Note
This repository represents an example of using a Chainlink product or service. It is provided to help you understand how to interact with Chainlink’s systems so that you can integrate them into your own. This template is provided "AS IS" without warranties of any kind, has not been audited, and may be missing key checks or error handling to make the usage of the product more clear. Take everything in this repository as an example and not something to be copy pasted into a production ready service.
This project is an educational example of how to create a minimal cross-chain name service using Chainlink CCIP.
Verify installation by typing:
node -vand
npm -v- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/smartcontractkit/ccip-cross-chain-name-service.git
cd ccip-cross-chain-name-service
- Install packages
npm install
- Compile contracts
npx hardhat compile
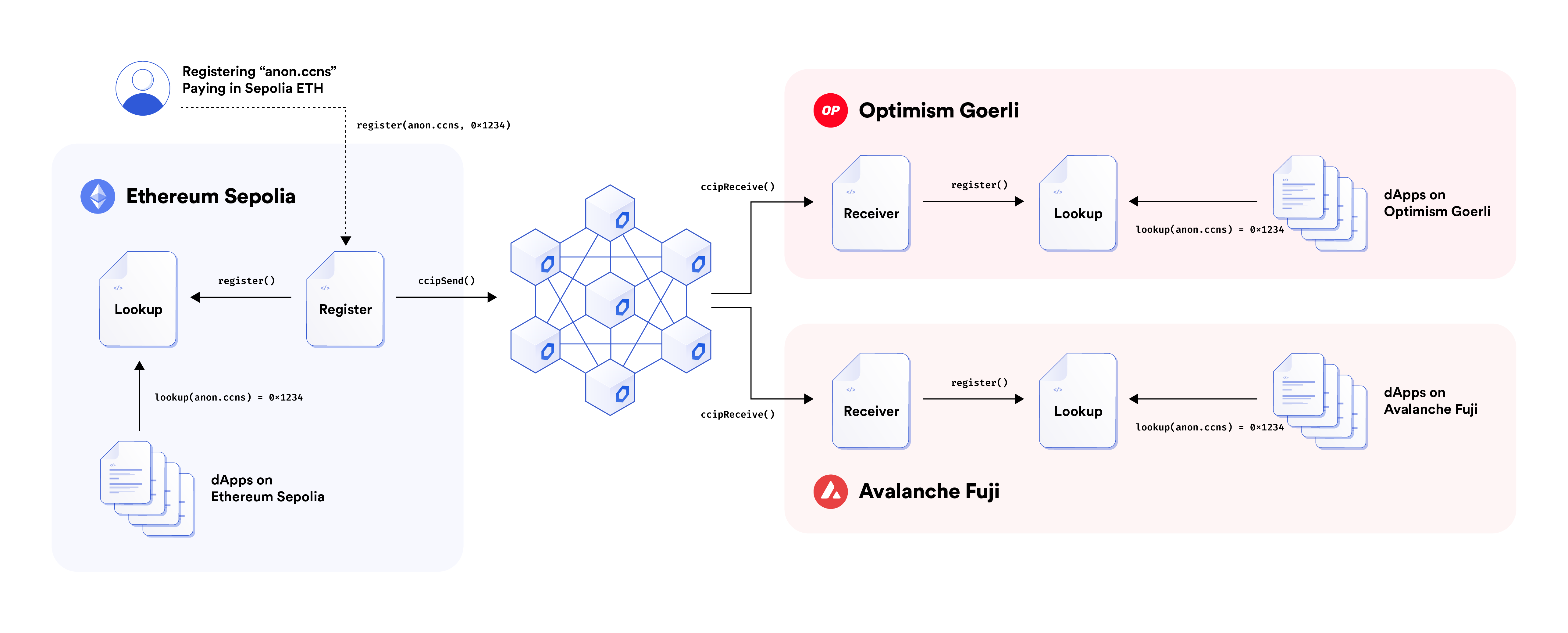
This is a basic architecture diagram, this project can have as many Chainlink CCIP-supported blockchains as possible, it is not limited to three as the diagram may suggest.
There is only one source blockchain on which we can register our .ccns handles. It is set by default to ethereumSepolia but you can change it by adjusting the defaultNetwork property of the config object in the hardhat.config.ts file:
const config: HardhatUserConfig = {
solidity: "0.8.19",
defaultNetwork: 'ethereumSepolia', // Source Chain
...
}There can be as many Chainlink CCIP-supported destination blockchains as possible.
There are two CrossChainNameService smart contracts per blockchain:
- On the source blockchain,
CrossChainNameServiceRegisterandCrossChainNameServiceLookup - On each of the destination blockchains,
CrossChainNameServiceReceiverandCrossChainNameServiceLookup
To register a new .ccns handle, you need to call the register() function of the CrossChainNameServiceRegister smart contract. It will send the CCIP message to all CrossChainNameServiceReceivers on each destination blockchain.
