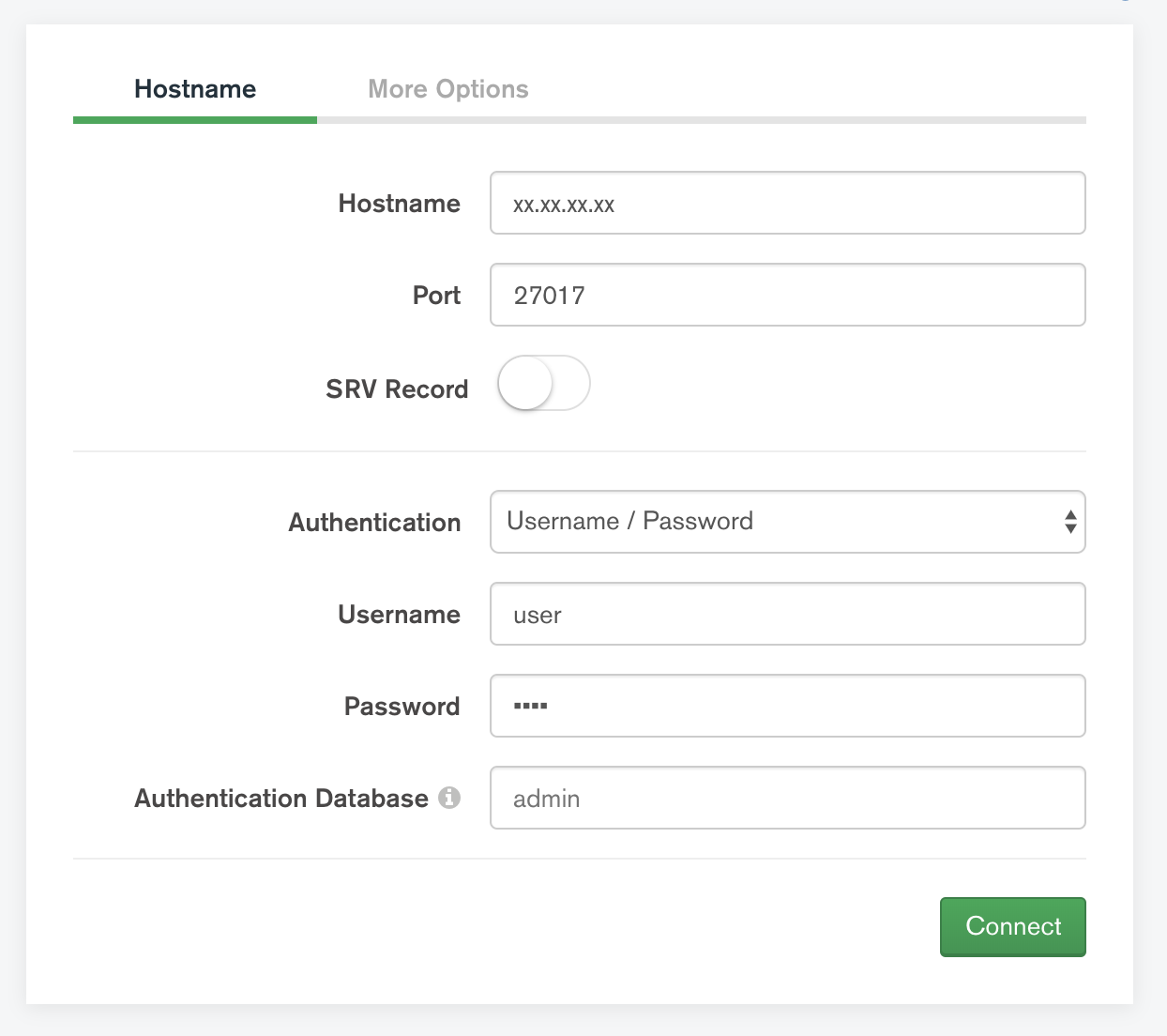
This is a docker-compose setup which will spin up a Docker container with MongoDB. A root user will be initialized, as well as an app (readWrite) and Data Scientist (read) role. Furthermore, authentication is enabled and a self-signed certificate will be created and enable transport encryption.
Clone the repo to your chosen host. Change the following things:
This is needed if you want the Docker container to mount out the log file. Run the following command
sudo chmod 777 data/log/Step 1
Change the Common Name (CN) property from xx.xx.xx.xx to the public IP address of your host (127.0.0.1 if you only plan to access your MongoDB from the same host) in the create_self_signed_certificate.sh file
-subj "/CN=xx.xx.xx.xx"Step 2
Make create_self_signed_certificate.sh executable
chmod +x create_self_signed_certificate.shStep 3
Create certificate by executing create_self_signed_certificate.sh
./create_self_signed_certificate.shStep 1: root user
Change root and secret to your desired username and password in mongo.env
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=root
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=secret... and in config/init-mongo-users.sh
mongo -u root -p secret --authenticationDatabase admin <<EOFStep 2: app and Data Scientist users
Change secret to your desired passwords for app and dataScientist users in config/init-mongo-users.sh
db.createUser({
user: "app",
pwd: "secret",
roles: ["readWriteAnyDatabase"]
});
db.createUser({
user: "dataScientist",
pwd: "secret",
roles: ["readAnyDatabase"]
});docker-compose upFirst of all, you need access to the created certificate on the machine you try to connect from.
