A template for flask applications sturcutured in the Model View Controller pattern Demo
- Python3/pip3
- Packages listed in requirements.txt
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Configuration information such as the database url/port, credentials, API keys etc are to be supplied to the application. However, it is bad practice to stage production information in publicly visible repositories. Instead, all config is provided by a config file or via environment varables.
When running the project in a development environment (such as gitpod) the app is configured via config.py file in the App folder. By default, the config for development uses a sqlite database test.db.
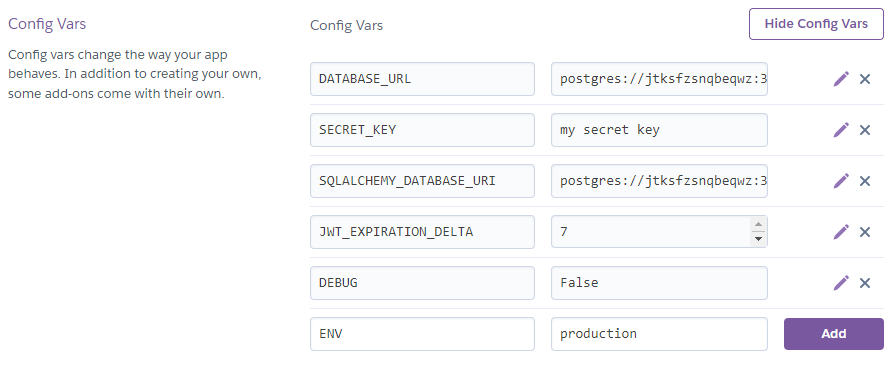
When deploying your application to production/staging you must pass in configuration information via enviornment variables. For heroku you need to navigate to your application's setting page (url should look like https://dashboard.heroku.com/apps/[app-name]/settings) and scroll down to config vars. Then provide your configuration as shown in the image below.
When deploying to production the "ENV" variable should be set to "production".
Note heroku provides a default variable "DATABASE_URL" for heorku postgres. If you want the app to use this database you must copy the value to the variable "SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL".
Manage.py is a utility script for performing various tasks related to the project. You can use it to import and test any code in the project. You just need create a manager command function, for example:
# inside manage.py
@manager.command
def hello():
print('hello')
...
Then execute the command by calling the funciton name as a parameter to the script
$ python3 manage.py hello
For development run the serve command (what you execute):
$ python3 manage.py serve
For production using gunicorn (what heroku executes):
$ gunicorn -w 4 App.main:app
You can deploy your version of this app to heroku by clicking on the "Deploy to heroku" link above.
When connecting the project to a fresh empty database ensure the appropriate configuration is set then file then run the following command. If you are using sqlite test.db would be created.
$ python3 manage.py initdb
If changes to the models are made, the database must be'migrated' so that it can be synced with the new models. Then execute following commands using manage.py. More info here
$ python3 manage.py db init
$ python3 manage.py db migrate
$ python3 manage.py db upgrade
$ python3 manage.py db --help