- Environment setup
- Create Microservice with Quarkus
- Running PostgreSQL in Kubernetes
- Connect Quarkus service to PostgreSQL
- MicroProfile OpenAPI Specification
- MicroProfile Metrics
- View Metrics with Prometheus and Grafana
- Centralized Logging with EFK
- Securing Service with Keycloak
- Add OpenID Connect to Quarkus service
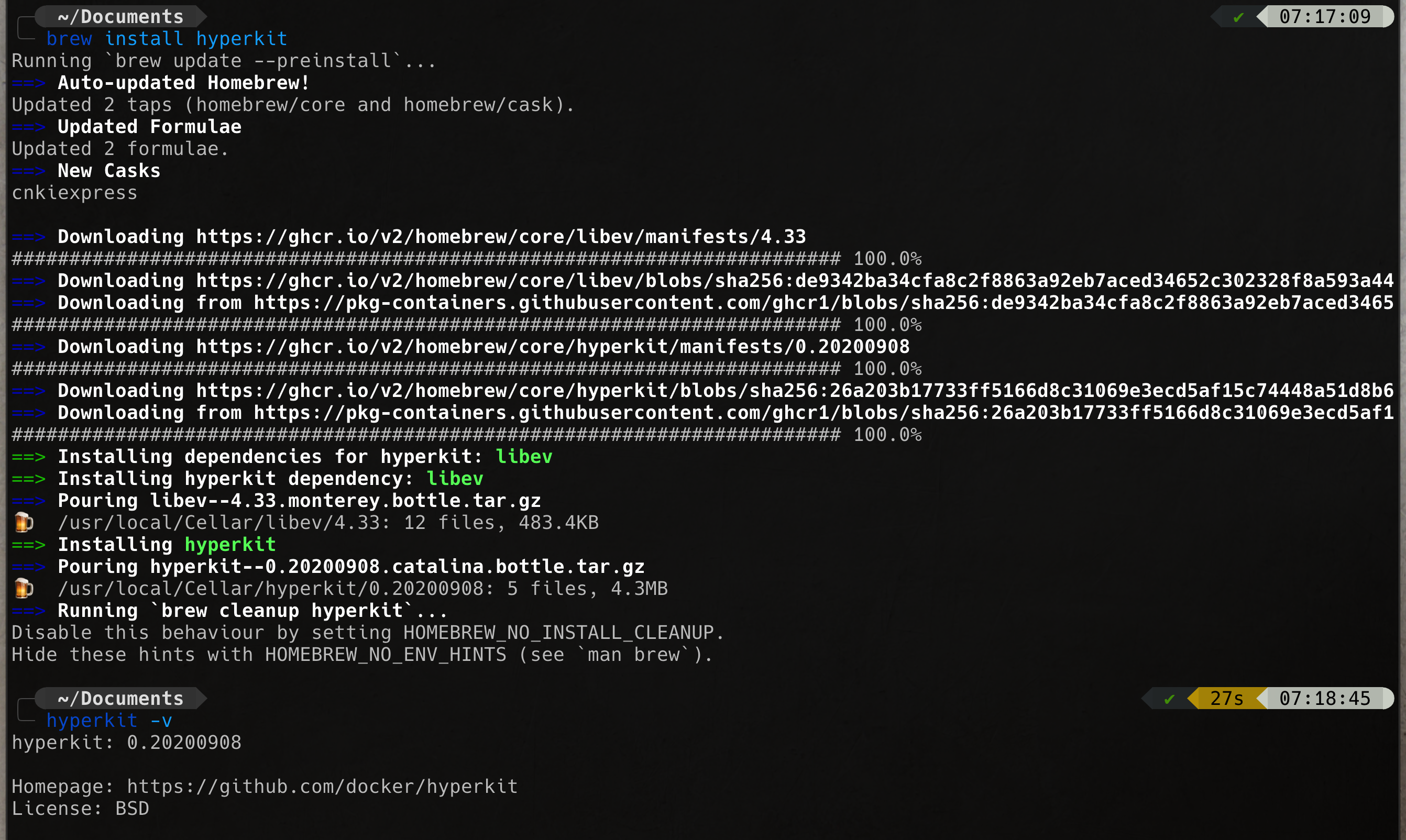
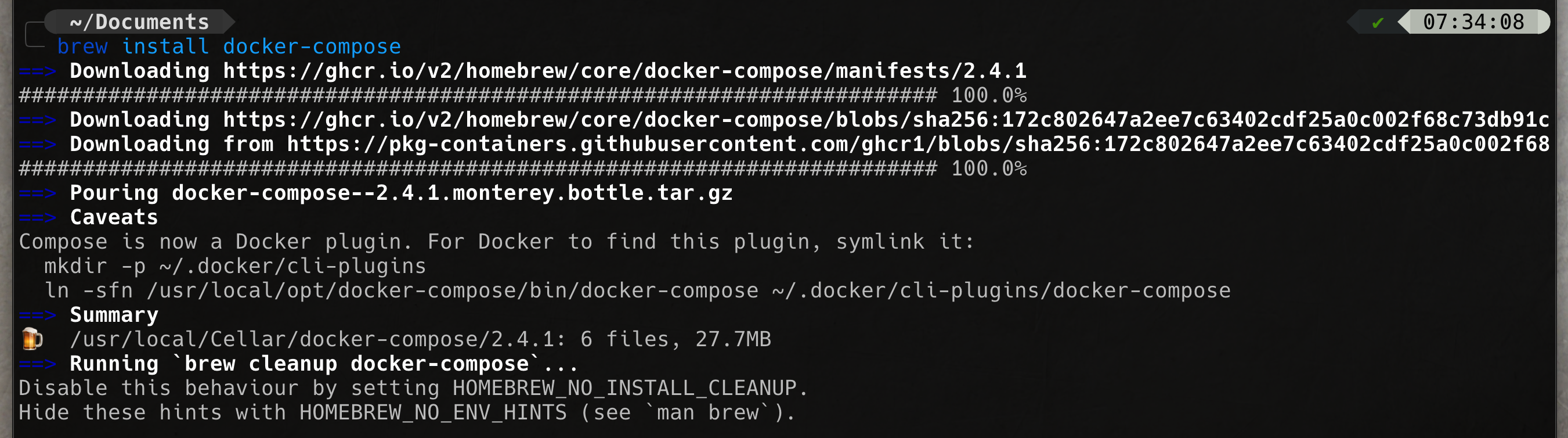
brew install hyperkitbrew install dockerNOTE: Do not run brew install --cask docker. This will install Docker Desktop and we will be back to where we started!
