pauNy
Nx curves and area-under-Nx metrics for python
This repository is based on a blog post by Heng Li discussing a better metric than N50 to assess assembly contiguity.
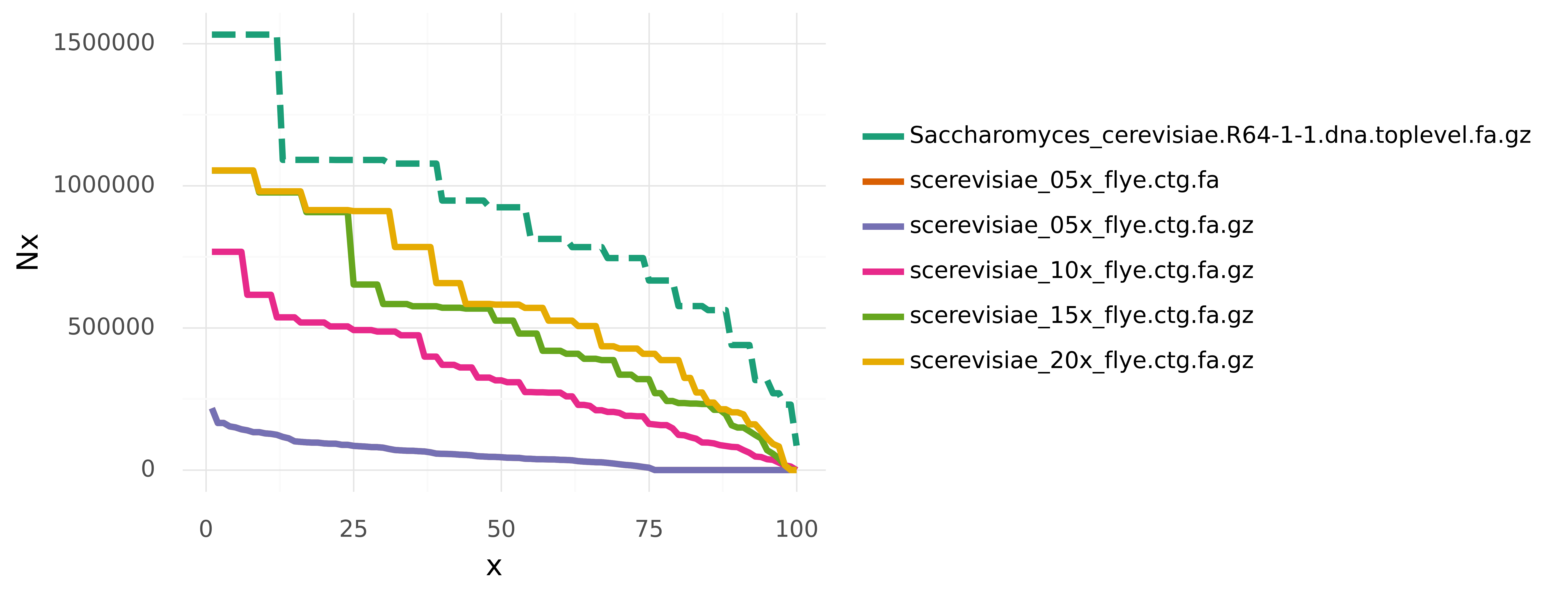
N50 is often used to quantify the contiguity of assemblies. In general, Nx describes that contigs longer than Nx cover x% of an assembly. An entire Nx curve shows Nx as a function of x, ranging from 0 to 100. N50 is only a single value on this Nx curve, which is not equivalent to a median or average contig length. And it might hide some interesting insight about the total contiguity of an assembly.
