIMIT
SNR limit in terms of ratio to SNR of first
frame at which to stop analyzing a time
sequence (type: Float64, default: 0.3)
--limit-outside limit search for peaks to outside of reference
channel
--maxdist MAXDIST maximum distance from reference channel within
which to search for peaks (type: Int64,
default: 0)
--debug-plots enable saving of plots and images for
debugging purposes
--enable-sigma-norm enable saving of plots and images for
debugging purposes
--name NAME
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Abstract
Antibody binding to cell surface proteins plays a crucial role in immunity and the location of an epitope can altogether determine the immunological outcome of a host-target interaction. Techniques available today for epitope identification are costly, time-consuming, and unsuited for high-throughput analysis. Fast and efficient screening of epitope location can be useful for the development of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and vaccines. In the present work, we have developed a method for imaging-based localization of binding sites on cellular surface proteins. The cellular morphology typically varies, and antibodies often bind in a non-homogenous manner, making traditional particle-averaging strategies challenging for accurate native antibody localization. Nanometer-scale resolution is achieved through localization in one dimension, namely the distance from a bound ligand to a reference surface, by using topological image averaging. Our results show that this method is well suited for antibody binding site measurements on native cell surface morphology.