We will be using 3rd party action https://github.com/peaceiris/actions-gh-pages
You need to do once:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "$(git config user.email)" -f gh-pages -N ""
# You will get 2 files:
# gh-pages.pub (public key)
# gh-pages (private key)
Next, Go to Repository Settings
Go to Deploy Keys and add your public key with the Allow write access Go to Secrets and add your private key as ACTIONS_DEPLOY_KEY
Now you can add fragment to your github workflow pipeline
- name: Deploy
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3.6.1
with:
publish_dir: ./site
deploy_key: ${{ secrets.ACTIONS_DEPLOY_KEY }}
publish_branch: gh-pages
Please find idea for automatic gitlab pages publishing on a pipeline below
image: python:3.9-buster
# CD/CI example for gitlab
# TODO: Introduce image with pre-built tools for easy run
before_script:
- pip install -r requirements.txt
- DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt update
- DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get -yq install plantuml graphviz
test:
stage: test
script:
- mkdocs build --verbose --site-dir test
artifacts:
paths:
- test
except:
- master
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- mkdocs build
artifacts:
paths:
- public
expire_in: 1 week
only:
- masterSo far, best working automated tool is https://github.com/kovetskiy/mark, although it is not ideal
MkDocs plugin that adds a {{ read_csv('table.csv') }} markdown tag to directly insert CSV files in a page.
This helps to enable building reproducible reports. For more complex use cases, consider pheasant or nbconvert.
Install the plugin using pip3:
pip3 install mkdocs-table-reader-pluginNext, add the following lines to your mkdocs.yml:
plugins:
- search
- table-readerIf you have no
pluginsentry in your config file yet, you'll likely also want to add thesearchplugin. MkDocs enables it by default if there is nopluginsentry set.
In your markdown documents you can now use:
{{ read_csv('path_to_table.csv') }}Where the path is relative to the location of your project's mkdocs.yml file.
Under the hood this is basically:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('path_to_table.csv')
df.to_markdown(showindex=False)Which means you can pass all parameters of pandas.read_csv().
The table reader functions implemented from pandas:
{{ read_csv() }}passed to pandas.read_csv().{{ read_table() }}passed to pandas.read_table()`.{{ read_fwf() }}passed to pandas.read_fwf().{{ read_excel() }}passed to pandas.read_excel().
https://github.com/fralau/mkdocs_macros_plugin
pip install mkdocs-macros-plugin
plugins:
- search
- macros
mkdocs-macros-plugin is a plugin that makes it easier for contributors of an MkDocs website to produce richer and more beautiful pages. It transforms the markdown pages into jinja2 templates that use variables, calls to macros and custom filters.
Regular variables can be defined in four ways:
- global (for designers of the website): in the
mkdocs.ymlfile, under theextraheading - global(for contributors): in external yaml definition files
- global (for programmers): in a
main.pyfile (Python), by adding them to a dictionary - local (for contributors): in the markdown file, with a
{%set variable = value %}statement
Similarly programmers can define macros and filters,
as Python functions in the main.py file, which the users will then be able to
use without much difficulty, as jinja2 directives in the markdown page.
You can leverage the power of Python in markdown thanks to jinja2 by writing this :
The unit price of product A is {{ unit_price }} EUR.
Taking the standard discount into account,
the sale price of 50 units is {{ price(unit_price, 50) }} EUR.If you defined a price() function, this could translate into:
The unit price of product A is 10.00 EUR.
Taking the standard discount into account,
the sale price of 50 units is 450.00 EUR.
The result of a macro can be HTML code: this makes macros especially useful to make custom extensions to the syntax of markdown, such as buttons, calls to email, embedding YouTube videos, etc.
It is possible to use the wide range of facilities provided by Jinja2 templates.
https://github.com/greenape/mknotebooks
mknotebooks is a plugin for MkDocs, which makes it more convenient to include Jupyter notebooks in your project documentation.
pip install mknotebooks
Simply include any notebooks you want to use in the docs source directory, and add mknotebooks to the plugin section of your mkdocs.yml as follows:
plugins:
- mknotebooks
You can optionally execute the notebooks, by setting execute: true in the config, and include a hidden preamble script, to be run before executing any cells using preamble: "<path/to/your/script>". The default cell execution timeout can be overridden by setting timeout: <timeout>, where <timeout> is an integer number of seconds.