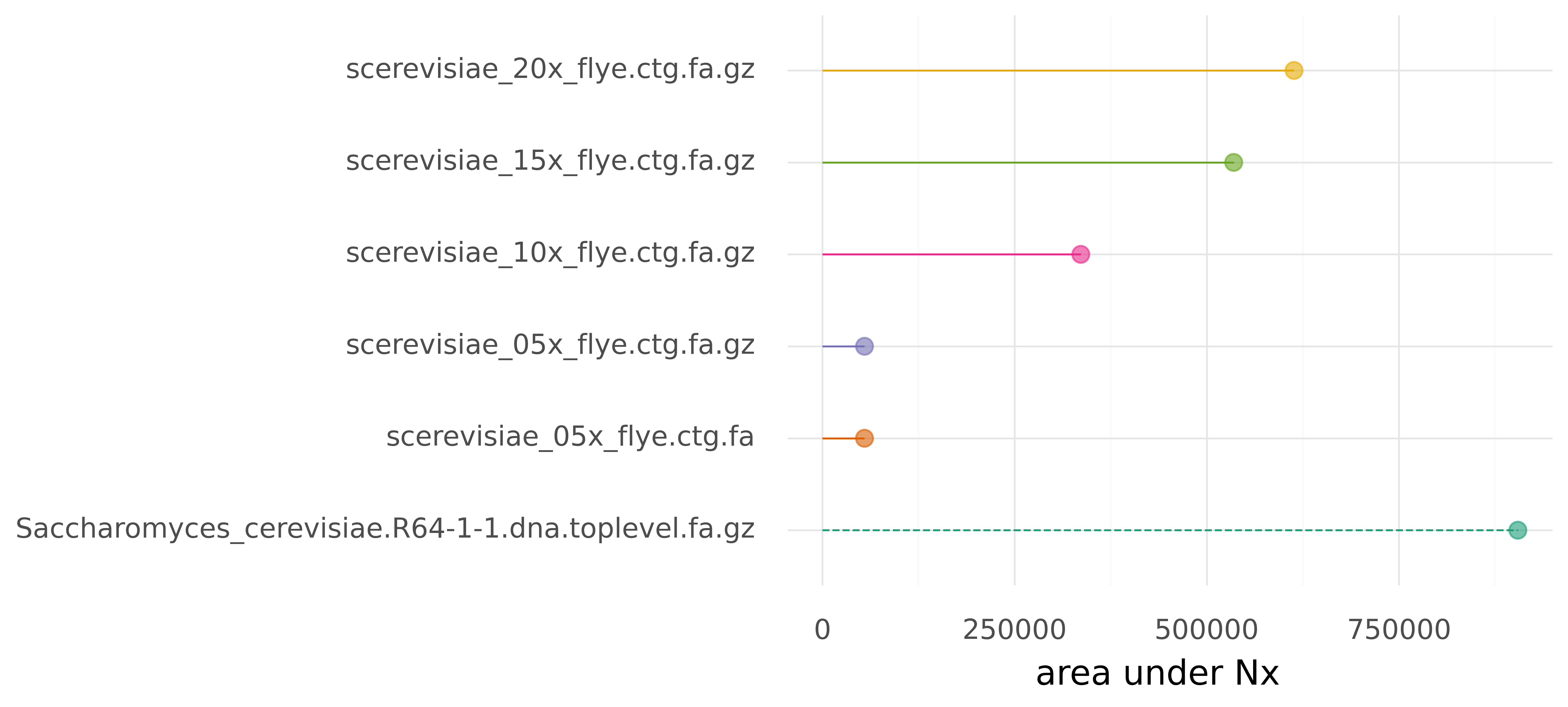
Further, area under Nx (auN) is the sum of the area under such an Nx curve. It does not suffer from the same issues that can affect N50 (see linked blog post), and would therefore be a better measure for assembly contiguity. N50 is extremely popular though, but maybe introducing a simple python module called p-auN-y can make a difference?
Installation
Clone the repository and install dependencies
git clone https://github.com/W-L/pauNy.git
cd pauNy/
python3 -m venv pauny-venv
source pauny-venv/bin/activate
pip install numpy pandas plotnineQuick usage
Required args
Execute the runscript with input -i / --input, which can be fasta/fastq files or one or more directories with fasta/fastq files in them. Files can be gzipped too.
Optional args
-o / --outcan specify a base name for output files-f / --formatspecify output filetype for visualisation, e.g. pdf or png-r / --reffor a path to a reference assembly. This triggers calculation of NGx and auNG values using the genome size. And will also mark this assembly as reference in output.-g / --genomesizealternatively to a reference file, a genome size (estimate) can be given for scaling values to NGx and auNG.
usage: pauNy [-h] -i INPUT [INPUT ...] [-o OUT] [-f FORMAT] [-r REF | -g GENOMESIZE]
Nx curves and area under Nx in python
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT [INPUT ...], --input INPUT [INPUT ...]
input fasta/fastq file(s) or director(ies) of files. Can be multiple (space-separated).
-o OUT, --out OUT base name for output files
-f FORMAT, --format FORMAT
output format for plots
-r REF, --ref REF path to reference sequence file
-g GENOMESIZE, --genomesize GENOMESIZE
genome size or estimate
Use as python module
Instead of using the runscript, this module can be imported into other scripts as import pauNy. The main functionalities are:
import pauNy
# for a single sequence file
asm = pauNy.Assembly(path, [gsize])
nx_values = asm.calculate_Nx()
auN_value = asm.calculate_auN()
# for multiple assemblies
asm_c = pauNy.AssemblyCollection(paths, [reference_path, genome_size])
asm_c.calculate_metrics()
asm_c.nx_values # metrics are available as dictionaries per input file
asm_c.nx_frame # or as pandas frames
asm_c.aun_values
asm_c.aun_frame
asm_c.plot() # generate visualisations (see example)For documentation check out the docstrings and type hints in the sources.
Example
As an example we can look at assemblies of yeast from different levels of subsampled coverage (5x, 10x, 15, 20x). These assemblies and a reference assembly are in data/.
You can reproduce the example csv-files and visualisations using:
./pauny.py -i data/ -r data/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae.R64-1-1.dna.toplevel.fa.gzRun tests
pip install coverage
coverage run -m unittest discover -s tests
coverage reportTODO
- allow other types of input: array/list of contig lengths
- the plotting breaks with plotnine >0.10.1