ART-SAFEBOX
A Group Project code implementation of The HK PolyU COMP3334 Computer System Security of Group 39. This is a Client/Server based system which is built as a safe guarded digital artwork exchanging platform.
Contents
- ART-SAFEBOX
System Design
- Client/Server Architecture
- Django Python Server
- jQuery AJAX JavaScript Front-end
- SQLite Database (with API support of Django)
- HTTPS SSL/TLS1.3 Protocol
- CSS supported by BootStrap5
- Web Image Viewer: Viewer.js
Backend Design
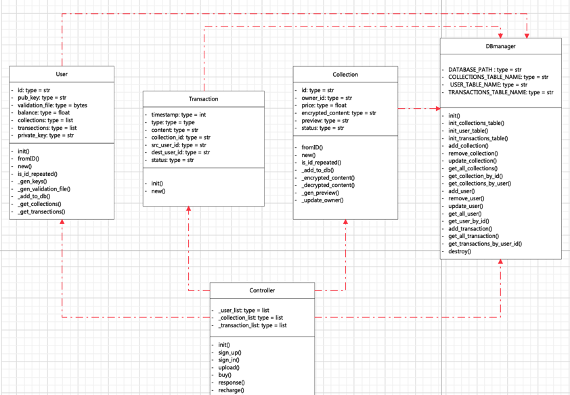
The UML Class Diagram
- DBmanager: The Database manager for creating un-existing table, doing write, read, update, delete in the database.
- User: The object represents the User.
- Transaction: Object for messages and requests sending from or to users.
- Collections: The object represents the artwork.
- Controller: Execute specific tasks of the website/server. For more updated backend library, visit this repo
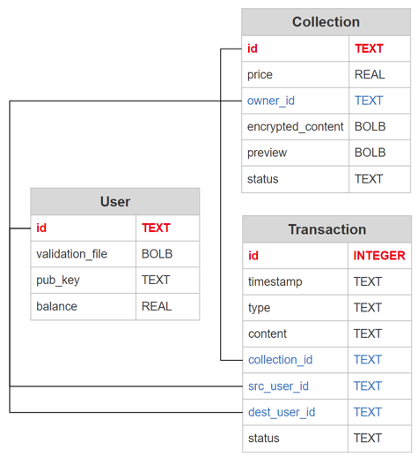
The Entity Relationship Diagram of Database
-
User:
- User ID: The primary key, indicating user's identity.
- Validation File: Decrypted by RSA Public Key. Containing the AES key for en/decrypting the user's collections.
- Public Key: The RSA Public Key of the User
- Balance: The balance of the user.
-
Collection:
- Collection ID: The primary key, indicating the collection's identity. The collection id is the title of the collection here.
- Owner ID: A user ID of the collection's Owner
- Encrypted Content: The content of the collection encrypted by the owner's RSA public key.
- Preview: The preview of the Collection. Here it is an image of the original content in 1/4 size.
- Statues:
- Pending (The collection is under exchanging)
- Confirmed(All except under exchanging).
-
Transaction:
- Transaction ID: The primary key, indicating the transaction's identity.
- Timestamp: At which time the transaction is made.
- Type:
- Message (A msg to notice the Dest User)
- Request (A buying request from buyer to seller)
- Content: The text message of the transaction. e.g.
- "You have accepted Xavier's buying request"(System -> User)/
- "I have rejected your Buying request."(Seller -> Buyer)
- Source User ID: The User ID of whom launch this transaction.
- Destination User ID: The User ID of whom the transaction is sent to.