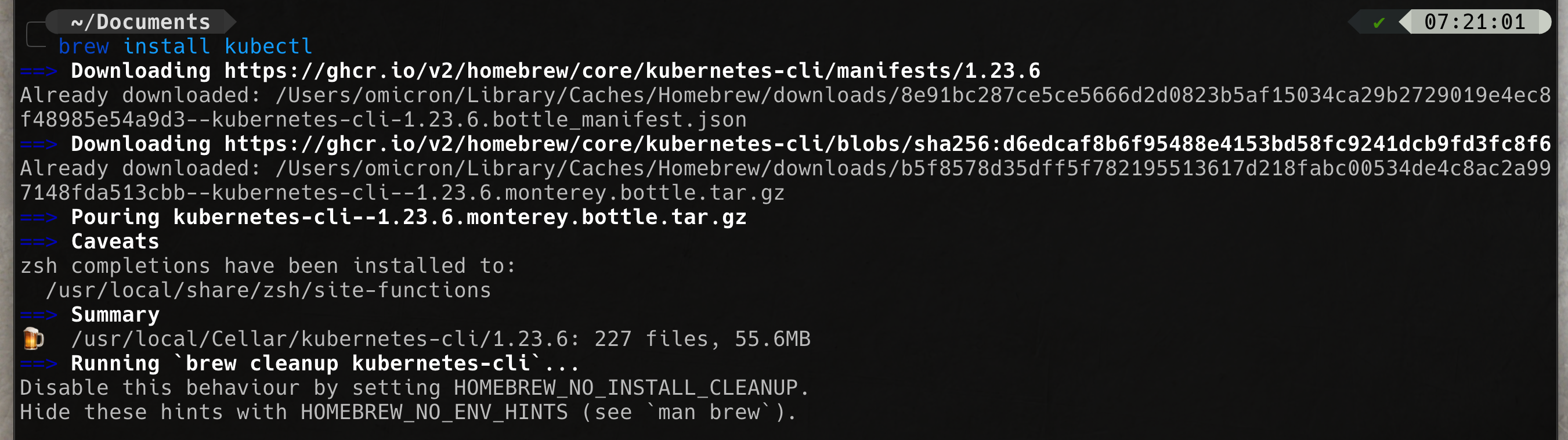
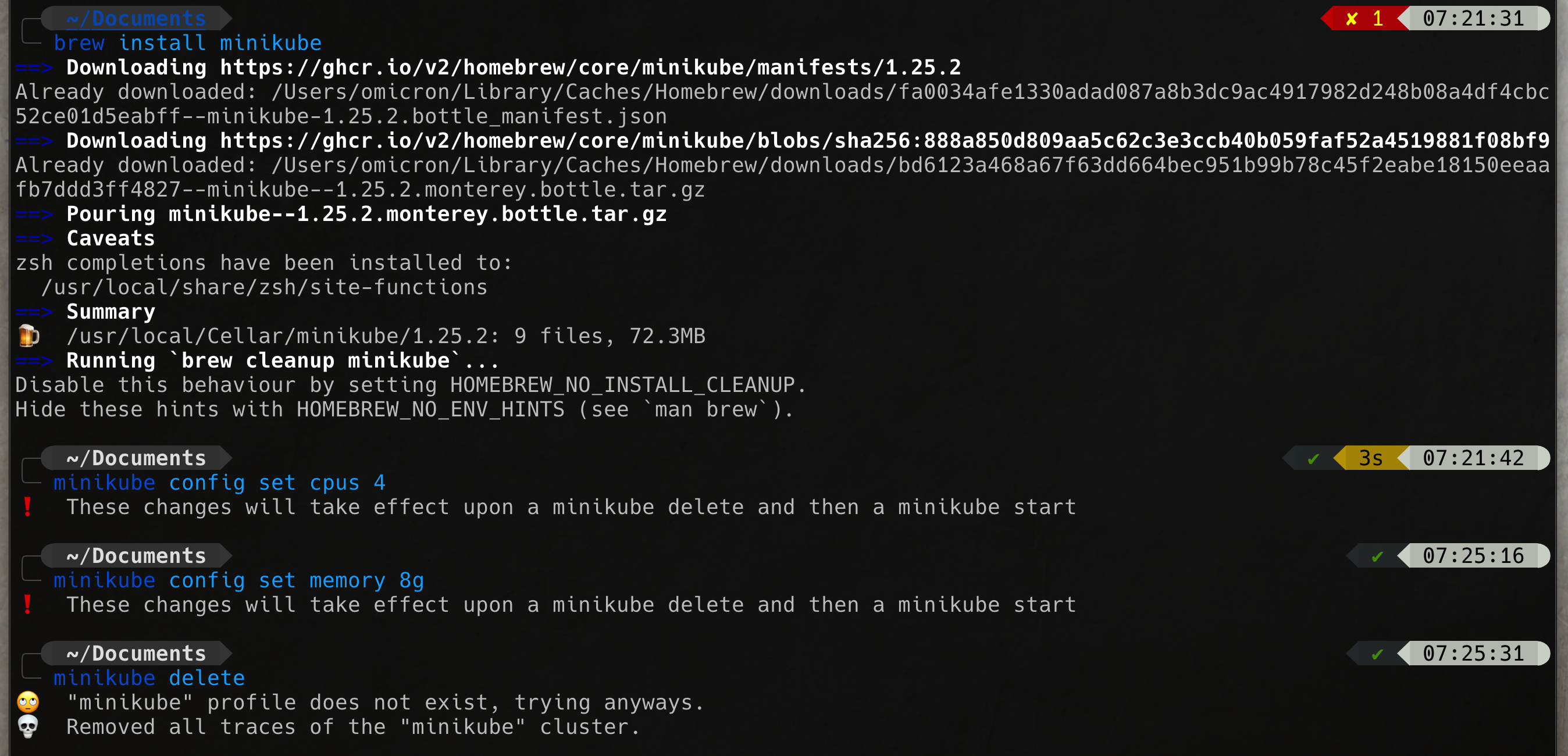
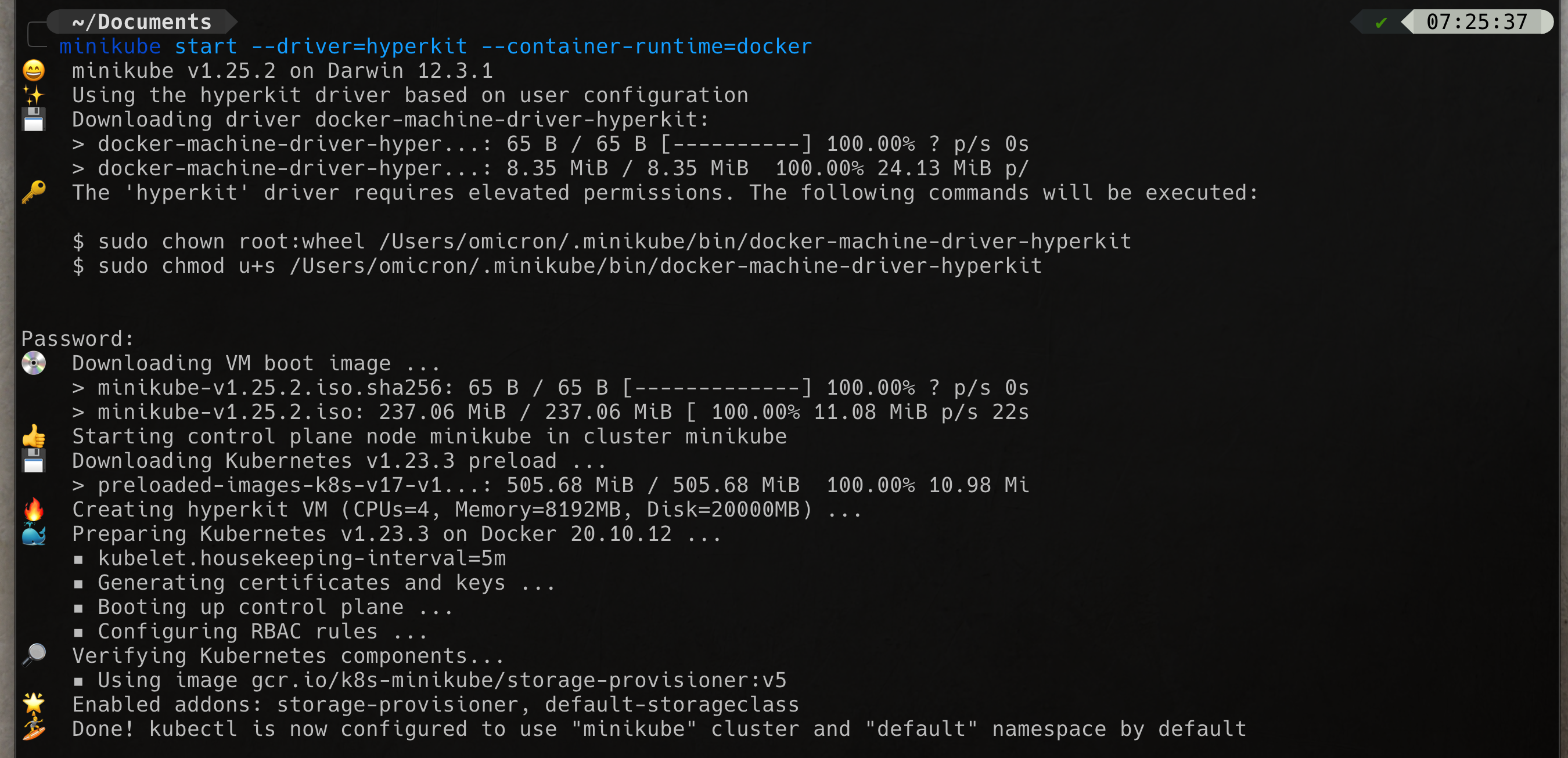
brew install kubectlbrew install minikubeminikube start --driver=hyperkit --container-runtime=dockerminikube -p minikube docker-env | sourcebrew install docker-composeminikube addons enable metrics-server
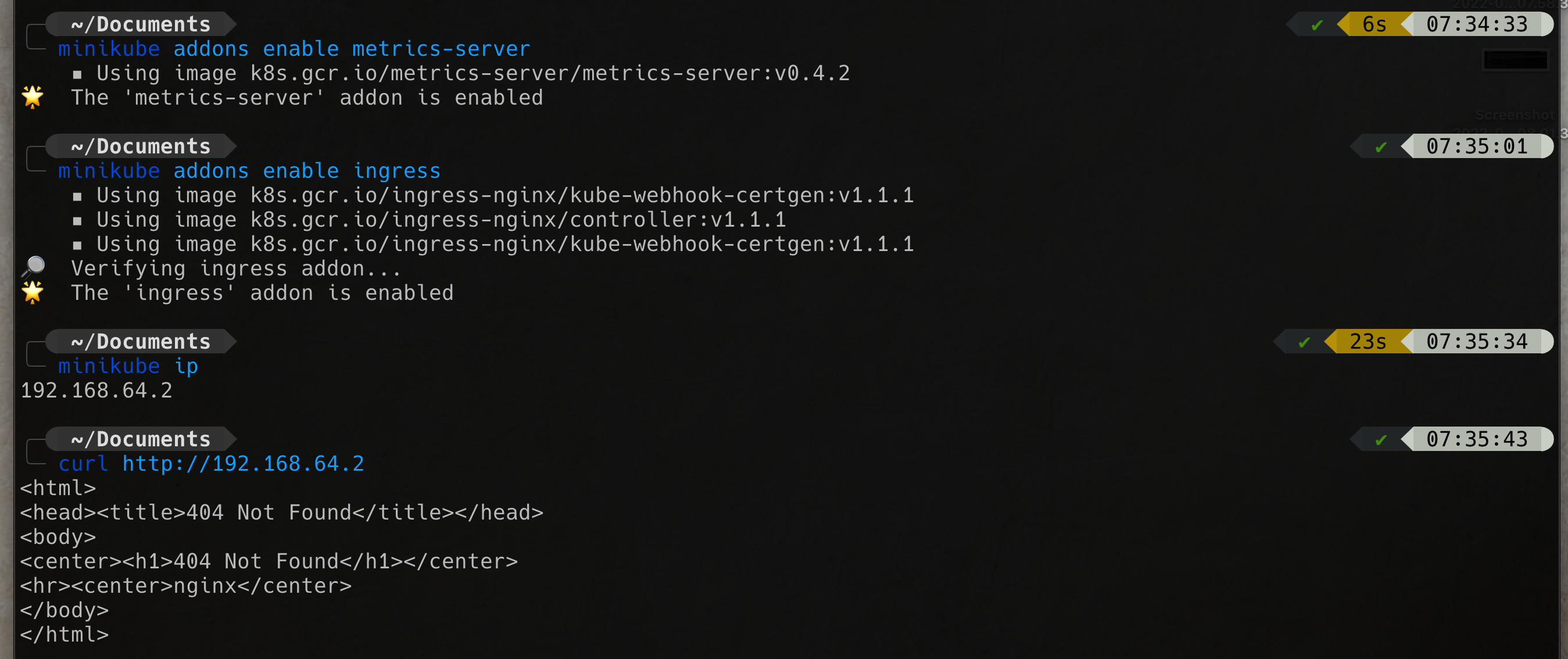
minikube addons enable ingress
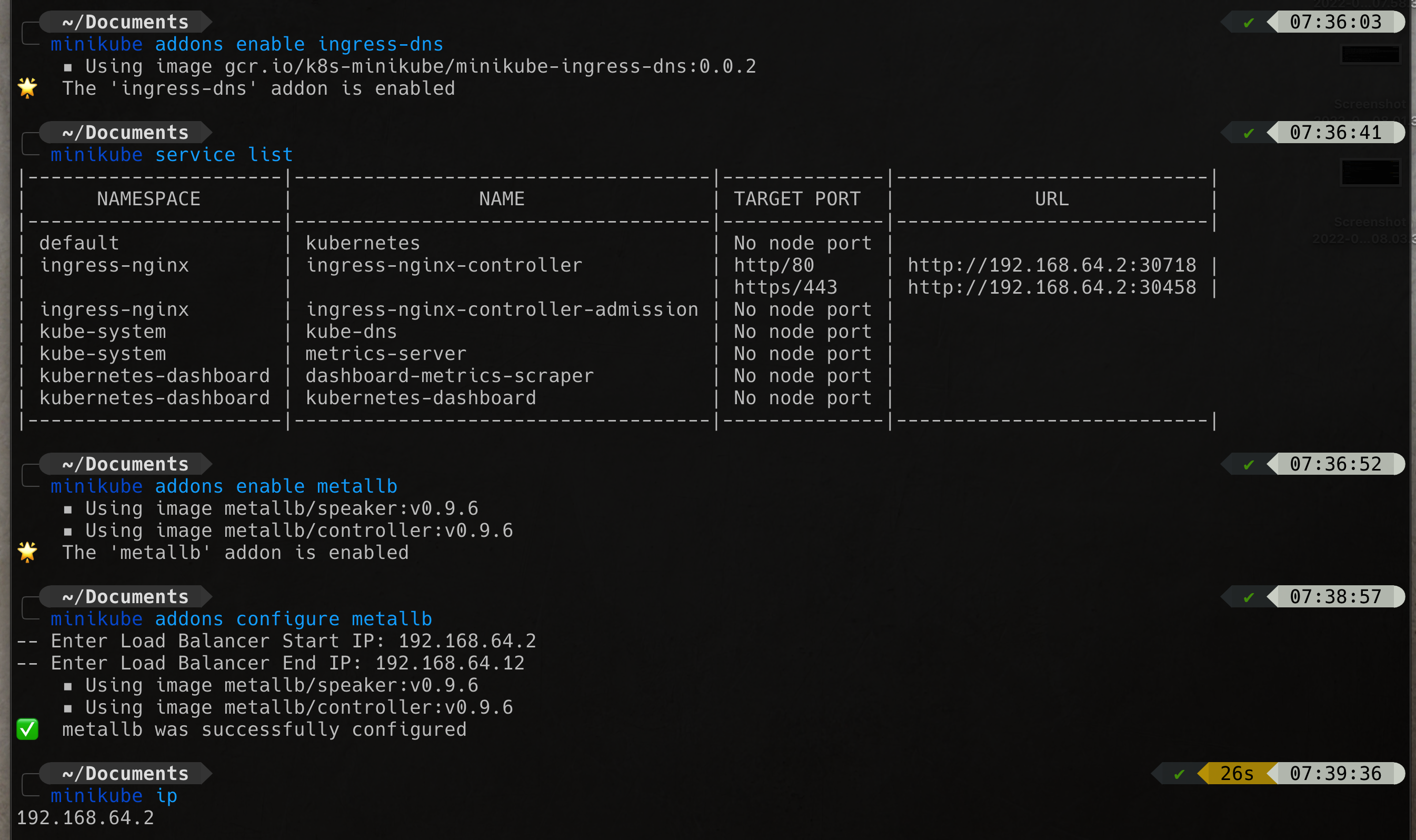
minikube addons enable ingress-dns