To resolve any give .ccns name, you just need to call a free view lookup(name) function of CrossChainNameServiceLookup on any blockchain. Because it is a cross-chain system, it will be exactly the same on all supported blockchains.
There are several Hardhat tasks available for deployment and interaction with this project. But before that, you need to set up some environment variables.
We are going to use the @chainlink/env-enc package for extra security. It encrypts sensitive data instead of storing them as plain text in the .env file, by creating a new, .env.enc file. Although it's not recommended to push this file online, if that accidentally happens your secrets will still be encrypted.
- Set a password for encrypting and decrypting the environment variable file. You can change it later by typing the same command.
npx env-enc set-pw
- Now set the following environment variables:
PRIVATE_KEY, Source Blockchain RPC URL, Destination Blockchain RPC URL. You can see available options in the.env.examplefile:
PRIVATE_KEY=""
ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL=""
OPTIMISM_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL=""
ARBITRUM_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL=""
AVALANCHE_FUJI_RPC_URL=""
POLYGON_AMOY_RPC_URL=""
BNB_CHAIN_TESTNET_RPC_URL=""
BASE_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL=""
KROMA_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL=""
WEMIX_TESTNET_RPC_URL=""
GNOSIS_CHIADO_RPC_URL=""
CELO_ALFAJORES_RPC_URL=""
To set these variables, type the following command and follow the instructions in the terminal:
npx env-enc set
After you are done, the .env.enc file will be automatically generated.
If you want to validate your inputs you can always run the next command:
npx env-enc viewAs being said, on the source blockchain there are CrossChainNameServiceRegister and CrossChainNameServiceLookup smart contracts. To deploy them we are going to use the deploy-source-chain task.
npx hardhat deploy-source-chain
--router <SOURCE_CHAIN_ROUTER_ADDRESS> # OptionalAs being said, the source chain is set up as defaultNetwork property of the config object in the hardhat.config.ts file.
For example, to deploy these two contracts on ethereumSepolia (default source chain), run:
npx hardhat deploy-source-chainOptionally, if you want to manually provide the CCIP Router.sol smart contract address, use the --router flag:
npx hardhat deploy-source-chain --router <SOURCE_CHAIN_ROUTER_ADDRESS>As being said, on each destination blockchain there are CrossChainNameServiceReceiver and CrossChainNameServiceLookup smart contracts. To deploy them we are going to use two tasks:
deploy-destination-chain-step1 & deploy-destination-chain-step2
To deploy these two smart contracts on the destination blockchain, you need to use the deploy-destination-chain-step1 task:
npx hardhat deploy-destination-chain-step1
--router <DESTINATION_CHAIN_ROUTER_ADDRESS> # Optional
--register <SOURCE_CHAIN_CCNS_REGISTER> # Optional
--source-chain-selector <SOURCE_CHAIN_SELECTOR> # OptionalFor example, if you want to deploy them to Avalanche Fuji testnet, run:
npx hardhat deploy-destination-chain-step1 --network avalancheFujiTo link these two contracts with the CrossChainNameServiceRegister smart contract on the source blockchain, you need to use the deploy-destination-chain-step2 task:
npx hardhat deploy-destination-chain-step2
--receiver-network <CCNS_RECEIVER_BLOCKCHAIN>
--register <CCNS_REGISTER_ADDRESS> # Optional
--receiver <CCNS_RECEIVER_ADDRESS> # Optional
--destination-chain-selector <DESTINATION_CHAIN_SELECTOR> # OptionalFor example, to enable Avalanche Fuji as a new network in the Cross Chain Name Service project, run:
npx hardhat deploy-destination-chain-step2 --receiver-network avalancheFujiEach time you want to enable a new blockchain, repeat the previous two steps.
For simplicity, this project supports paying for CCIP fees in native coins only.
To fund the CrossChainNameServiceRegister contract, we are going to use the fund task:
npx hardhat fund
--amount <AMOUNT_IN_WEI>
--register <CCNS_REGISTER_ADDRESS> # OptionalFor example, to fund your CrossChainNameServiceRegister smart contract on Ethereum Sepolia with 0.1 ether (in wei), run:
npx hardhat fund --amount 100000000000000000To check the balance (in wei) of CrossChainNameServiceRegister smart contract, you can use the get-balance task:
npx hardhat get-balance
--register <CCNS_REGISTER_ADDRESS> # OptionalFor example, to check the balance of CrossChainNameServiceRegister smart contract, run:
npx hardhat get-balanceTo withdraw all of the locked funds in the CrossChainNameServiceRegister contract, you can use the withdraw task:
npx hardhat withdraw
--beneficiary <ADDRESS_TO_WITHDRAW_FUNDS_TO>
--register <CCNS_REGISTER_ADDRESS> # OptionalFor example, to withdraw everything from CrossChainNameServiceRegister, run:
npx hardhat fund --beneficiary <PUT_YOUR_ADDRESS_HERE>Now comes the fun part, using the project!