- Status:
- Pending (Waiting for Dest User responding)
- Rejected (Dest User rejected the request)
- Accepted (Dest User accepted the request)
- Closed (Transaction done)
- Seen (Visible to User)
- Unseen(Invisible to User, for debug purpose)
Client Design
index.html
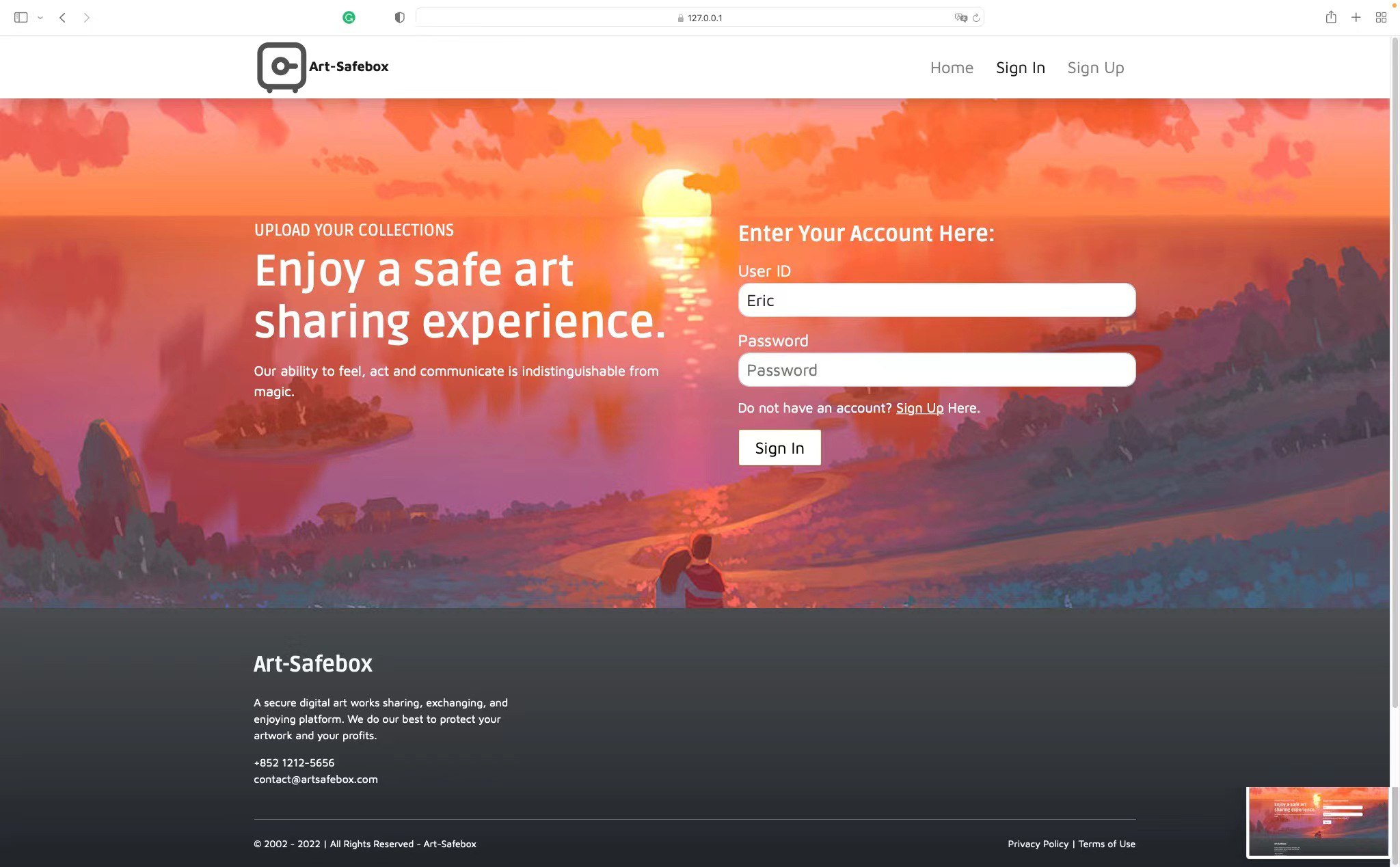
signin.html
signup.html