minikube addons enable metallb
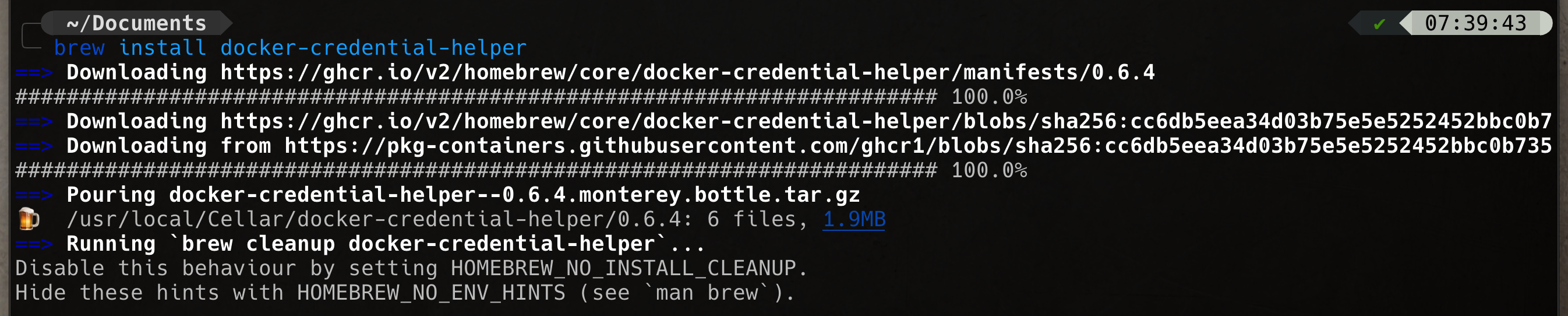
minikube addons configure metallbbrew install docker-credential-helperRun this maven command to creat project scaffold
mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:2.8.1.Final:create -DprojectGroupId=prajumsook -DprojectArtifactId=country-service -DclassName="org.wj.prajumsook.countries.CountryResource" -Dpath="/countries"For detail please checkout the video.