To register a new CCNS handle we are going to use the ccns-register task. Keep in mind that provided handle must end with `.ccns``:
npx hardhat ccns-register
--ccns-name <NAME.CCNS>
--register <CCNS_REGISTER_ADDRESS> # OptionalFor example, if you want to register the anon.ccns handle, run:
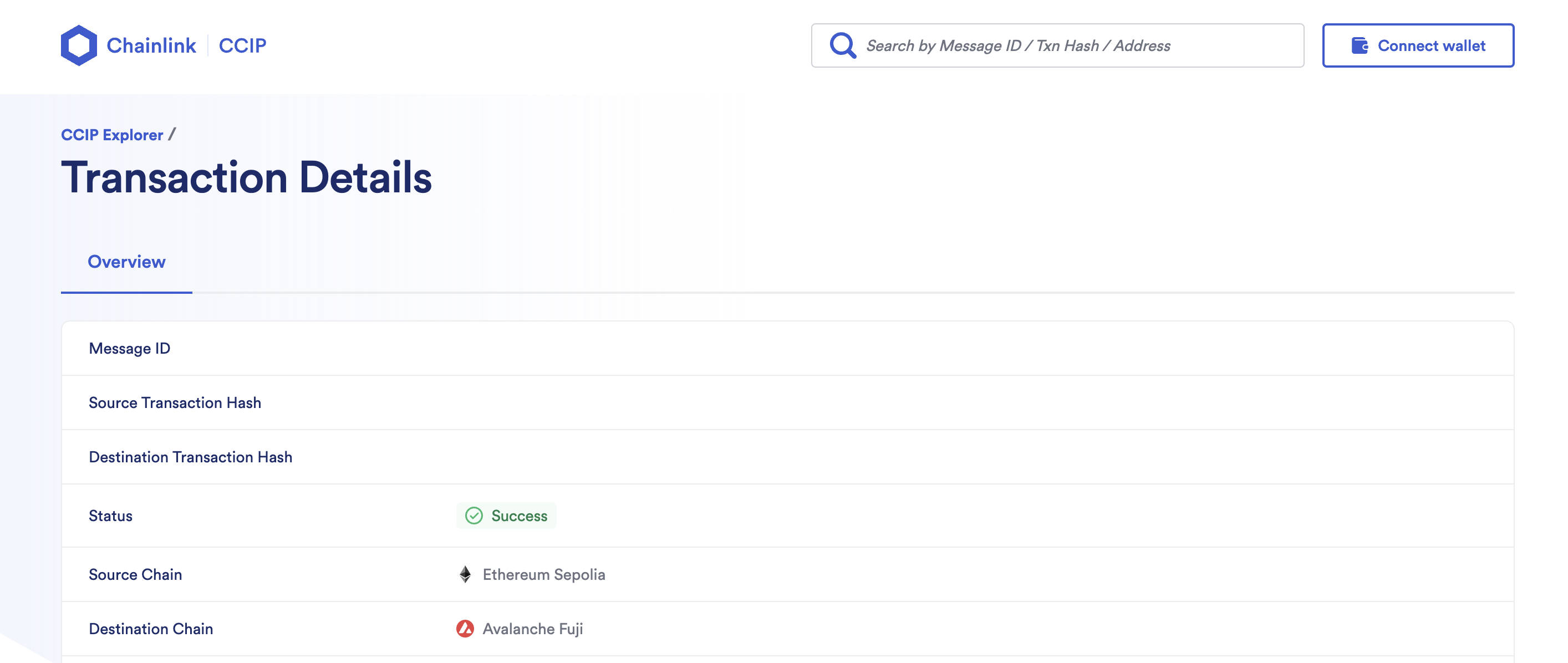
npx hardhat ccns-register --ccns-name anon.ccnsThe task will output the transaction hash in the terminal. Using it, search for your CCIP message(s) in the CCIP Explorer, one per destination blockchain. Once all of them are finalized, you have successfully registered your new & unique .ccns handle.
To check which address is associated with which .ccns handle you can use the ccns-lookup task or query the CrossChainNameServiceLookup smart contract manually on each supported blockchain:
npx hardhat ccns-lookup
--ccns-name <NAME.CCNS>
--lookup <CCNS_LOOKUP_ADDRESS> # OptionalTo resolve the anon.ccns handle to an actual address on Ethereum Sepolia, run:
npx hardhat ccns-lookup --ccns-name anon.ccns --network ethereumSepoliaTo do the same thing on Avalanche Fuji, run:
npx hardhat ccns-lookup --ccns-name anon.ccns --network avalancheFujiIt should log the same address. If it logs the zero address on any of the destination blockchains double-check the CCIP explorer to confirm that the register message is being finalized.