By default, execution will be aborted if any of the cells throws an error, but you can set allow_errors: true to continue execution and include the error message in the cell output.
Any static images, plots, etc. will be extracted from the notebook and placed alongside the output HTML.
Mknotebooks applies default styling to improve the appearance of notebook input/output cells and pandas dataframes. If these interfere with any other CSS stylesheets that you're using, you can disable these via the following options.
- mknotebooks:
enable_default_jupyter_cell_styling: false
enable_default_pandas_dataframe_styling: false
In order to enable syntax highlighting for code blocks, pygments has to be installed and codehilite extension has to be enabled in mkdocs.yml.
- Install pygments:
pip install Pygments
- Enable
codehiliteextension inmkdocs.yml:
markdown_extensions:
- codehilite
https://github.com/midnightprioriem/mkdocs-autolinks-plugin
An MkDocs plugin that simplifies relative linking between documents.
The Autolinks plugins allows you to link to pages and images within your MkDocs site without provided the entire relative path to the file in your document structure.
Install the plugin using pip:
pip install mkdocs-autolinks-plugin
Activate the plugin in mkdocs.yml:
plugins:
- search
- autolinks Note: If you have no
pluginsentry in your config file yet, you'll likely also want to add thesearchplugin. MkDocs enables it by default if there is nopluginsentry set, but now you have to enable it explicitly.
More information about plugins in the [MkDocs documentation][mkdocs-plugins].
To use this plugin, simply create a link that only contains the filename of file you wish to link to.
For example, say you have a document structure like this:
docs/
├── guides/
│ ├── onboarding.md
│ └── syntax_guide.md
├── software/
│ ├── git_flow.md
│ └── code_reviews.md
└── images/
├── avatar.png
└── example.jpg
Normally, if you want create a link to git_flow.md from inside onboarding.md, you would need to provide the relative path:
# onboarding.md
[Git Flow](../software/git_flow.md)This link is fragile; if someone decides to rearrange the site structure, all of these relative links break. Not to mention having to figure out the relative path.
With the Autolinks plugin, you simply need to provide the filename you wish to link to. The plugin will pre-process all of your markdown files and replace the filename with the correct relative path, given that the file exists in your document structure:
# onboarding.md
[Git Flow](git_flow.md)The Autolinks plugin also works with jpg and png files:
# onboarding.md
Plugin for mkdocs to create page redirects (e.g. for moved/renamed pages).
Note: This package requires MkDocs version 1.0.4 or higher.
Install with pip:
pip install mkdocs-redirectsTo use this plugin, specify your desired redirects in the plugin's redirect_maps setting in your mkdocs.yml:
plugins:
- redirects:
redirect_maps:
'old.md': 'new.md'
'old/file.md': 'new/file.md'
'some_file.md': 'http://external.url.com/foobar'Note: don't forget that specifying the plugins setting will override the defaults if you didn't already have it set! See this page for more information.
The redirects map should take the form of a key/value pair:
- The key of each redirect is the original markdown doc (relative to the
docs_dirpath).- This plugin will handle the filename resolution during the
mkdocs buildprocess. This should be set to what the original markdown doc's filename was (or what it would be if it existed), not the final HTML file rendered by MkDocs
- This plugin will handle the filename resolution during the
- The value is the redirect target. This can take the following forms:
- Path of the markdown doc you wish to be redirected to (relative to
docs_dir)- This plugin will handle the filename resolution during the
mkdocs buildprocess. This should be set to what the markdown doc's filename is, not the final HTML file rendered by MkDocs
- This plugin will handle the filename resolution during the
- External URL (e.g.
http://example.com)
- Path of the markdown doc you wish to be redirected to (relative to
During the mkdocs build process, this plugin will create .html files in site_dir for each of the "old" file that redirects to the "new" path.