Create database instance script
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: postgres
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: postgres
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: postgres
spec:
containers:
- name: postgres
image: postgres:12
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 5432
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: POSTGRES_DB
value: quarkus_db
- name: POSTGRES_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: db-credentials
key: username
- name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: db-credentials
key: password
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: postgres
name: postgres
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 5432
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: postgres
type: NodePortCreate database secret
kubectl create secret generic db-credentials --from-literal=username=quarkus_user --from-literal=password=quarkus_passStart PostgreSQL instance
kubectl apply -f postgresql_db.yaml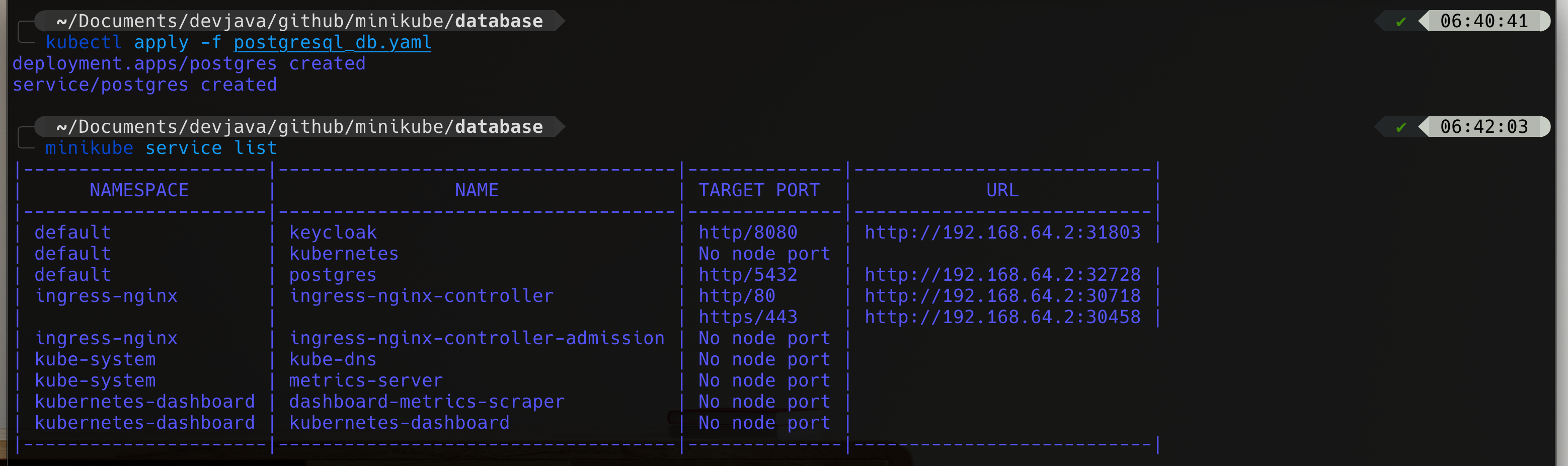 Now you should see that PostgreSQL running on port
Now you should see that PostgreSQL running on port 32728 (In this tutorial but you should have a differns on your env.)
http://192.168.64.2:32728Add hibernate-orm and PostgreSQL extension to the project
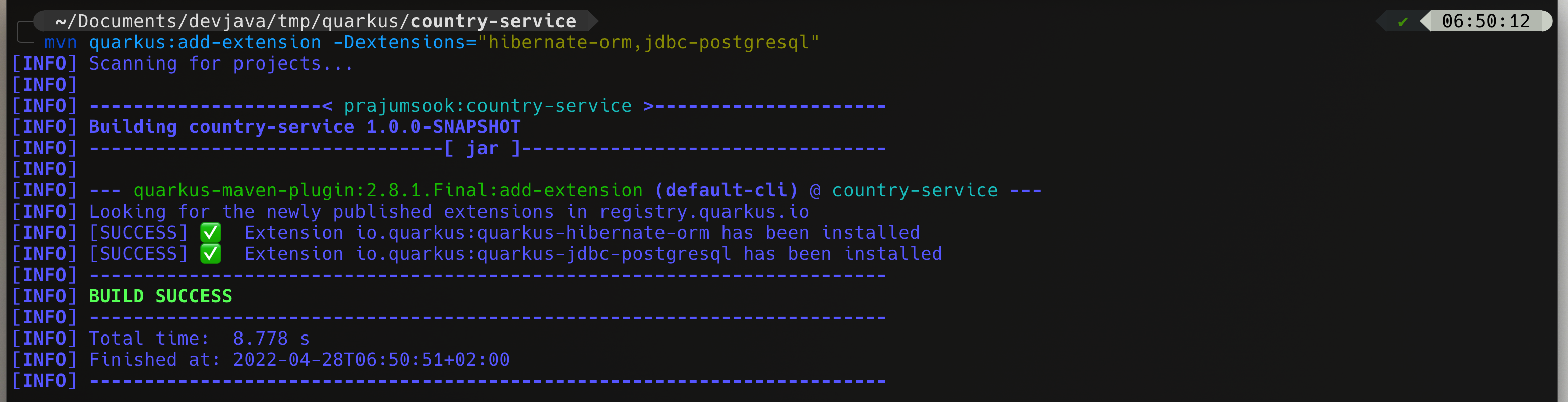
mvn quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="hibernate-orm,jdbc-postgresql"Please check out video for complete changes in the service.
Add OpenAPI extension
mvn quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="quarkus-smallrye-openapi"Please watch video for complete changes.
Add extension
mvn quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="quarkus-smallrye-metrics"Please watch video for complete implementation.
Code using in this secstion is from:
https://github.com/prometheus-operator/kube-prometheusPlease clone the latest from the repo