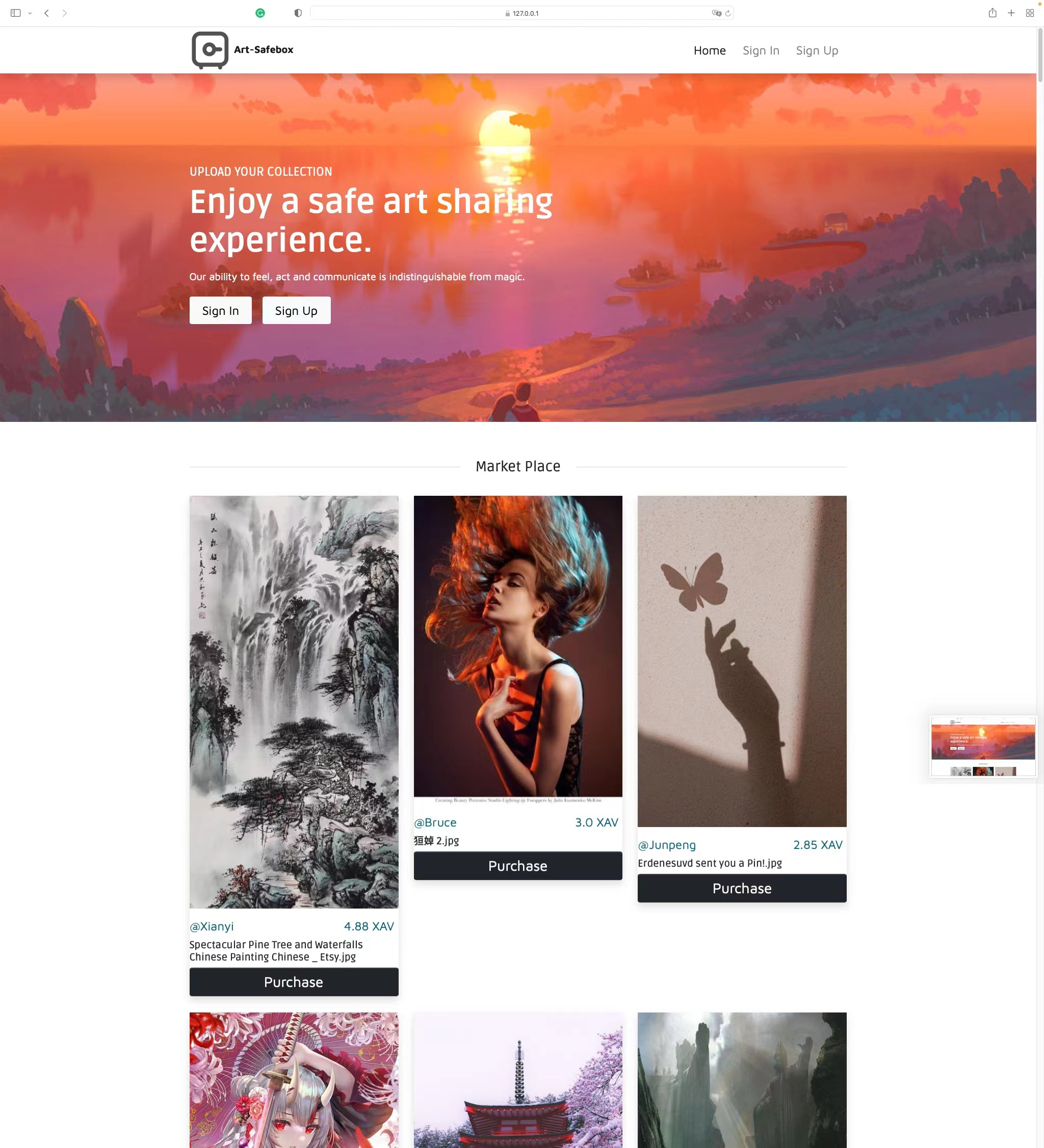
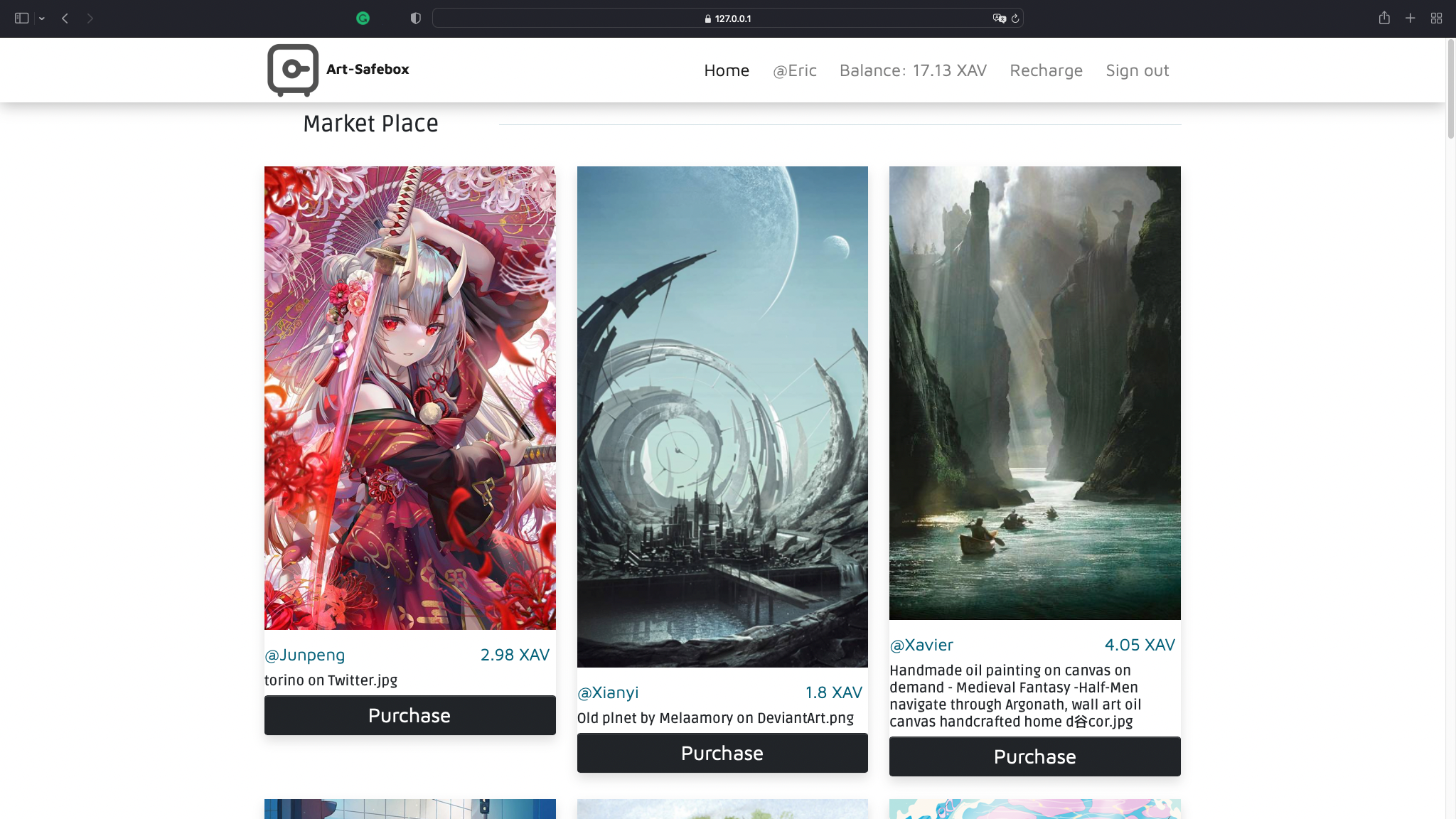
home.html
The home page after signin. Purchase request can be sent here.
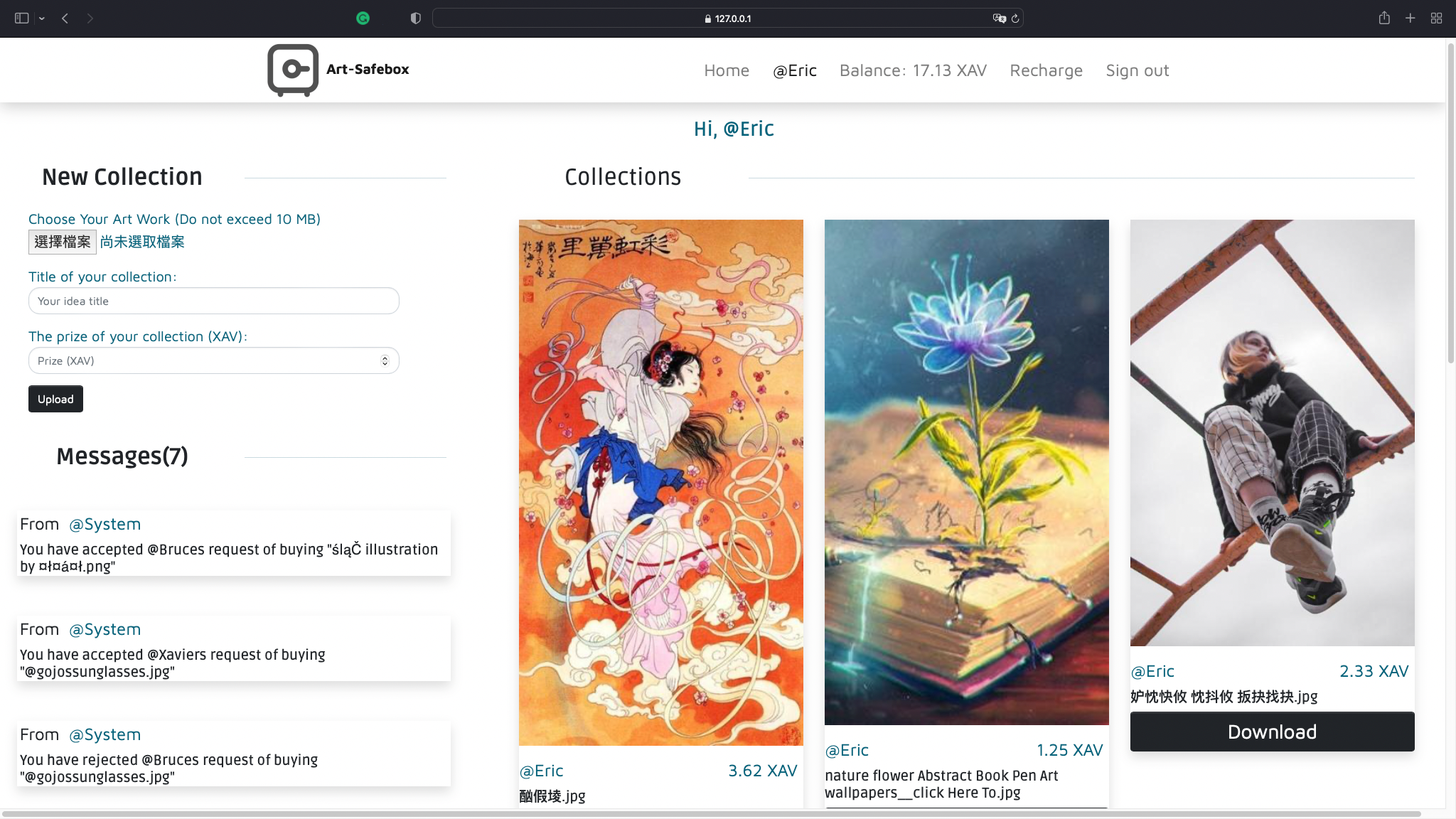
personal.html
The personal main page after signin. Downloading/uploading collections, accept/reject other's buying request can be done
