NoiseBuster is an advanced Python application designed to monitor and log noise levels using a USB-connected sound meter. It not only records noise events but also integrates with various services like InfluxDB, MQTT, Discord, and more to provide a comprehensive noise monitoring solution. With features like weather data integration and traffic data collection, NoiseBuster offers a versatile tool for environmental monitoring and analysis.
🚀 Click here to see NoiseBuster in action!
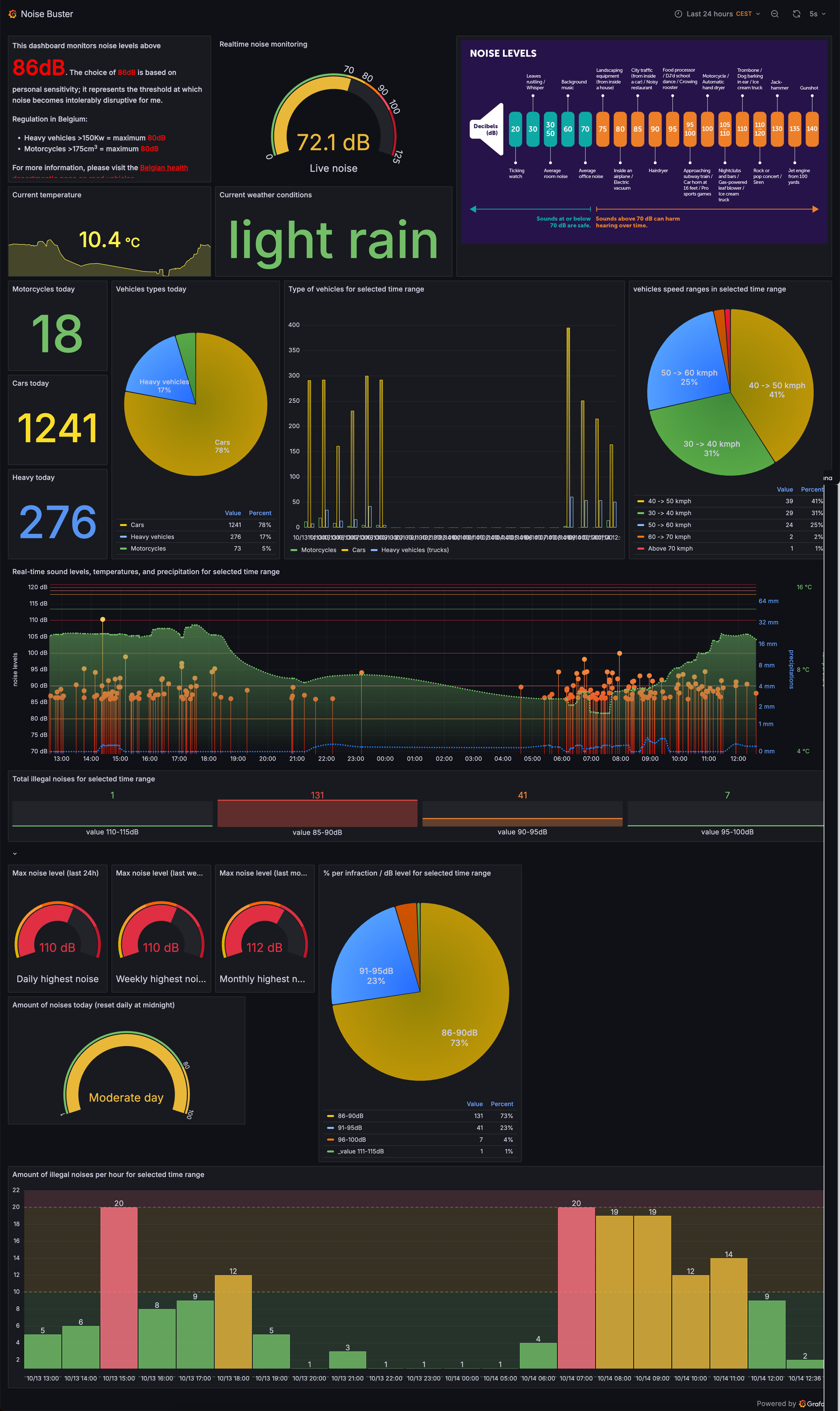
NoiseBuster Dashboard in Grafana showing noise events over time.