Install mongo client and then run the command (type in the public IP address of the server hosting the MongoDB container instead of xx.xx.xx.xx)
mongo -u user -p pass --authenticationDatabase admin --host xx.xx.xx.xx --port 27017 --tls --tlsCAFile mongodb.pemInstall pymongo with conda install -c anaconda pymongo or pip install pymongo and use these configurations
import pymongo
configs = {
"username": "user",
"password": "pass",
"host": "xx.xx.xx.xx",
"port": 27017,
"tls": True,
"tlsAllowInvalidCertificates": True,
"tlsCAFile": 'mongodb.pem'
}
client = pymongo.MongoClient(**configs)
client.list_database_names()
>> ['admin', 'config', 'local']Note: the tlsAllowInvalidCertificates doesn't mean, the traffic will not be encrypted. It just allow self-signed certificates.
const fs = require("fs");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
await mongoose.connect(
"mongodb://user:pass@xx.xx.xx.xx:27017/?authSource=admin",
{
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
ssl: true,
sslValidate: true,
sslCA: fs.readFileSync(`${__dirname}/mongodb.pem`),
}
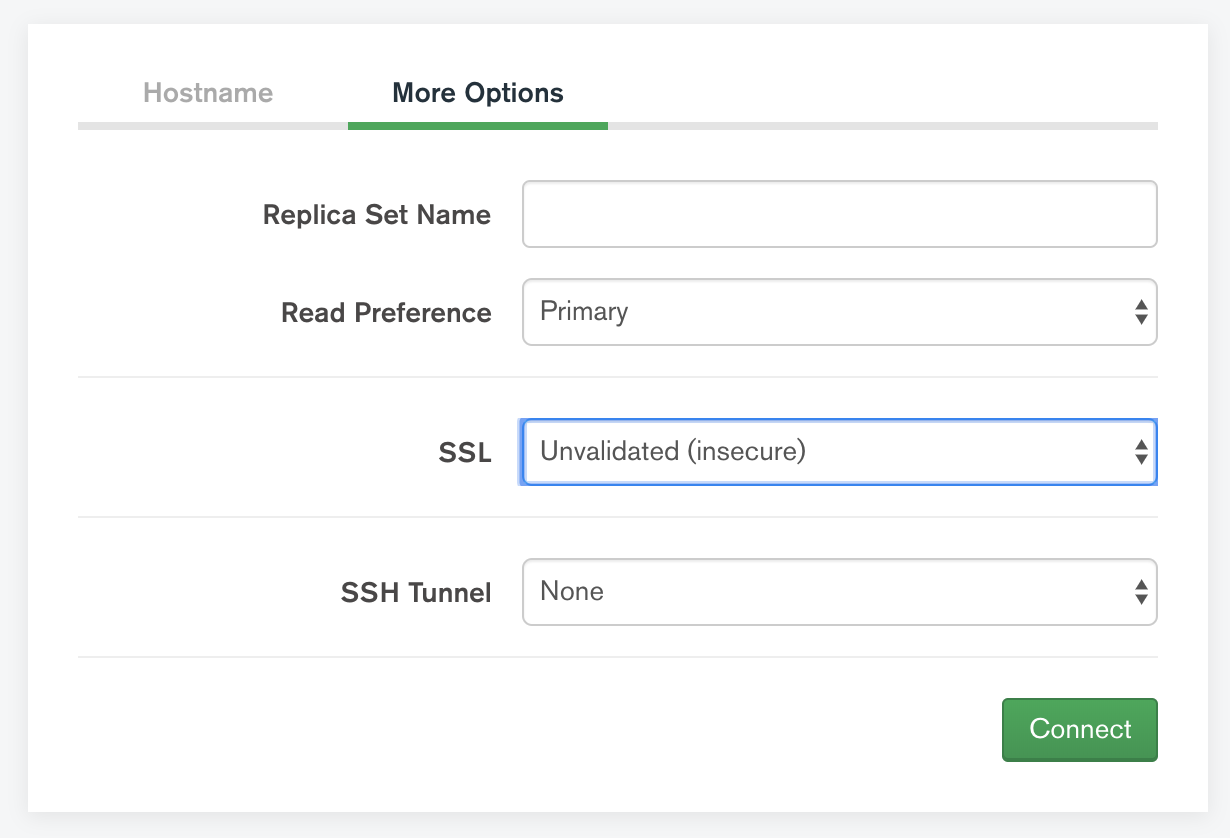
);Unfortunately, it is not possible to connect to MongoDB Compass with self-signed certificate. You are still able to connect, but only in an unvalidated and insecure way