It will produce a warning if any problems are encountered or of the redirect target doesn't actually exist (useful if you have strict: true set).
If you have use_directory_urls: true set (which is the default), this plugin will modify the redirect targets to the directory URL, not the actual index.html filename.
However, it will create the index.html file for each target in the correct place so URL resolution works.
For example, a redirect map of 'old/dir/README.md': 'new/dir/README.md' will result in an HTML file created at $site_dir/old/dir/index.html which redirects to `/new/dir/.
Additionally, a redirect map of 'old/dir/doc_name.md': 'new/dir/doc_name.md' will result in $site_dir/old/dir/doc_name/index.html redirecting to /new/dir/doc_name/
This mimcs the behavior of how MkDocs builds the site dir without this plugin.
This plugin allows you to host a tiny blog section in your MkDocs site. Move away, WordPress... well, not really.
It's quite simple. 90% of the work is already done by MkDocs itself. Each time you will build your MkDocs site or serve it, this plugin will try to find a specific directory in your documentation folder. If it finds it, every document and every subdirectory nested in it will be listed in reverse on the navbar. Plus, if you will have too many documents to be listed at once, the plugin will try to organize your remaining documents in subfolders.
You can install it through pip with this command:
pip install mkdocs-blog-plugin
Then, open your mkdocs.yml configuration file and add these lines:
plugins:
- blog
Last but not least, enter you docs folder and create a new subfolder and name it blog. This plugin will try to find blog articles inside this directory. Then you are ready to begin.
Inside docs/blog create a folder for each year you are planning to add new articles. Then, inside each year folder create twelve folders, numbered from 01 to 12 for each month. Finally, in each month folder for each day create a corresponding folder but remember to add a leading zero (for example: 08, 09, 10, ...) Now, for every article you will go inside the corresponding `year/month/day folder and you will create a new file there. While it is not necessary that you keep this strict naming convention, this will help the plugin to understand when your article was made.
For example, this is how I manage my blog folder:
docs
├── blog
│ ├── 2019
│ └── 2020
│ ├── 01
│ │ ├── 20
│ │ │ └── first-article.md
│ │ └── 26
│ │ └── second-article.md
│ ├── 02
│ │ ├── 01
│ │ │ └── third_article.md
│ │ └── 09
│ │ └── fourth-article.md
│ └── 03
│ └── 16
│ └── fifth-article.md
└── index.md
You can customize this plugin by adding some parameters in the mkdocs.yml file, like this:
- plugin:
- blog:
format: "(%m/%d/%y)"
text-align: "right"
Here is a brief list of every parameters supported by the current version of the plugin:
-
folder This is the section / folder in which we'll try to build our blog Default value: "blog"
-
articles How many articles do we have to display on our blog at once? More articles will be displayed in the corresponding subsection Default value: 6 articles
-
more-articles Let's allow our user to slightly customize the "previous articles" section. How do we have to name this section if it will contains more articles? Remember to put a percentage character wherever you want this plugin to insert the number of available articles. Default value: "More articles (%)"
-
pagination Which name do we have to give to each subsection inside our "more articles" section? Remember to put two percentage characters wherever you want this plugin to insert the actual number page and the total amount of pages made. Default value: Page % of %"
-
display-more-articles Can we display the previous articles section, or is it better if we hide it? Default: True
-
display-article-date Can we display the article date in the navbar, or is it better if we hide it? Default: True
-
format How we have to display an article publication date on our navbar? You can use these placeholders inside your string:
%d = Day
%m = Month
%y = Year (2-digits)
%Y = Year (4-digits)
Default value: "[%d/%m]"
- text-align Do we have to display an article publication date on the left side ("left") or on the right side ("right")? Default value: "left"
https://github.com/spotify/mkdocs-monorepo-plugin https://github.com/byrnereese/mkdocs-git-committers-plugin