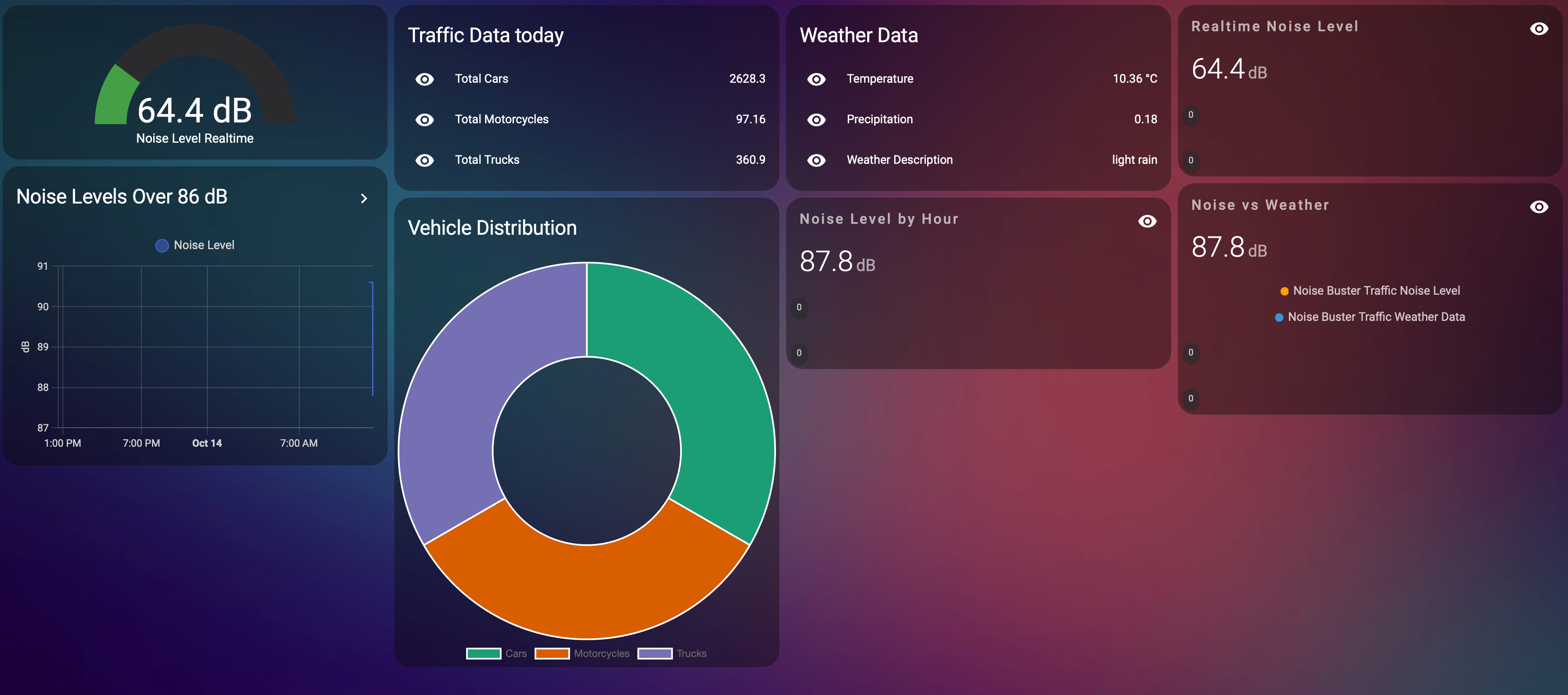
Analysis of noise levels in Home Assistant.
Note: This project, NoiseBuster, created by Raphael Vael, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC) License, which means it is free for non-commercial use only. Commercial use requires explicit permission from the project owner.