here and other notices can be seen here.
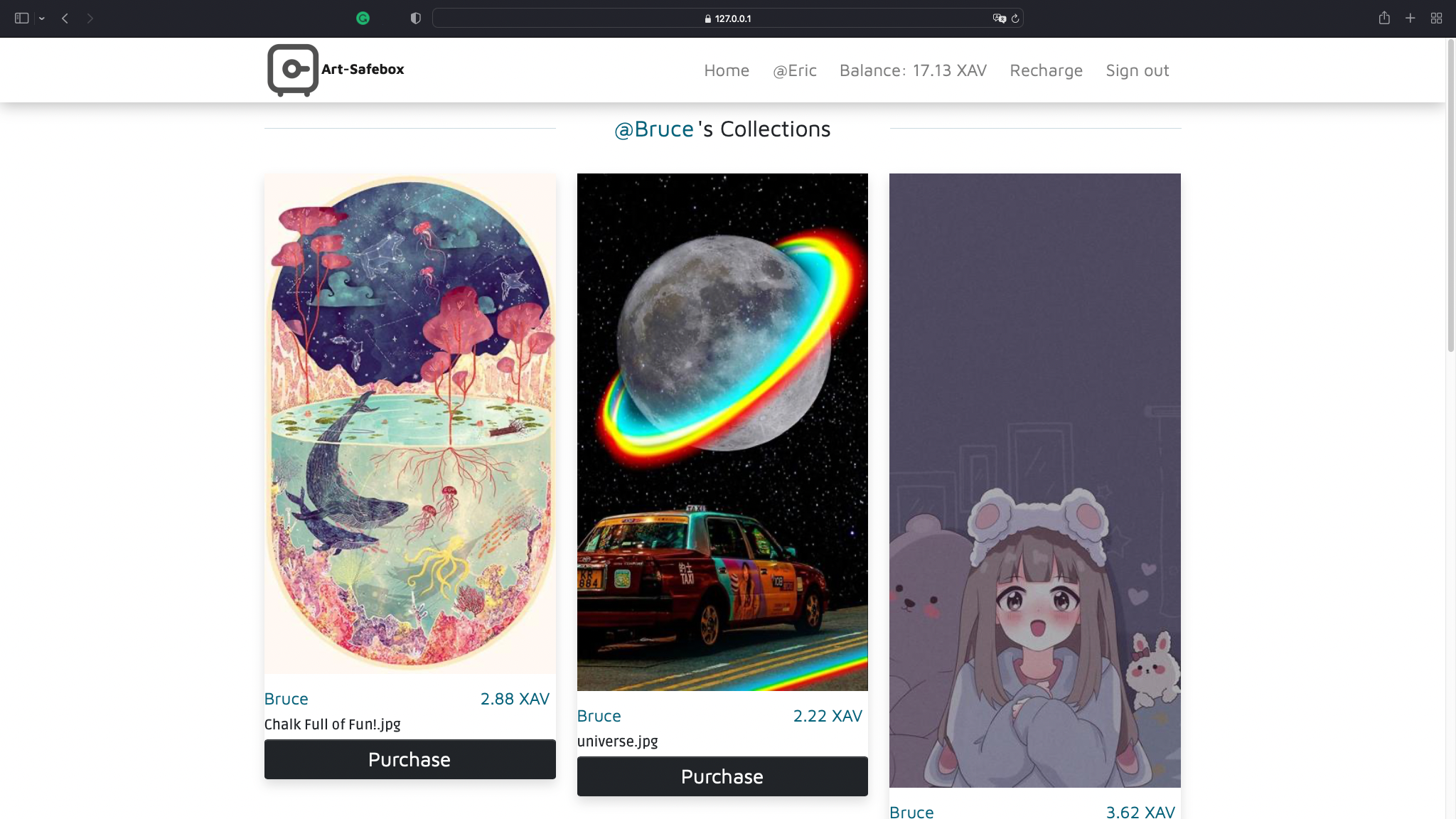
others.html
The other's personal main page after signin.
others_unsigned.html
The other's personal main page before signin.
Security
Backend
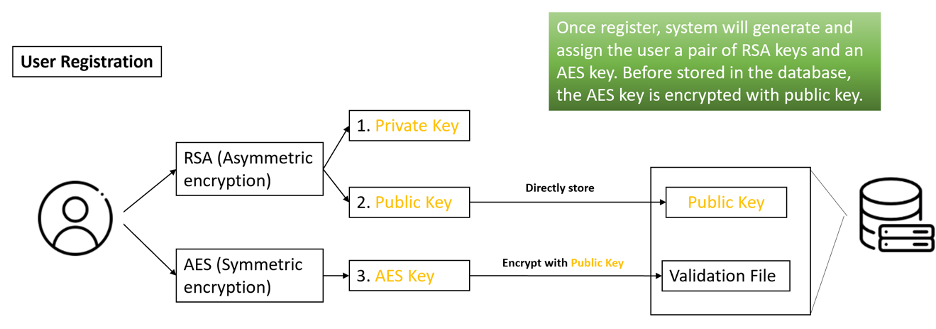
User Register
During the register, a key pair of RSA cipher, an AES key are randomly generated. The AES key will be encrypted by the RSA public key and stored in the validation file. The RSA public key will be store in the server database while the private will be returned to the user as the login password. The server won't store the RSA private key, only cache and use it when necessary.
Methods to verify whether the account and password match: The validation file contains the user's AES key and ID. During signin, the server will try to decrypt the validation file by the password(RSA private key), if decryption failed or the decrypted user ID is not equal to the user ID then the account and password is not match. Otherwise, they are match.