Plugin docs https://github.com/aklajnert/mkdocs-simple-hooks
Let's say you want to copy the README.md file to docs/index.md. To do that, create a new file, e.g.: docs/hooks.py, and put the following function there:
import shutil
def copy_readme(*args, **kwargs):
shutil.copy("README.md", "docs/index.md")Now, register the hook in your mkdocs.yml:
plugins:
- mkdocs-simple-hooks:
hooks:
- on_pre_build: "docs.hooks:copy_readme"Idea for list of hooks can be obtained on https://www.mkdocs.org/user-guide/plugins/#events and ideas what you could generally intercept on which level can be obtained from https://github.com/mkdocs/mkdocs/wiki/Event-Based-Plugin-API
| event | vars | Possible usage |
|---|---|---|
| post-config | config | Alter config or prepossessing based on config values |
| pre-nav | config, nav-item | Alter/intercept a nav item's creation |
| post-nav | config, nav-item, global nav (so far) | Alter a just created nav item |
| pre-build | config, global template vars, global nav | Alter global nav, template vars, etc. |
| pre-page | config, template, context | Alter single page and/or template |
| post-page | config, rendered template | Page specific post-processing |
| post-build | config | project wide postprocessing |
| deploy | config | provide a deploy script (only fired from deploy command) |
| pre-serve | config, server_instance | add addition files/dirs to watcher (only fired from serve command) |
The first step is to initialize ADRs for our project
adr init doc/architecture/decisions
docs/architecture/decisions/0001-record-architecture-decisions.mdAfterwards, our project directory structure looks similar to this one:
├── docs
│ └── architecture
│ └── decisions
│ └── 0001-record-architecture-decisions.md
As we can see, a first decision already has been added to the project: It’s the decision to record our architecture decisions.
When opening the ADR file we’re able to read the following Markdown file:
# 1. Record architecture decisions
Date: 2020-11-03
## Status
Accepted
## Context
We need to record the architectural decisions made on this project.
## Decision
We will use Architecture Decision Records, as [described by Michael Nygard](http://thinkrelevance.com/blog/2011/11/15/documenting-architecture-decisions).
## Consequences
See Michael Nygard's article, linked above. For a lightweight ADR toolset, see Nat Pryce's [adr-tools](https://github.com/npryce/adr-tools).
Creating new Architecture Decision Records We’re ready now to create our first ADR. The command adr new allows us to create a new ADR with the given title.
./bin/adr new Use sphinx as our knowledge base systemWe’re adding another ADR:
./bin/adr new Use PlantUML for diagramming
./docs/architecture/decisions/0003-use-plantuml-for-diagramming.mdListing Architecture Decision Records We may list existing ADRs using adr list like this:
./bin/adr list
./docs/architecture/decisions/0001-record-architecture-decisions.md
./docs/architecture/decisions/0002-use-sphinx-as-our-knowledge-base-system.md
./docs/architecture/decisions/0003-use-plantuml-for-diagramming.mdSuperseding a Decision Now we will supersede a decision, for example if a new ADR supersedes our decision #2, we would type in the following command:
./bin/adr new -s 2 Use mkdocs as a knowledge base system
./docs/architecture/decisions/0004-use-mkdocs-as-a-knowledge-base-system.mdThis produces new ADR file with a reference to the superseded ADR.
Of course our old decision is changed, too including a reference to the new ADR and setting its status to “Superseded”
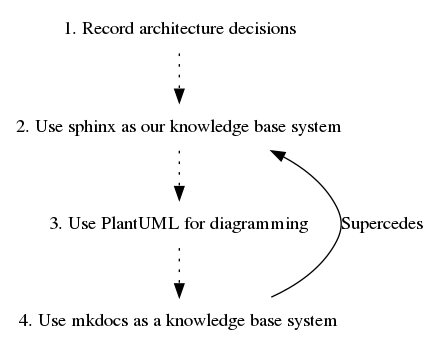
Generating Graphs To gain an overview of our ADR’s relations we may generate a graph in the DOT format using adr generate graph like this:
./bin/adr generate graph
digraph {
node [shape=plaintext];
subgraph {
_1 [label="1. Record architecture decisions"; URL="0001-record-architecture-decisions.html"];
_2 [label="2. Use sphinx as our knowledge base system"; URL="0002-use-sphinx-as-our-knowledge-base-system.html"];
_1 -> _2 [style="dotted", weight=1];
_3 [label="3. Use PlantUML for diagramming"; URL="0003-use-plantuml-for-diagramming.html"];
_2 -> _3 [style="dotted", weight=1];
_4 [label="4. Use mkdocs as a knowledge base system"; URL="0004-use-mkdocs-as-a-knowledge-base-system.html"];
_3 -> _4 [style="dotted", weight=1];
}
_4 -> _2 [label="Supercedes", weight=0]We may write this output to a file e.g.
