Self-Driving Car Engineer Nanodegree Program
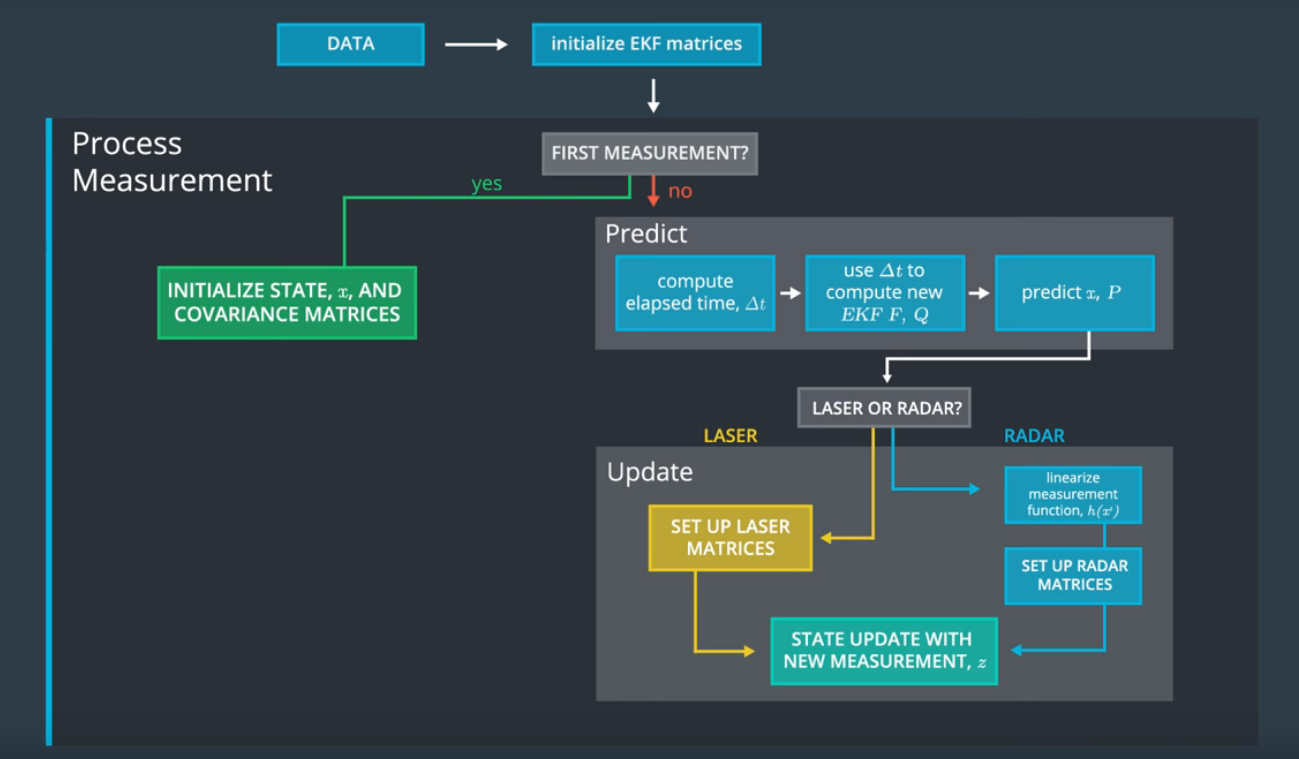
This project implements an Extended Kalman Filter in C++ which uses inputs from LIDAR and RADAR for object tracking. The algorithm represents a sensor fusion system that combines the inputs from both LIDAR and RADAR in order to achieve maximum precision in object tracking. The algorithm utilizes the strengths of both sensors and by combining them disregards their weaknesses. The LIDAR data can provide a good estimation of where the object position is, but not its velocity. While the RADAR data provides the object velocity and not its position. The combination of the two is used in the Kalman Filter algorithm to achieve tracking the object position and velocity. For this certain compatibility steps needed to be implemented in the code, since the two types of sensors interpret the world differently. RADAR measurements are in the polar coordinate system, while the LIDAR are in the cartesian. In the code the conversion from polar to cartesian for RADAR data is applied.
The Kalman Filter Algorithm is a 2 step algorithm: Predict and Update. When a new measurement arrives, assuming it is not the first measurement, the algorithm makes a prediction of objects position and velocity based on the previous measurements. After the prediction step the algorithm compares the predicted location and the new sensor measurement location. The Kalman filter will put more weight on either the predicted location or the measured location depending on the uncertainty of each value.
This project dependency is uWebSocketIO.
The main program can be built and run by doing the following from the project top directory.
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ..
- make
The make file builds two binaries ExtendedKF which is a binary that uses uWebSocketIO library and requires simulator to be running. The second one is the InputFromFIleExtendedKF which uses data from the input file ./data/obj_pose-laser-radar-synthetic-input.txt and does not require you to install the uWebSocketIO library and does not require the use of the simulator. The main function for that binary is the src/input_from_file_main.cpp file.
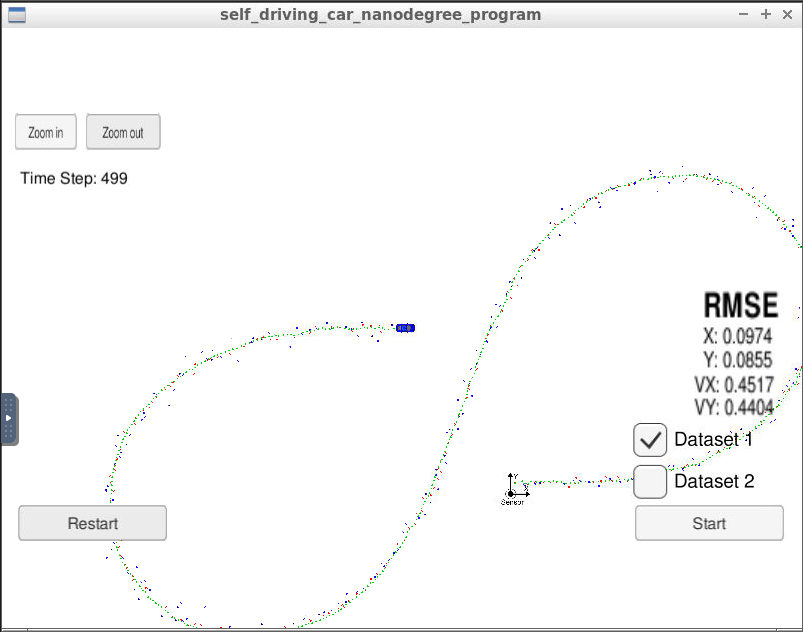
The measurements in the ./data/obj_pose-laser-radar-synthetic-input.txt file are the same as the simulator used for this project. Based on this input data and by running the project in the simulator the code produced the following output:
The metric used for evaluating the algorithm performance is the RMSE metric. Based on all the measurements and predictions collected by running the algorithm on the input data the following values where calculated:
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| px | 0.0974 |
| py | 0.0855 |
| vx | 0.4517 |
| vy | 0.4404 |
Upon first running the algorithm the accuracy was slightly below than the required accuracy in the project rubric. So in order to increase the accuracy several techniques were applied. First was changing the float variables to doubles, since double gives a higher precision. The second was the normalization of the values in the y vector in the UpdateEKF step. With these adjustments the resulting accuracy was achieved.