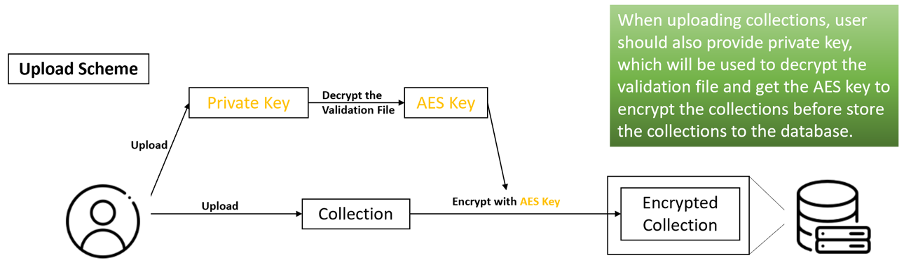
User Uploading an Artwork
Once an artwork along with its title(recognized as collection ID) and price is upload to the server. The server will decrypt the validation file(containing the user's AES key) of the user and use the AES key to encrypt the content of the artwork. The preview (1/4 size of the raw data here) of the artwork is generated at the same time.
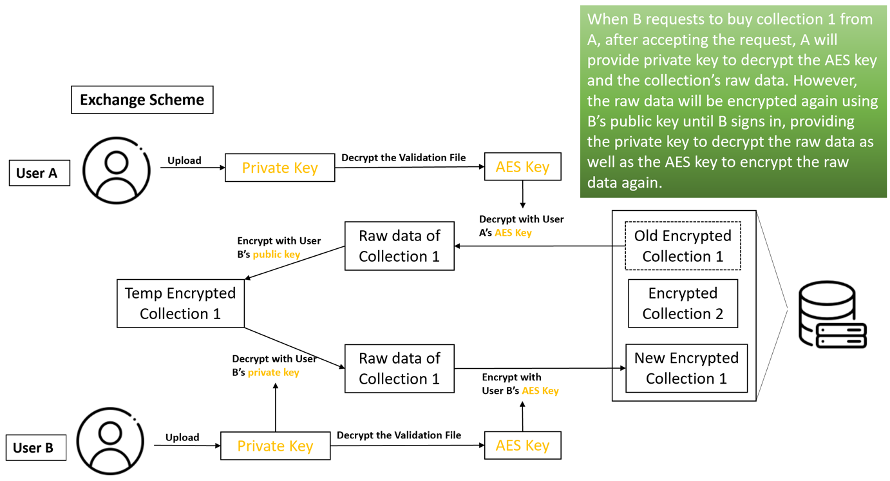
Artwork Exchange Scheme
Once the owner of an artwork accepts a buyers buying request. The encrypted data of the collection will be decrypted by the owner's AES key and be encrypted again by the buyer's RSA public key (which may take a while) because we are not sure whether the buyer is online. At the next signin of the buyer, the artwork will be decrypted by the buyer's private key automatically and be encrypted again by the buyer's AES key.
Because the private key will not be stored on the server, and the artwork data on the server is encrypted, the loss of data can be guaranteed to be very small even if the database is leaked or subjected to a short-term scripting attack and control scramble.
Communication
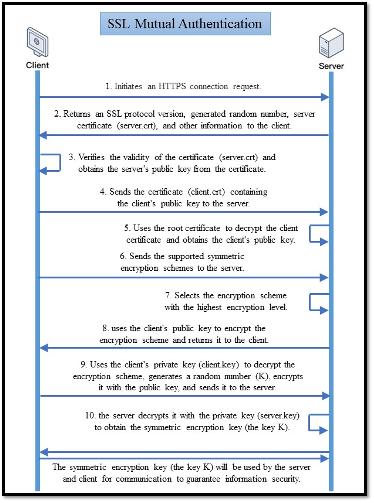
HTTPS SSL/TLS1.3
An RSA shake-hand for exchanging the AES key, then using the AES key for communication.
Session and Cookies
During signin, the server will check whether the account(user ID) and password(the RSA private key) are match. If so, the account and password along with the sign in time will be decrypted by random generated AES key and stored in python objects. The AES key will be returned as cookies item "info". The user ID will be returned as the cookies item "uid" as well. Thus, if the request sent to the server has cookies content i.e. "info" and "uid", the server will try to decrypt the account and password stored before, if failed, the cookies will be erased, and a 404 respond will be sent back. If not, the server will handle the request in a pre-defined way. The expiry time is set to 20 minutes. If no request is sent for more than 20 mins, at next request, the cookies will be erased, and the user will be asked to signin again. The account, password, and signin time of the user will be deleted as well. Otherwise, the signin time will be reset.
Details in views.py, accounts.py, AESCipher.py.