./bin/adr generate graph > ./docs/architecture/graph.dotFrom this DOT file we may create an image e.g. using GraphViz like this:
dot -Tpng ./docs/architecture/graph.dot -o./docs/architecture/graph.pngThis is what the generated graph looks like as png-image:
Generating Table of Contents To include the ADRs in other documents we may generate a table of contents for our ADRs using adr generate toc like this:
./bin/adr generate tocThis returns the following Markdown code:
# Architecture Decision Records
* [1. Record architecture decisions](0001-record-architecture-decisions.md)
* [2. Use sphinx as our knowledge base system](0002-use-sphinx-as-our-knowledge-base-system.md)
* [3. Use PlantUML for diagramming](0003-use-plantuml-for-diagramming.md)
* [4. Use mkdocs as a knowledge base system](0004-use-mkdocs-as-a-knowledge-base-system.md)
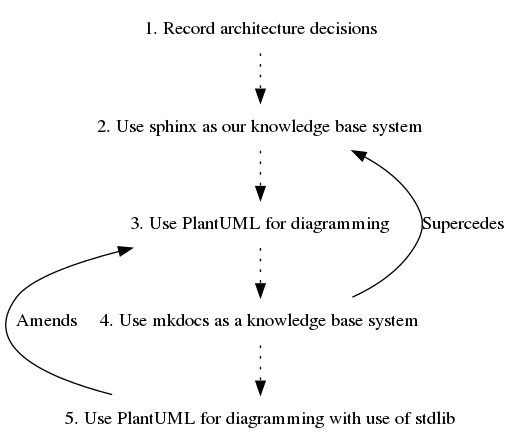
Linking Architecture Decision Records When ADRs are linked somehow we want to document this and adr link eases this for us.
Let’s use an example where ADR #5 amends ADR #3 so that we could link both with the following command:
./bin/adr link 5 Amends 3 "Amended by"Now graph will look like
./bin/adr generate graph
digraph {
node [shape=plaintext];
subgraph {
_1 [label="1. Record architecture decisions"; URL="0001-record-architecture-decisions.html"];
_2 [label="2. Use sphinx as our knowledge base system"; URL="0002-use-sphinx-as-our-knowledge-base-system.html"];
_1 -> _2 [style="dotted", weight=1];
_3 [label="3. Use PlantUML for diagramming"; URL="0003-use-plantuml-for-diagramming.html"];
_2 -> _3 [style="dotted", weight=1];
_4 [label="4. Use mkdocs as a knowledge base system"; URL="0004-use-mkdocs-as-a-knowledge-base-system.html"];
_3 -> _4 [style="dotted", weight=1];
_5 [label="5. Use PlantUML for diagramming with use of stdlib"; URL="0005-use-plantuml-for-diagramming-with-use-of-stdlib.html"];
_4 -> _5 [style="dotted", weight=1];
}
_4 -> _2 [label="Supercedes", weight=0]
_5 -> _3 [label="Amends", weight=0]
}
Or as an image:
Note, that in addition both ADR files were updated.
More to read:
- http://thinkrelevance.com/blog/2011/11/15/documenting-architecture-decisions
- https://github.com/npryce/adr-tools
- https://www.fabian-keller.de/blog/documenting-architecture-decisions
- https://adr.github.io/
- https://github.com/joelparkerhenderson/architecture_decision_record/blob/01cc3c801b1cc61f82391a0a08986e4145e21c56/README.md