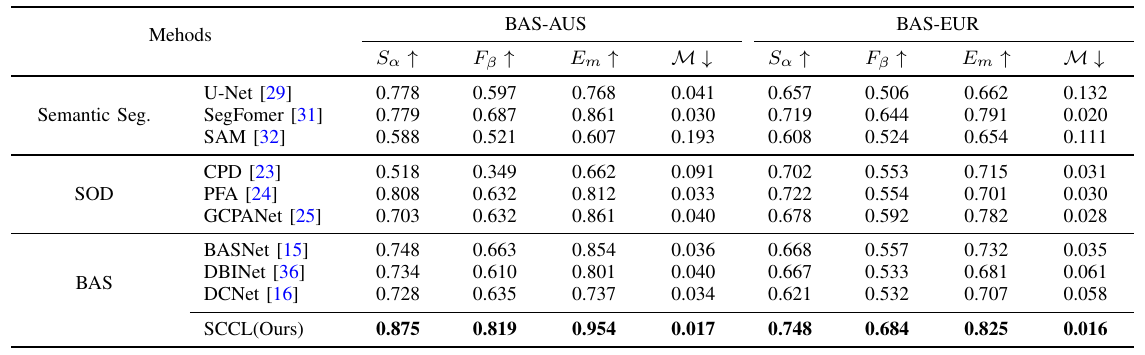
SCCL: Exploring Self-image and Cross-image Consistency Learning for Remote Sensing Burned Area Segmentation
The increasing global wildfires in recent years have destroyed a large number of forests and wetlands. Non-contact remote sensing technologies for burned area segmentation (BAS) offer accurate identification and delineation of burned areas.
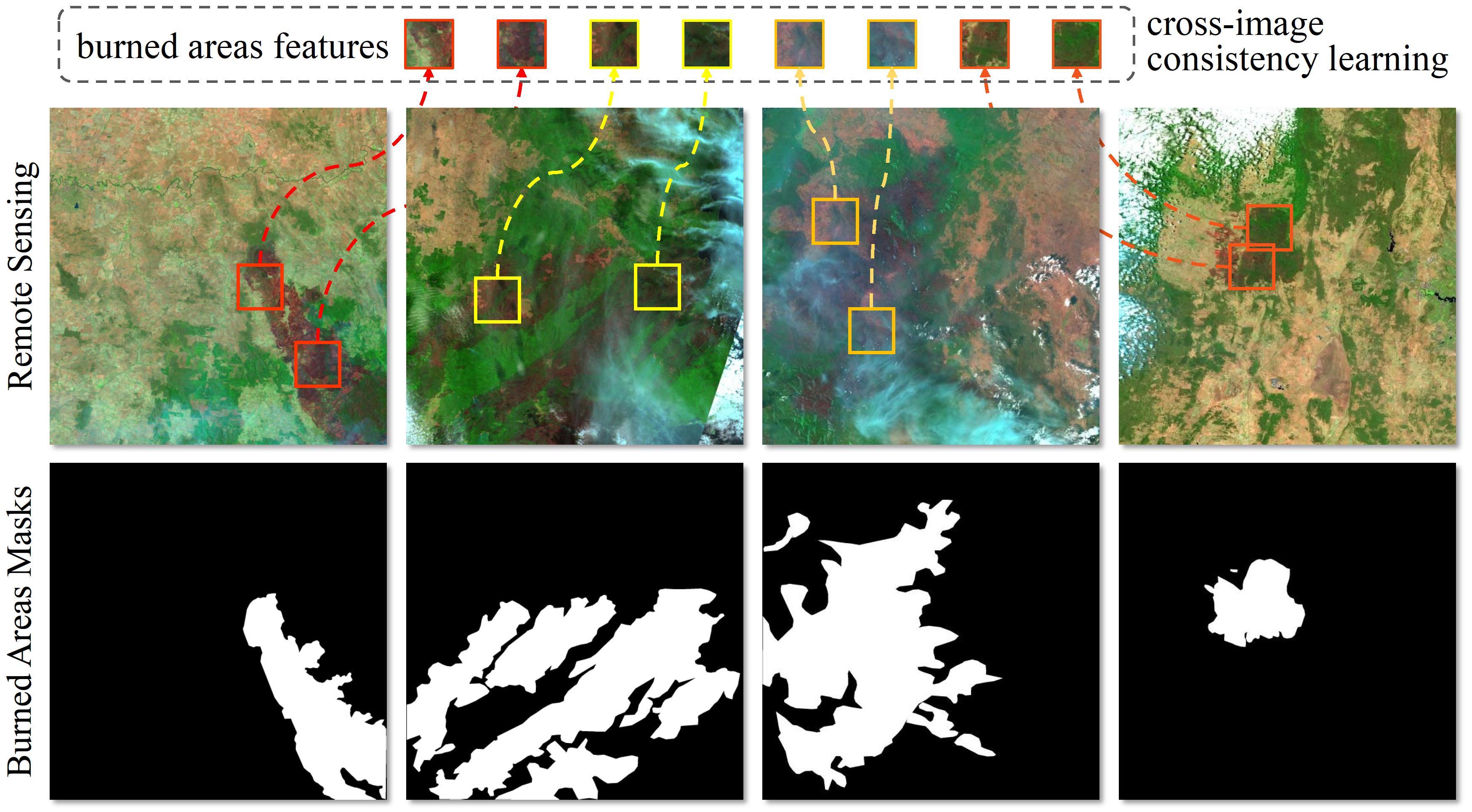
Fig. 1 Remote sensing burned area segmentation (BAS).