The good thing of this procedure is that, the plaintext password(private key) of the user won't be stored at either server or browser(client) which improves the security. The user is only allowed to sign in at a single device in a single browser, because the AES key is random generated for each single sign in. In addition, signin timed out will be logged out automatically.
Demonstration
 If you cannot access the demo video via YouTube, you can download it here.
If you cannot access the demo video via YouTube, you can download it here.
Limitations
Long and unchangeable password.
Since the password is the randomly generated RSA private key, which is long and cannot be changed by the user, it is very inconvenient for users to store or remember it. In addition, once the user lost his/her password, s/he will no long use this account. New procedures needs to be added to fix the problem, e.g. email servers to send emails to the user to acquire passwords; use some hash algorithms and mapping to make it possible for user defining their password themselves.
Time-consuming en/decryption of RSA
This is a reason why we use blended AES, RSA cipher to en/decryption the data. However, during exchanging artworks, RSA will be used for directly en/decrypting an artwork. We found that it costs about 5 mins for a single thread to decrypt a 10MB image and about 90s for 10 threads (which is dangerous) to do the same task. So we decided to use asynchronous threads to encrypt/decrypt data, but it seems Django doesn't support using the native Python Thread class to do so, because even if you put a task into a child Thread, the parent Thread will wait for the child Thread to finish before continuing. Therefore, celery may need to be added for asynchronous task deployment.
Poor concurrent processing capability
Django's design flaw prevents it from processing multiple requests at the same time, and Django runs on Python, which means it is not efficient to execute. Therefore, the project will require users to wait for a long time to process large artwork, but we have tried our best to ensure that the program does not go wrong.
File Structures:
../
├── ART_SAFEBOX/
│ └── __init__.py (Empty file)
│ └── accounts.py (Online accounts manager)
│ └── AESCpiher.py (AES Cipher support for accounts.py)
│ └── asgin.py (Empty file)
│ └── backend.py (Database, User states, Collections, and Transactions manager)
│ └── models.py (Function caller of backend.py)
│ └── settings.py (Django configs)
│ └── urls.py (Urls setter)
│ └── views.py (Request handler)
│ └── wsgi.py (Empty file)
├── Certificate/ (Folder of certificate)
│ └── ...
├── static/ (static folder of Django)
│ └── blocks.css (Custom .css)
│ └── js/custom.js (Custom JavaScript)
│ └── previews/ (Folders of collection previews)
│ └── ...
├── templates/ (.html folder of Django)
│ └── ...
├── db.sqlite3 (Database)
├── makeCA.sh (.sh file for generating a certificate)
├── Start.sh (.sh file for starting the server)
├── manage.py (main of Django)
└── README.md
└── ...
System Installation Guide
Requirements
- Operating System: OS X, Windows(not tested)
- Suggested IDE: Pycharm
- Suggested Browser: Chrome, Safari
- Package Dependencies: Run
pip install requreiments.txt
Set the certificate for SSL communication:
cdthe current working path to the same path where the filemakeCA.shis.- Run
sh makeCA.sh - Then you can find the generated certificate under directory Certificate.
- There is also a selection to generate a certificate: mkcert. But please note that the created certificate will be stored on your computer permanently and have the ability to bypass the browsers' security mechanism.
- Please never share your certificate to others.
Start the server:
cdthe current working path to the same path where the fileStart.shis.- Run
sh Start.sh
Start the client:
- Go to Chrome or Safari, enter
https://127.0.0.1:8000 - If Chrome prevents you from opening the website, type
thisisunsafeanywhere, the website will be opened. - Here are some collections and users are already stored in the database, you can find the account and password from
accounts.txt
Notes:
- Currently, only
*.JPGor*.PNGimages can be uploaded, and the size cannot exceed 10MB. Otherwise, the server will reject the request. - Since Django can't handle more than one request at a time, wait patiently for the server to respond when performing time-consuming requests (upload, download, accept a transaction, first signin after the request is accepted).
- It is normal for terminal to display exceptions because we add
traceback.print_exc()to all except parts oftry:except:pair for debugging purposes. The server can perform tasks properly. - Once the server is restarted, all users need to sign in again because session information is stored only in variables.
Team Members
- Bruce: Bruce312
- Eric: WPCJATH
- David: Yang0303PP
- Xavier: X3vvv
- Ryan: Azunyan-bot