git clone https://github.com/prometheus-operator/kube-prometheus.gitCreates the Kubernetes CRDs
kubectl create -f manifests/setupAnd then
kubectl create -f manifestsCreate servicemonitor.yaml file
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: country-service
namespace: default
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: country-service
spec:
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- default
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: country-service
endpoints:
- port: http
interval: 3s
path: /q/metricsAnd to get service monitor service run command
kubectl get servicemonitors --all-namespacesAccess grafana dashboard
kubectl port-forward -n monitoring service/grafana 3000:3000And on browser navigate to http://lcalhost:3000
Login with user admin and pass admin
Please watch video for complete implementation
Create yaml file as follow
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
component: elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: elasticsearch
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearch
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.3
env:
- name: discovery.type
value: single-node
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: http
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 4Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 4Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
labels:
service: elasticsearch
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
component: elasticsearch
ports:
- port: 9200
targetPort: 9200Create deployment and service
kubectl create -f elasticsearch.yamlCreate yaml file as follow
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kibana
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: kibana
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: kibana
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.3
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
value: http://<MINIKUBE IP>:<EXPOSED ELASTIC PORT>
- name: XPACK_SECURITY_ENABLED
value: "true"
ports:
- containerPort: 5601
name: http
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kibana
labels:
service: kibana
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
run: kibana
ports:
- port: 5601
targetPort: 5601
You can find MINIKUBE IP with this command
minikube ipAnd
kubectl get servicesYou should be able to find elasticsearch port
Create deployment and service
kubectl create -f kibana.yamlCreate Fluentd RBAC so that Fluentd can access to logs components yaml file as follow
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: fluentd
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: fluentd
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-systemAnd run the create
kubectl create -f fluentd-rbac.yamlCreate yaml file as follow
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: fluentd
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: fluentd
spec:
serviceAccount: fluentd
serviceAccountName: fluentd
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: fluentd
image: fluent/fluentd-kubernetes-daemonset:v1.3-debian-elasticsearch
env:
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
value: "<MINIKUBE IP>"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
value: "<ELASTICSEARCH EXPOSE PORT>"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_SCHEME
value: "http"
- name: FLUENT_UID
value: "0"
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
You need to change MINIKUBE IP and ELASTICSEARCH EXPOSE PORT
Then create the daemonset
kubectl create -f fluent-daemonset.yamlPlease watch the video for complete implementation
Create a keycloak.yaml file as follow
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: keycloak
labels:
app: keycloak
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: keycloak
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: keycloak
labels:
app: keycloak
