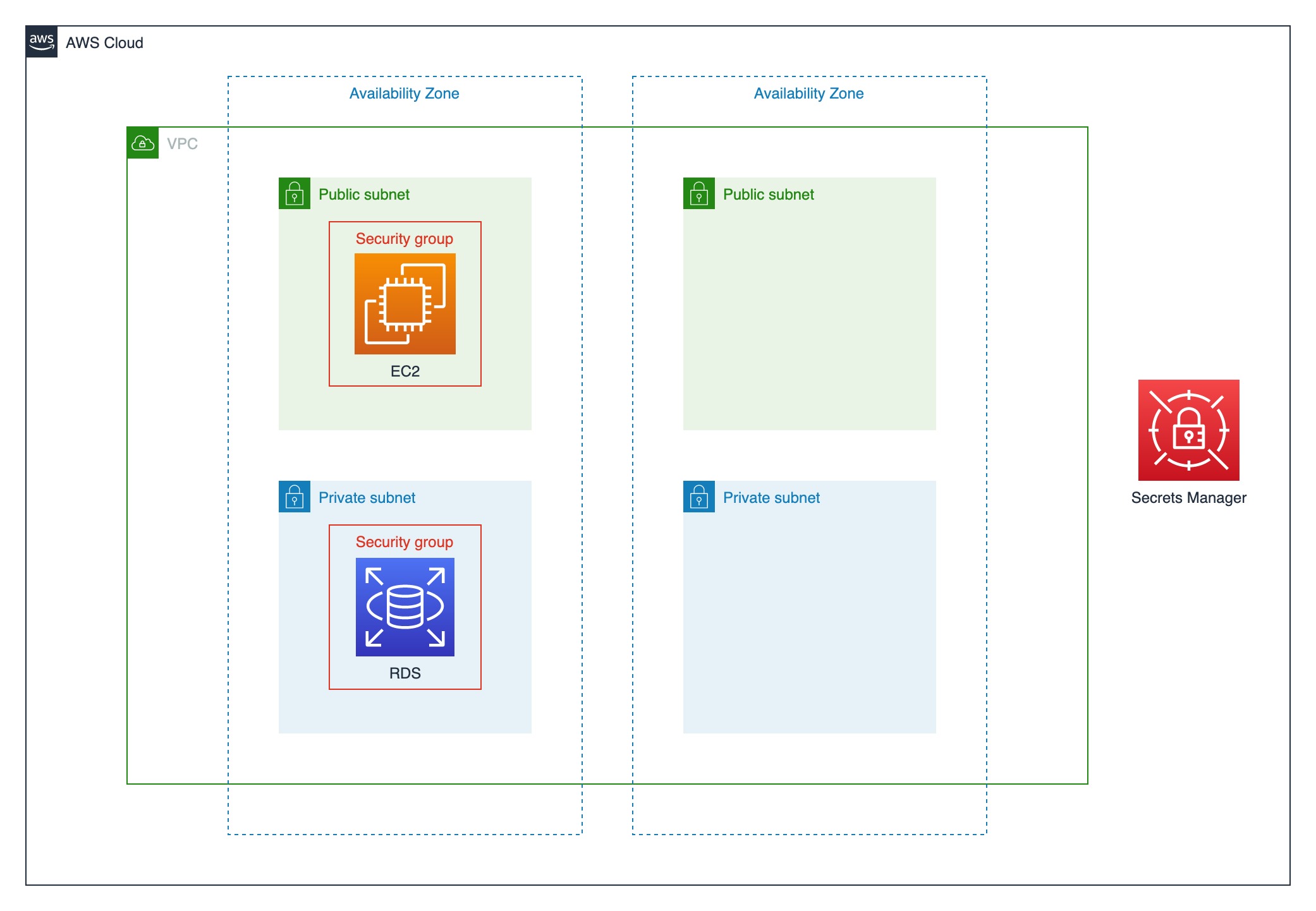
This is a simple Lab environment for quickly building a Database and its peripheral infrastructures.
- IAM Stack (
cdk-<prefix>-iam-stack)- A secret contains the necessary information to login database, including database identifier, username and password
- A role called
EC2SSMInstanceProfilewith some policiesAmazonSSMManagedInstanceCoremanaged policy to connect to the EC2 instance used as development environmentReadDBSecretPolicycustom policy to read the secretDescribeDBInstancesPolicycustom policy to list the database's name
- VPC Stack (
cdk-<prefix>-vpc-stack)- A brand new VPC with 2 Availability Zones to create subnets
- 2 public subnets in each AZ
- 2 private subnets in each AZ
- A security group for EC2 instances
- A security group for RDS database instances, allow inbound connection to connect database from the instance with EC2's security group
- EC2 Stack (
cdk-<prefix>-ec2-stack)- A
t3.microfree instance with- A
EC2SSMInstanceProfilerole attached - Pre-installed database command line client
- 2 scripts to help users manipulate the database:
/srv/install_example_database.sh: Load the example database into RDS database instance/srv/login_database.sh: Login to the database
- A
- A
- RDS Stack (
cdk-<prefix>-rds-stack)- A RDS for MySQL/MariaDB/PostgreSQL database instance in private subnets
Either provide a .env file or set the environment variables before deploy the stacks. The easy way is copying the .env.example file to .env and replace the variables, including:
REGION: The default region to create the resources (e.g.us-east-2)STACKNAME_PREFIX: The prefix string of each stackDB_ENGINE: Choose one fromMySQL,MariaDBorPostgreSQLDB_IDENTIFIER: Database identifierDB_USERNAME: Database's default usernameDB_PASSWORD: Database's default password. Please make sure the password meets the complexity requirement of the database engine
Here is a sample .env file:
REGION=us-east-2
STACKNAME_PREFIX=mylab
DB_ENGINE=MySQL
DB_IDENTIFIER=database
DB_USERNAME=username
DB_PASSWORD=password
- Set environment variables
- Deploy all stacks at once by executing
cdk deploy --allcommand - Login to AWS console, enter EC2 service, check the instance we just created and click "Connect" button, navigate to "Session Manager" tab and click "Connect" button
- Execute
/srv/install_example_database.shto load the example database into RDS database instance - Execute
/srv/login_database.shto login to the database with the command line client
Deploy stacks:
cdk deploy <stack name> # Deploy specitic stack
cdk deploy cdk-iam # e.g: Deploy the IAM stack if no STACKNAME_PREFIX specified
cdk deploy cdk-mylab-iam # e.g: Deploy the IAM stack if the STACKNAME_PREFIX is assigned as "mylab"
cdk deploy --all # Deploy all stacks
cdk deploy --all --require-approval=never # Deploy all stacks without asking yes or noDestroy stacks:
cdk destroy <stack name> # Destroy specitic stack
cdk destroy cdk-iam # e.g: Destroy the IAM stack if no STACKNAME_PREFIX specified
cdk destroy cdk-mylab-iam # e.g: Destroy the IAM stack if the STACKNAME_PREFIX is assigned as "mylab"
cdk destroy --all # Destroy all stacksAll available stacks:
cdk-<STACKNAME_PREFIX>-iamcdk-<STACKNAME_PREFIX>-ec2cdk-<STACKNAME_PREFIX>-vpccdk-<STACKNAME_PREFIX>-rds