Join the community on our Discord server to discuss, contribute, and get support: NoiseBuster Discord Server
- Noise Monitoring: Interfaces with a USB sound meter to monitor and record noise levels in real-time.
- Data Storage: Stores recorded noise events in InfluxDB for easy retrieval and analysis.
- MQTT Integration (Optional): Publishes noise levels and events to an MQTT broker for integration with home automation systems like Home Assistant.
- Weather Data Collection (Optional): Fetches current weather data from OpenWeatherMap API to correlate noise events with weather conditions.
- Traffic Data Collection (Optional): Integrates with Telraam API to collect traffic data, allowing analysis of noise levels in relation to traffic conditions. Note: A dedicated YOLO-powered traffic counting script is in development and will be available soon.
- Image Capture (Optional): Captures images using an IP camera when noise levels exceed a specified threshold.
- Notifications (Optional): Sends notifications via Discord and Pushover when certain events occur (e.g., high noise levels, API failures).
- Configurable Timezone: Adjusts timestamps according to the specified timezone offset.
- Error Handling and Logging: Robust error handling with detailed logging for troubleshooting.
- Monitor loud traffic, planes, live events, and more.
- Create insightful graphics to share statistics with authorities.
- Analyze environmental noise in correlation with weather and traffic data.
Before using NoiseBuster, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Operating System: Linux-based system (e.g., Ubuntu, Debian, Raspberry Pi OS).
- Python: Python 3.6 or higher installed.
- Sound Meter: A USB-connected sound level meter. All models with USB communication capabilities should work. Other types like RS485 models and ESP devices with calibrated microphones could be used but may require additional setup by the user.
- Internet Connection: Required for API integrations (e.g., OpenWeatherMap, Telraam).
- Optional but Recommended:
- InfluxDB 2.x and Grafana: For data storage and visualization. If you want to use these, you need to install them on your own
- Optional:
- MQTT Broker: If you wish to publish data to an MQTT broker.
- Docker: Installed for containerized deployment.
- PoE Splitter: If you want to power your device using PoE, consider using a PoE Splitter.
- IP65 Box: For outdoor usage of your volume meter, I recommend using an IP65 box to protect the device.
- Volume Meter: I use this USB volume meter, which runs smoothly on a Raspberry Pi and is powered directly through USB.
- Linux-Compatible Board: Use a Raspberry Pi or any other board capable of running Linux.
- Virtual Machines and Containers: You can also run NoiseBuster in a VM, LXC, or other virtual environment, and simply pass through the USB volume meter, avoiding dedicated hardware.
-
USB Sound Meter:
-
The application is designed to work with USB-connected sound level meters.
-
Example Device: USB Sound Level Meter on AliExpress
-
Ensure the device supports USB communication.
-
For devices not automatically detected, you may need to specify the USB vendor ID and product ID in the configuration. Use the
lsusbcommand to find these IDs.
-
-
Camera (Optional):
- IP Camera: Supports RTSP or HTTP protocols. Provide the camera's URL in the configuration.
- Raspberry Pi Camera: Connects directly to the Raspberry Pi. Requires the
picameralibrary.
All configuration settings are stored in the config.json file. Here is how to set up your configuration:
-
Open
config.jsonin a text editor.
Keep all default IP addresses aslocalhostor127.0.0.1to ensure it works out of the box. -
Configure each section:
-
InfluxDB Configuration:
- Set
"enabled": trueto store data in InfluxDB. - Provide your InfluxDB
host,port,token,org, andbucketnames. - Ensure you create buckets named
"noise_buster"and"noise_buster_realtime". - API Keys: Follow the InfluxDB setup guide to create your organization, buckets, and API tokens.
- Set
-
Pushover Configuration (Optional):
- Set
"enabled": trueto receive Pushover notifications. - Provide your
user_keyandapi_token. Register at Pushover.
- Set
-
Weather Configuration (Optional):
- Set
"enabled": trueto fetch weather data. - Provide your OpenWeatherMap
api_keyandlocation. Sign up at OpenWeatherMap API.