Different from general object segmentation, burned areas in BAS have not only 1) local context within a single image, but also 2) global context across images.
After preparing data set, the BAS_AUS data folder should be like the format below:
├── BAS_AUS
│ ├── test
│ │ ├── edge
│ │ │ ├── xxxxx.jpeg
│ │ │ ├── ......
│ │ ├── image
│ │ │ ├── xxxxx.jpeg
│ │ │ ├── ......
│ │ └── mask
│ │ ├── xxxxxx.jpeg
│ │ ├── ......
│ └── train
│ ├── edge
│ │ ├── xxxxx.jpeg
│ │ ├── ......
│ ├── image
│ │ ├── xxxx.jpeg
│ │ ├── ......
│ └── mask
│ ├── xxx.jpeg
│ ├── ......
TABLE I. Quantitative comparisons on two BAS datasets. The best results are shown in bold.
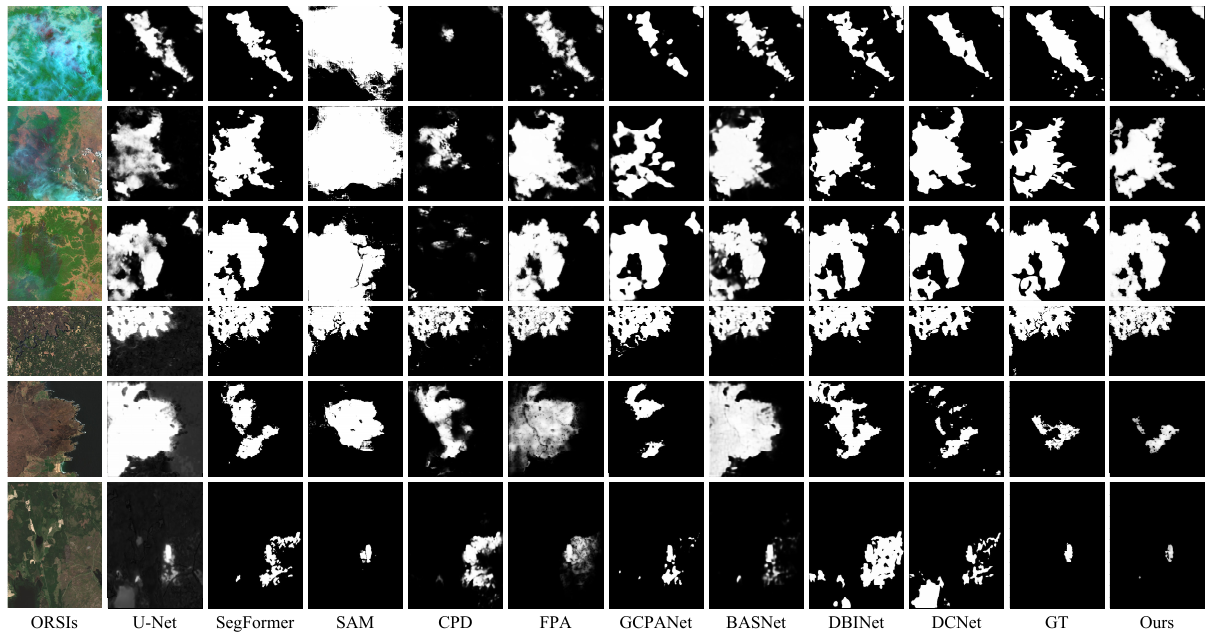 Fig. 2 Visual comparisons of different SOTA methods.
This figure shows that our proposed method (Ours) consistently generates burned masks close to the Ground Truth (GT).
Zoom in for details.
Fig. 2 Visual comparisons of different SOTA methods.
This figure shows that our proposed method (Ours) consistently generates burned masks close to the Ground Truth (GT).
Zoom in for details.
train.py contains the main training function code, and some parameters and dataset loactions need to be specified.
python train.py --model_name "SCCL" --mode "train" --data_dir "dataset/BAS-AUS" We use this Saliency-Evaluation-Toolbox for evaluating all BAS results.