Made by Viktor Kim Christiansen, Chris Rosendorf & William Pfaffe
School assignment with focus on performance with sample databases.
- Run the DB with Docker
docker run --rm --name my_mysql -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=tropaadet -d mysql:latest - Connect with Workbench to
localhostwithtropaadetas the password¨ - Import the base databases
classicmodels.sql&stackflow.sqlin workbench. (Left panel -> Data Import/Reuse -> Import from Self-Container File -> Start Import) - Paste in the queries
- WHEN YOU ARE DONE: Stop & Remove the Docker container ``docker stop my_mysql`
We were unable to import the StackExchange files into our Docker Container. We resorted to running it outside a container, running the command in the stackexchange.sql file after having downloaded the xml files onto our droplet, or you can import them directly through our dump called stackdump.sql
The files were extracted onto root/home/[FILES HERE]
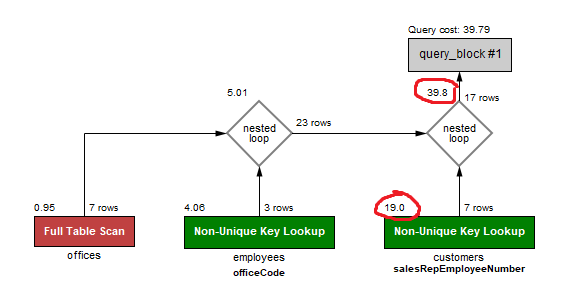
In the classicmodels database, write a query that picks out those customers who are in the same city as office of their sales representative.
SELECT customers.* FROM customers
INNER JOIN employees ON employees.employeeNumber = customers.salesRepEmployeeNumber
INNER JOIN offices ON offices.officeCode = employees.officeCode
WHERE customers.city = offices.city
We see the biggest prefix cost at the Non-Unique Key Lookup for customers salesRepEmployeeNumber
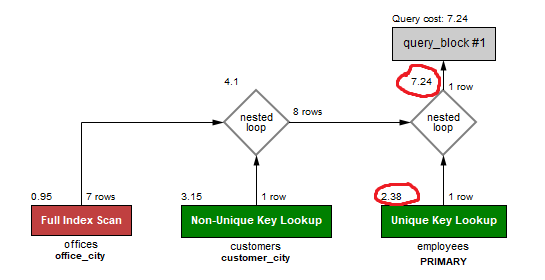
Create index office_city ON offices (city);
Create index customer_city ON customers (city);
We add indexes for office_city on the office table & customer_city on the customer table. That way we can circumvent the salesRepEMployeeNumber lookup, and just use the unique indexes the cities give us instead, as well as the employees primary key.
We want to find out how much each office has sold and the max single payment for each office. Write two queries which give this information
- using grouping
SELECT offices.officeCode, sum(payments.amount) as paymentPrice, max(payments.amount) as maxSingle FROM payments
INNER JOIN customers ON payments.customerNumber = customers.customerNumber
INNER JOIN employees ON customers.salesRepEmployeeNumber = employees.employeeNumber
INNER JOIN offices ON employees.officeCode = offices.officeCode
GROUP BY offices.officeCode
ORDER BY paymentPrice DESC;
In the stackexchange forum for coffee (coffee.stackexchange.com), write a query which return the displayName and title of all posts which with the word groundsin the title.
SELECT DisplayName, Title FROM posts INNER JOIN users ON posts.OwnerUserId = users.Id where Title LIKE '%grounds%'
Add a full text index to the posts table and change the query from exercise 4 so it no longer scans the entire posts table.
In order to create the index use the following script:
ALTER TABLE posts
ADD FULLTEXT(Title)
And then run:
SELECT DisplayName, Title FROM posts INNER JOIN users ON posts.OwnerUserId = users.Id WHERE MATCH(Title) AGAINST ('grounds' IN natural language mode)