- Set
-
MQTT Configuration (Optional):
- Set
"enabled": trueto publish data to an MQTT broker. - Provide your MQTT
server,port,user, andpassword. Learn more at mqtt.org.
- Set
-
Camera Configuration (Optional):
- Set
"use_ip_camera": trueor"use_pi_camera": truebased on your setup. - If using an IP camera, provide the
ip_camera_url.
- Set
-
Device and Noise Monitoring Configuration:
- Specify the
device_namefor identification. - Set
minimum_noise_levelin decibels to trigger events. - Specify
image_save_pathwhere images will be stored. - If automatic USB detection fails, provide
usb_vendor_idandusb_product_id. Use thelsusbcommand to find these IDs.
- Specify the
-
Telraam API Configuration (Optional):
- Set
"enabled": trueto collect traffic data. - Provide your Telraam
api_keyandsegment_id. More info at Telraam.
- Set
-
Timezone Configuration:
- Set
timezone_offsetrelative to UTC.
- Set
-
Discord Configuration (Optional):
- Set
"enabled": trueto send notifications to Discord. - Provide your Discord
webhook_url. Create one at Discord Webhooks.
- Set
-
-
Save
config.json.
-
Ensure the USB sound meter is connected to your computer.
-
Clone the repository using Git:
git clone https://github.com/silkyclouds/NoiseBuster.git
-
Navigate to the
NoiseBusterdirectory:cd NoiseBuster -
Create a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv env
-
Activate the virtual environment:
source env/bin/activate -
Install the required dependencies based on your device type:
-
For Raspberry Pi users:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
For non-Raspberry Pi users:
pip install -r requirements_no_pi.txt
-
-
Run the application:
python noisebuster.py
-
Clone the repository using Git:
git clone https://github.com/silkyclouds/NoiseBuster.git
-
Navigate to the
NoiseBusterdirectory:cd NoiseBuster -
Copy the appropriate requirements file based on your device type:
-
For Raspberry Pi users:
cp requirements.txt docker/requirements.txt
-
For non-Raspberry Pi users:
cp requirements_no_pi.txt docker/requirements.txt
-
-
Build the Docker image:
Make sure to specify the correct Dockerfile in the build context.docker build -t noisebuster -f docker/Dockerfile . -
Run the Docker container:
Ensure the necessary ports and devices are mapped if required.docker run -d --name noisebuster noisebuster
-
Check the logs:
This will help you verify if the application is running as expected.docker logs noisebuster
-
Access the application (if applicable):
Follow any additional instructions specific to accessing the app, such as exposed ports or mapped volumes.Check if everything is running fine, if you configured your usb device correctly in your config.json file, you should see dB levels being reported. If you didn't, don't panic, the usb_ids file should get you covered and allow to autodetect your device.
This project is licensed under the GNU GPLv3 License. This license allows for free usage and modification of the code for non-commercial purposes. For commercial use, explicit permission from the project owner is required. By choosing this option, I aim to encourage open-source collaboration while maintaining control over commercial applications of NoiseBuster.
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch for your changes.
- Submit a pull request with a detailed explanation of your changes.
I'm actively developing a vehicle detection and counting module based on YOLOv11 to correlate noise events with specific vehicle types. If you're interested in helping improve this model or contributing in other ways, please reach out! Any contributions to the detection and accuracy of vehicle classification would be invaluable.
- Adding vehicle detection using OpenCV to correlate noise events with specific vehicles.
- Providing a centralized InfluxDB instance for users to contribute data.
- Investigating other hardware options like ESP devices for sound monitoring.
- Implementing better data retention policies to manage database size.
- A dedicated YOLO-powered traffic counting script is in development and will be available soon.
This project was initiated by Raphael Vael. I welcome anyone interested in improving NoiseBuster to join the effort. Whether it's refining the vehicle detection model, optimizing the noise detection algorithms, or expanding functionality, your input is greatly valued!
This project, NoiseBuster, created by Raphael Vael, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