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: keycloak
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: keycloak
spec:
containers:
- name: keycloak
image: quay.io/keycloak/keycloak:18.0.0
args: ["start-dev"]
env:
- name: KEYCLOAK_ADMIN
value: "admin"
- name: KEYCLOAK_ADMIN_PASSWORD
value: "admin"
- name: KC_PROXY
value: "edge"
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /realms/master
port: 8080Then run this command
kubectl create -f keycloak.yamlThis will start keycloak on Kubernetes and it will also create and initial admin user with username admin and password admin
keycloak-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: keycloak
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- KEYCLOAK_HOST
rules:
- host: KEYCLOAK_HOST
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: keycloak
port:
number: 8080Replace KEYCLOAK_HOST with keycloak.{minikube ip address}.nip.io
To find out the minikube ip address you can run this command
minikube ipThen run this command to create ingress for Keycloak
kubectl create -f keycloak-ingress.yamlNext check out minikube service list
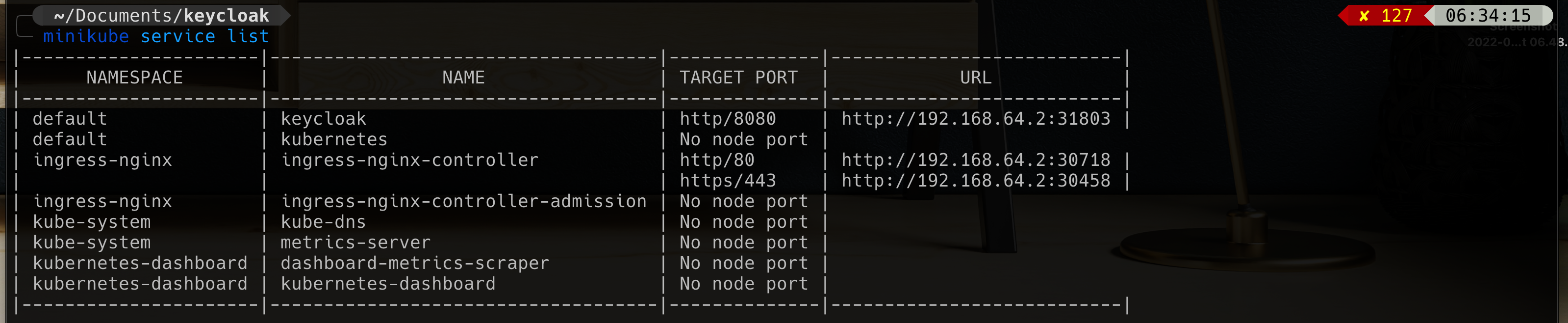
Run command
minikube service listYou should see keycloak url, open your browser and enter keycloal url
Login with username admin and password admin
You should see the Keycloak dashboard
Create new Realm name quarkus
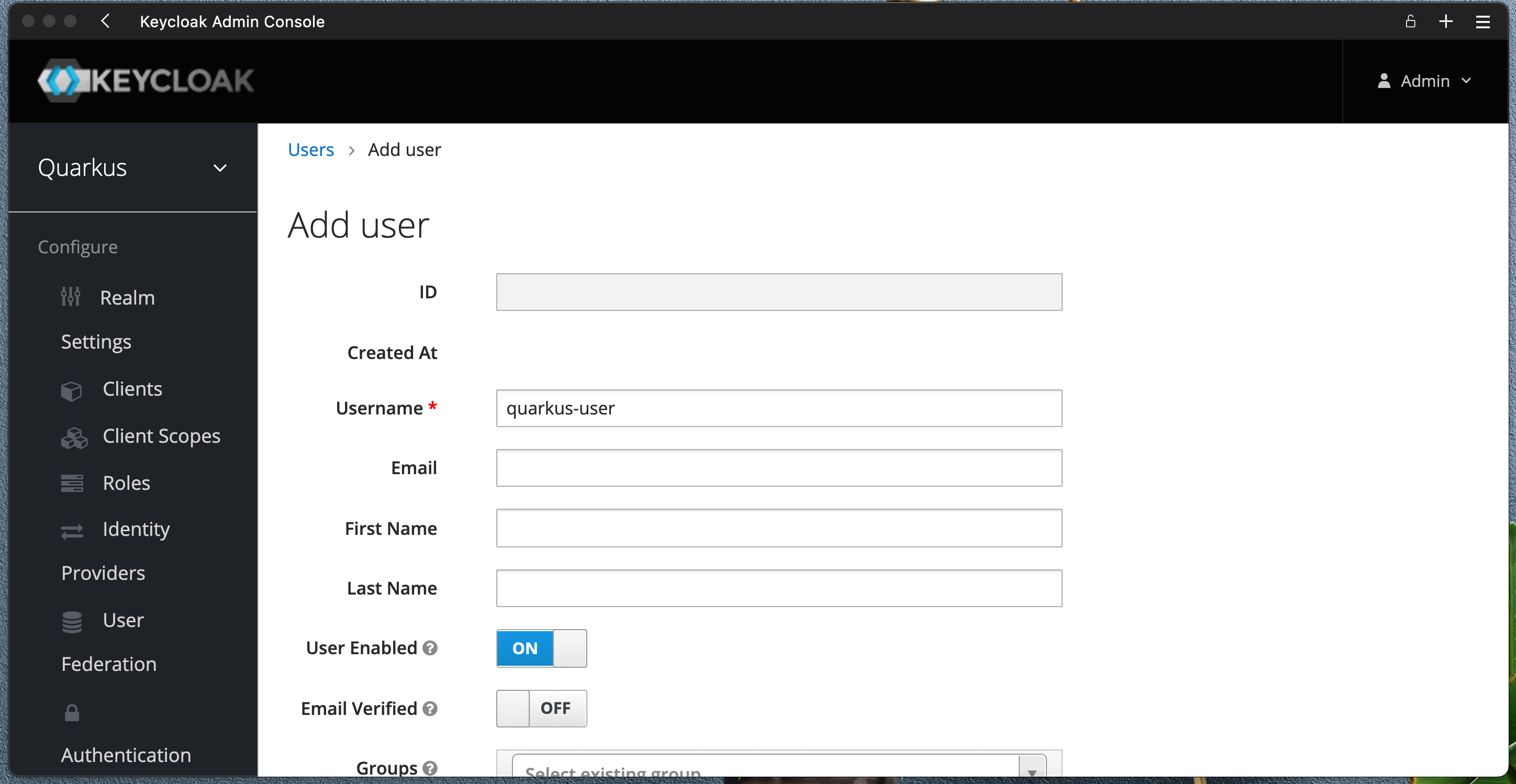
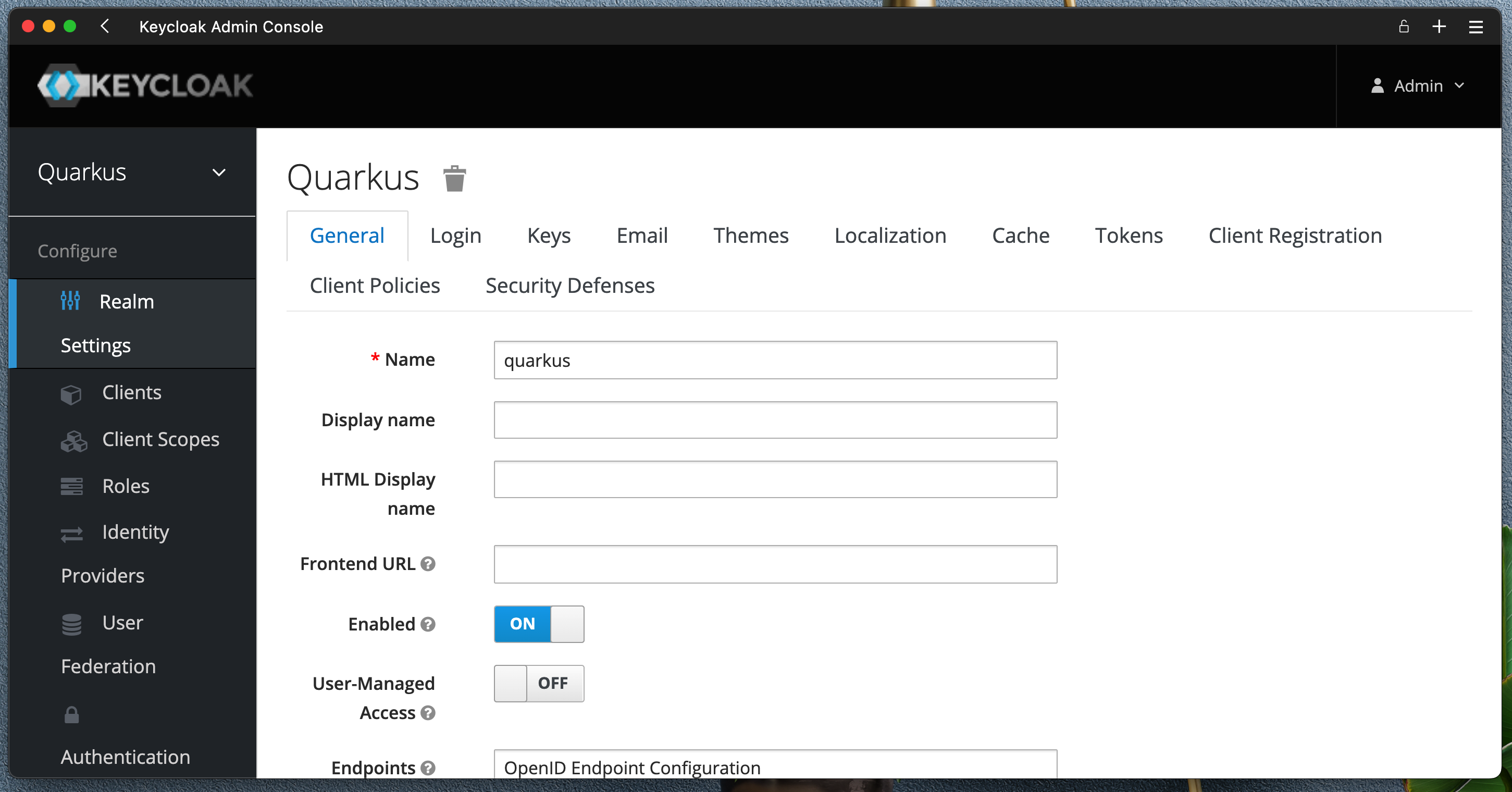 Create a new User
Create a new User quarkus-user
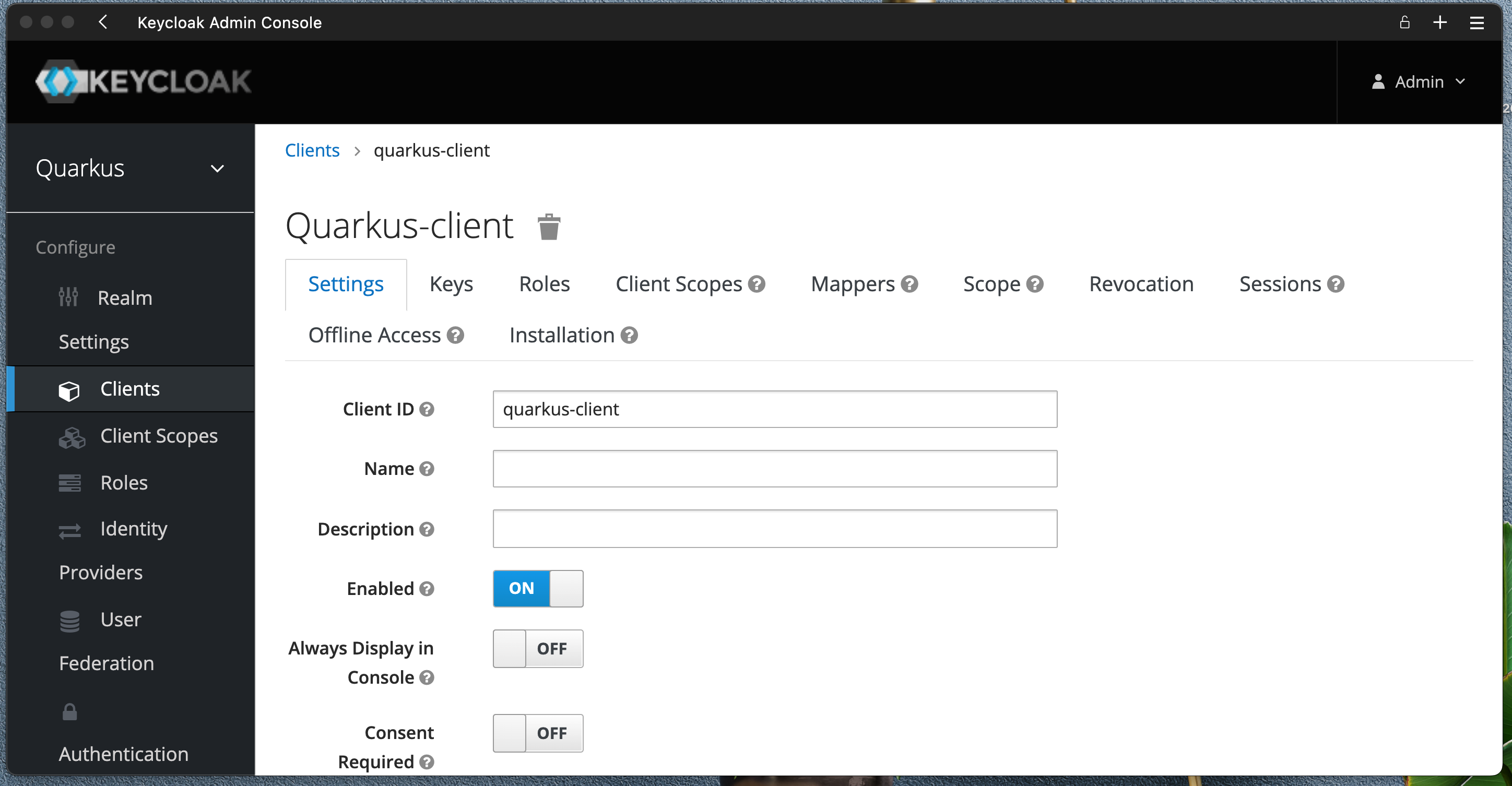
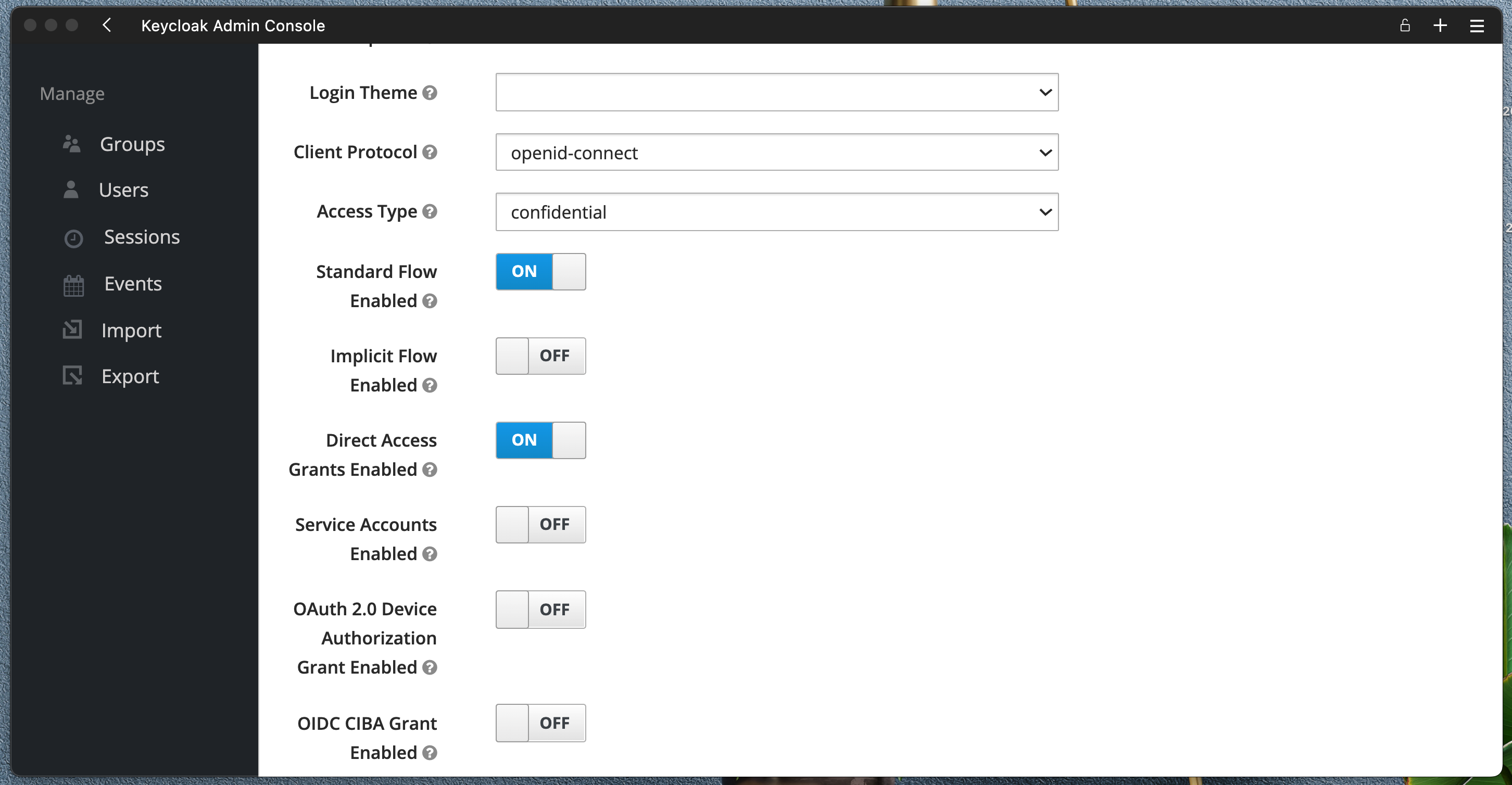
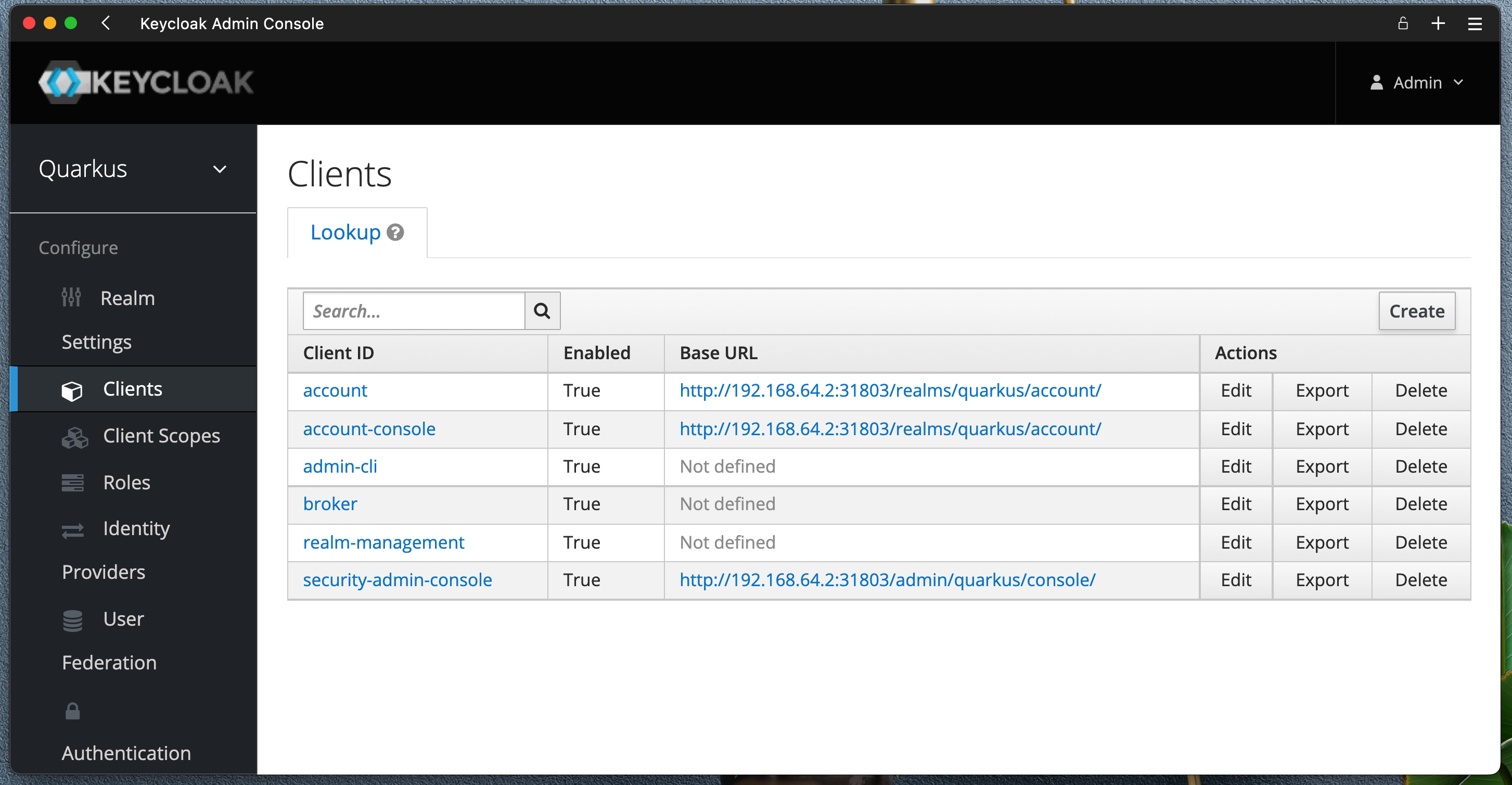
Create new client quarkus-client with Client Protocol openid-connect, Access Type confidential, Standard Flow on and Direct Access Grants Enabled on
Create new client quarkus-client
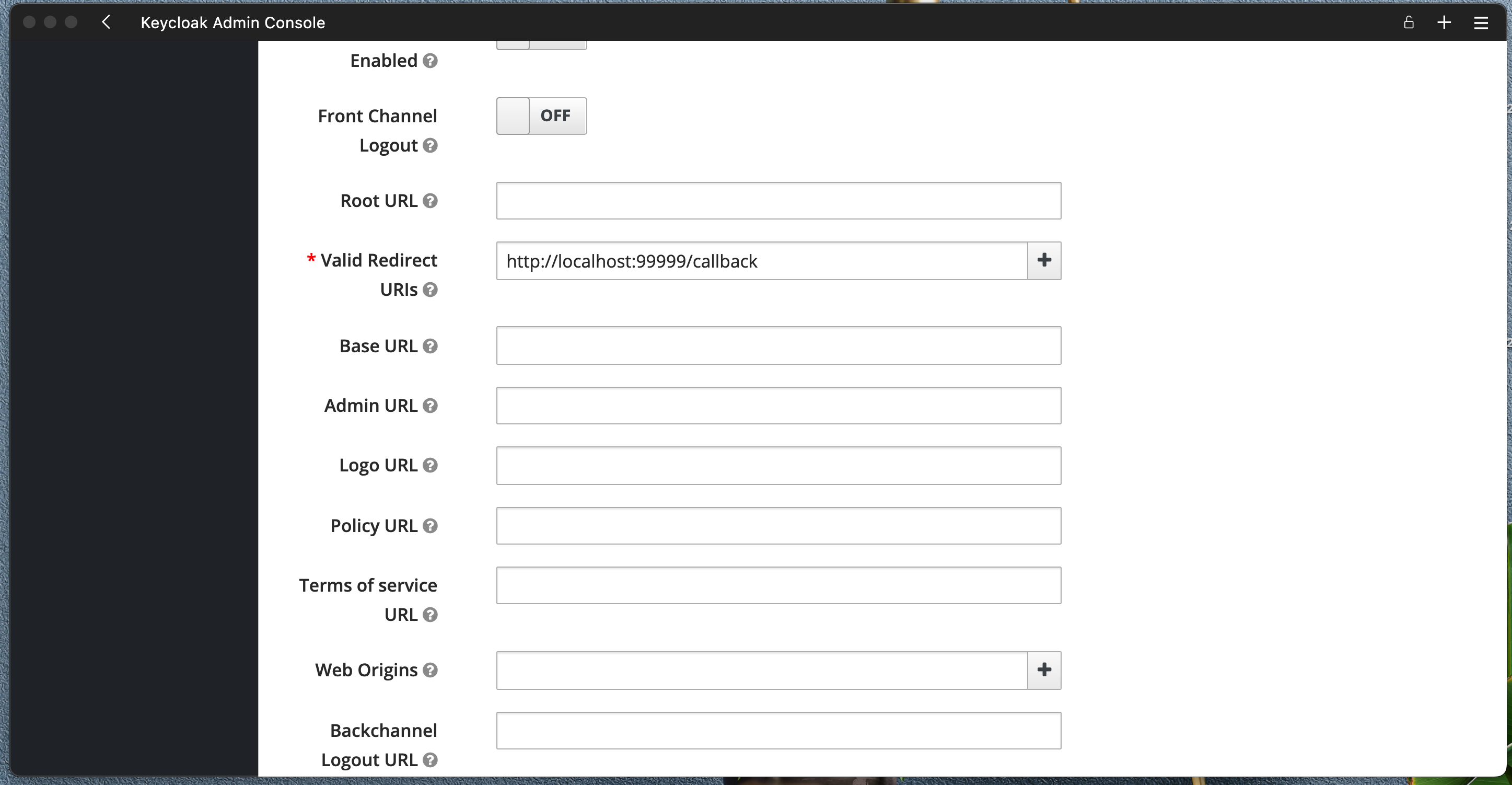
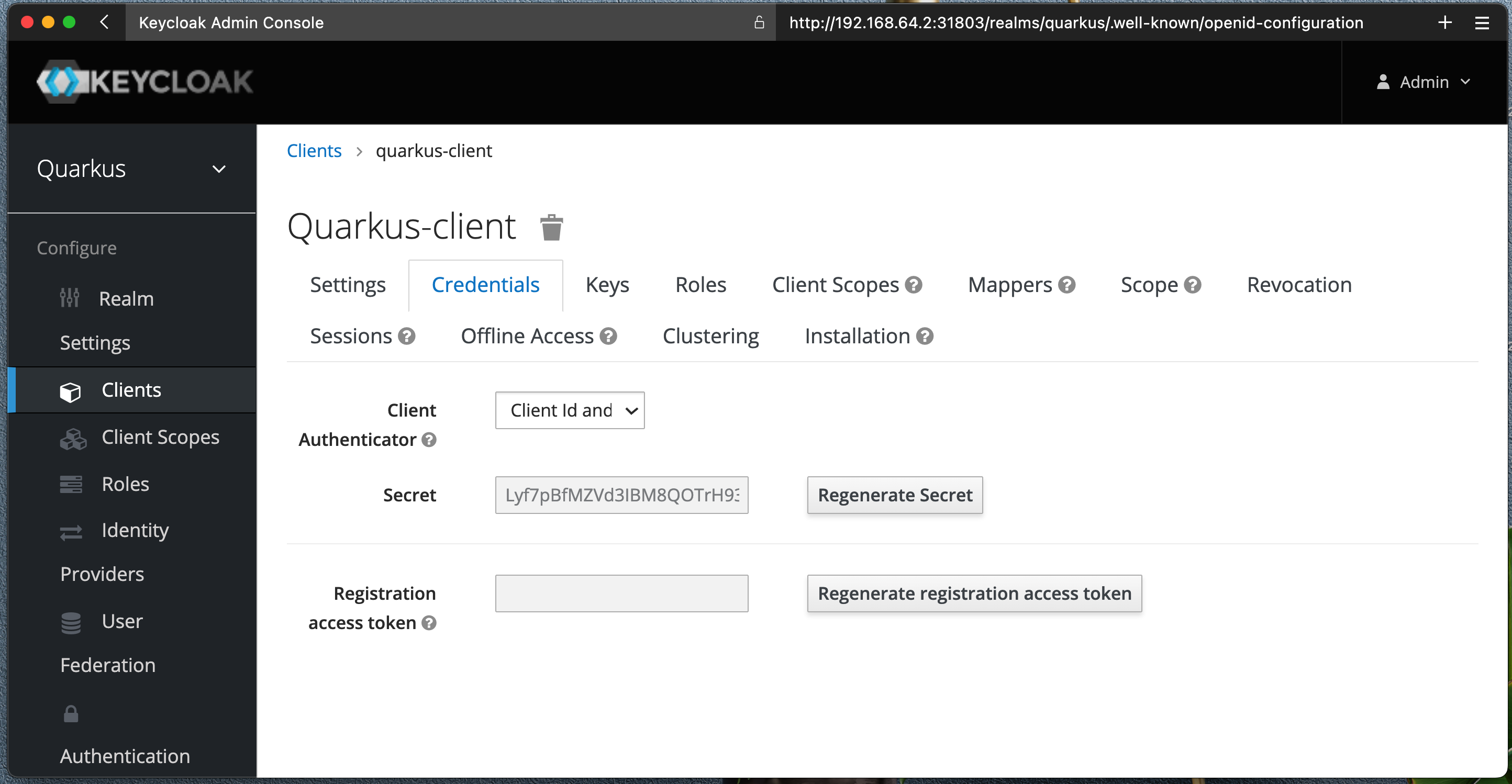
Set Valid Redirect URIs to somthing like http://localhost:99999/callback for now.
