Binary Search is an algorithm used to optimize finding an item in a sorted set. A sequential search (iterating from the begining of a set and comparing each item) has a big O time complexity of O(n), whereas binary search has a time complexity of O(log^2n). In other words, given a sorted array of 1000 items, finding one specific item in the array by iterating from the begining will take an average of 500 itereations, with a worst case of 1000 iterations. Binary Search can complete this same task in an average of 10 iterations. That's awesome!
- fork and clone this repo
- use
search.pyto create an implementation of Binary Search
Given a target value an a sorted list of values, return the index of the target value in the list. If the value is not in the list, return
-1
- run
python3 search.pyto check you work
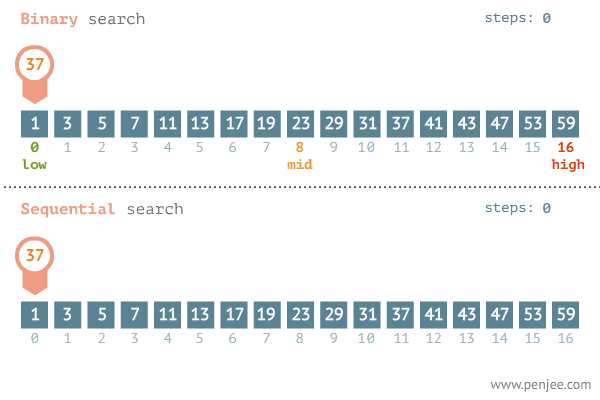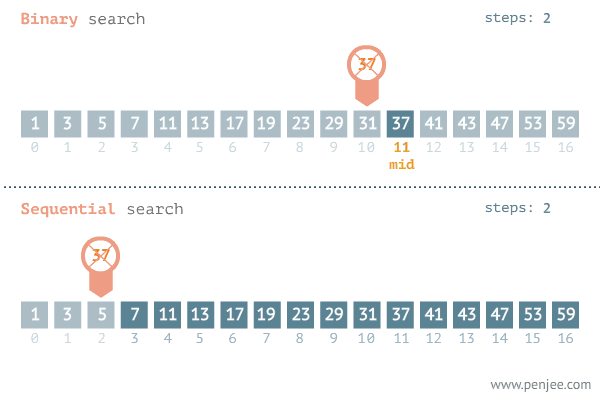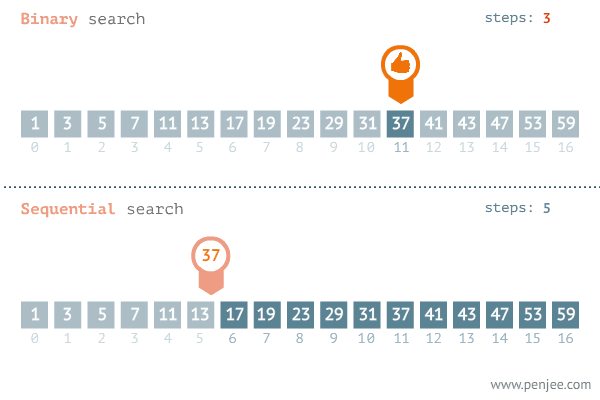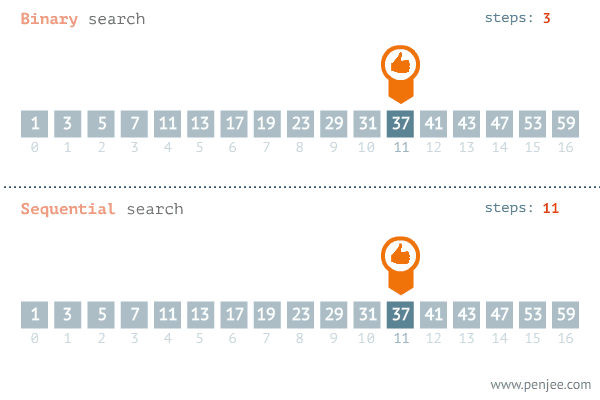
Lets say you are given the following list of numbers, and you task is to find the index of 37:
# for illustration purposes, the indexes of each elements are shown on the line below
li = [ 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59]
# idx 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16If we were to iterate through the list comparing each number to the target of 37, it would take 12 iterations to find its index. Binary Search avoids comparing every element in the list by using a range of values that the value we want to find falls inside of. To do this we need to keep track of the minimum of the range, the maximum of the range, and the middle of the range. First, we assume that the entire list is the range of possible values. Using comparisons, we narrow the range to either left or the right until we find our desired value.
Here is a visualization of the process:
When learning a new algorithm, it is best to research and understand it without immediately looking at source code. Why? It helps the learning process by working through the problem yourself. Always try the following when learning a new algorithm to understand it most effectively:
- research and understand how the algorithm works
- break the algorithm down into steps, 'rubber ducking' or talking through the algorithm aloud can be a great help
- reacreate the algorithmic steps in your physical space, for example use a deck of cards to execute each step of the alhgorithm
- write the alogorithm out using pseudocode, try rubber ducking as you do this
- implement the pseudocode code you wrote and test your code, try to think of edge cases that you need to test and account for
- if something isn't working, loop back to step 1.
Also:
- remember to take breaks, this is hard!
- its okay to sneak a peak at solution code, but put in an earnest effort to solve it on your own first.
- if possible try to find generic pseudocode first before looking up langauge specific solutions.
- Explanation: Gitbook
- Explanation: Khan Academy
- Explanation: Technopedia
- Algorithm Visualization: usfca
- Explanation with Psuedocode: Wikipedia
The Binary Search algorithm can be implemented using recursion. Try your hand at that!
- All content is licensed under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- All software code is licensed under GNU GPLv3. For commercial use or alternative licensing, please contact legal@ga.co.