Save your settings and click on Credentials tab, make note of your Client name and Clent secret.
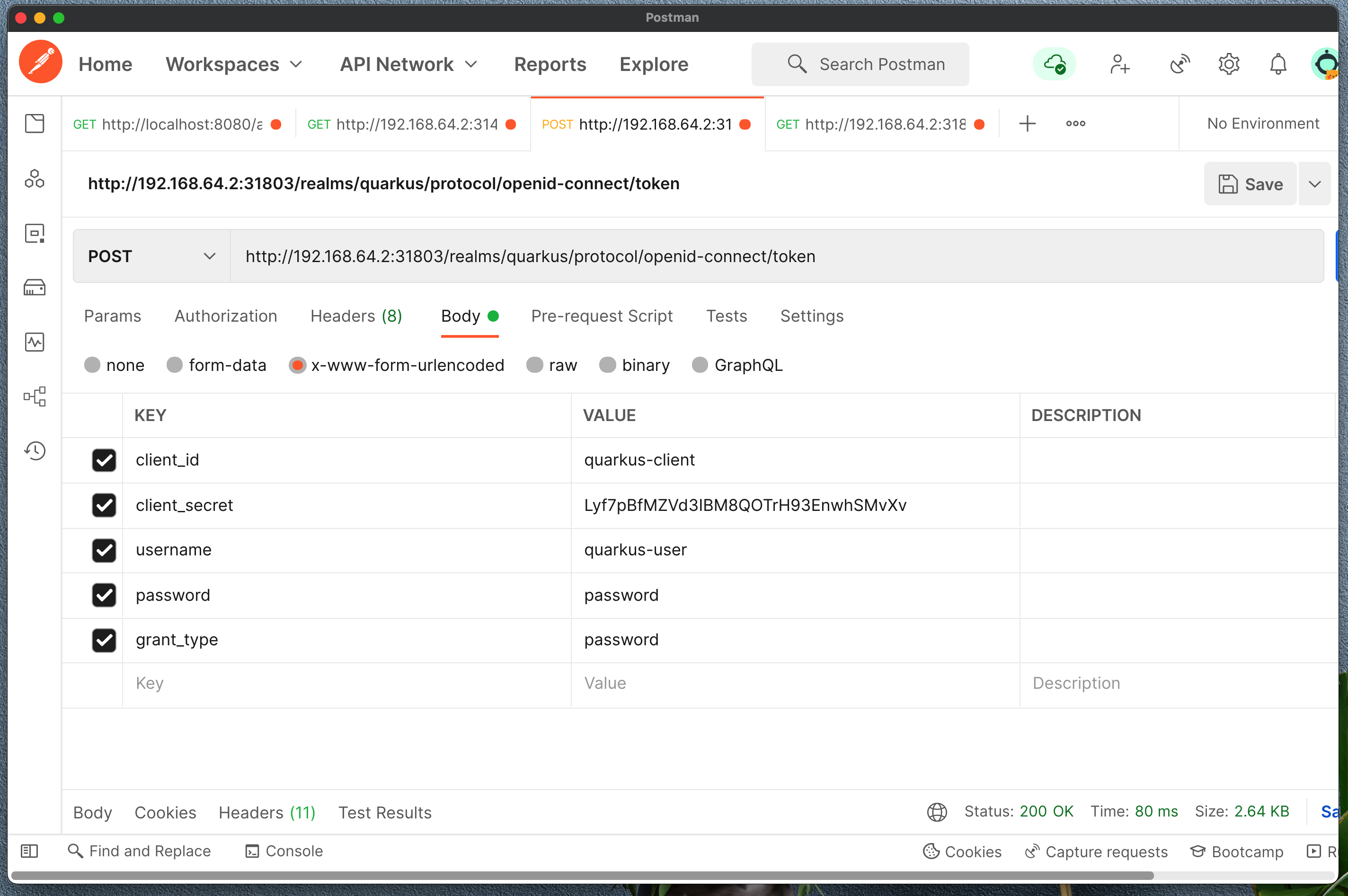
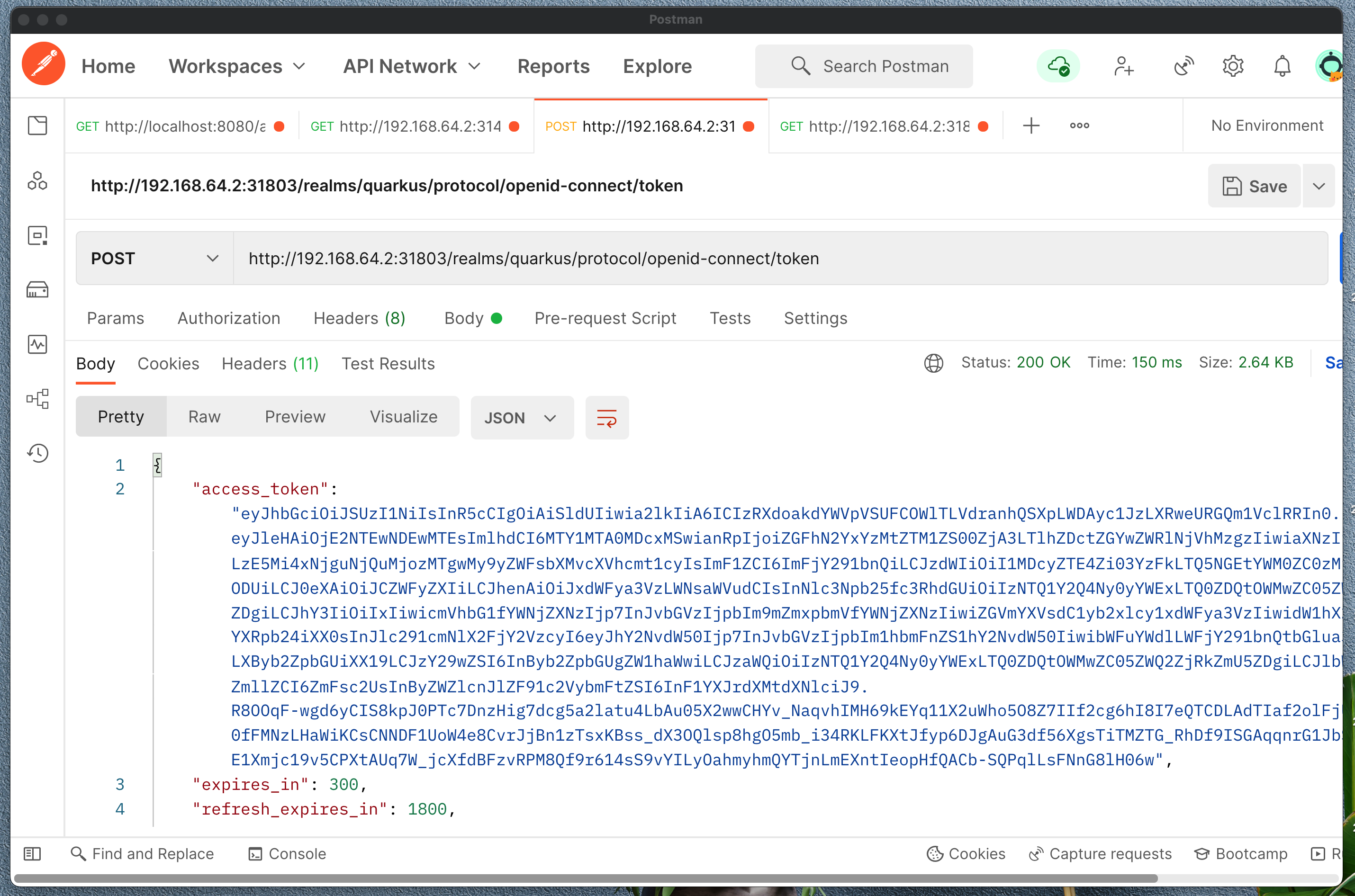
Open up Postman and enter this url:
http://192.168.64.2:31803/realms/quarkus/.well-known/openid-configurationWe are interested in token_endpoint, copy that and enter to new Postman request as POST.
Enter post body as x-www-form-urlencoded:
client_id = quarkus-client
client_secret = <copy from Client page>
username = quarkus-user
password = password
grant_type = passwordYou should get the response with access_token, refresh_token and more. This access_token you will need to identify you service calls.
Add quarkus extension
mvn quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="quarkus-oidc"Please watch the video for complete implementation