This repository is a PyTorch implementation of Voxel2Mesh architecture proposed in Voxel2Mesh: 3D Mesh Model Generation from Volumetric Data; Udaranga Wickramasinghe, Edoardo Remelli, Graham Knott and Pascal Fua; MICCAI 2020.
CNN-based volumetric methods that label individual voxels now dominate the field of biomedical segmentation. However, 3D surface representations are often required for proper analysis. They can be obtained by post-processing the labeled volumes which typically introduces artifacts and prevents end-to-end training. In this paper, we therefore introduce a novel architecture that goes directly from 3D image volumes to 3D surfaces without post-processing and with better accuracy than current methods. We evaluate it on Electron Microscopy and MRI brain images as well as CT liver scans. We will show that it outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods.
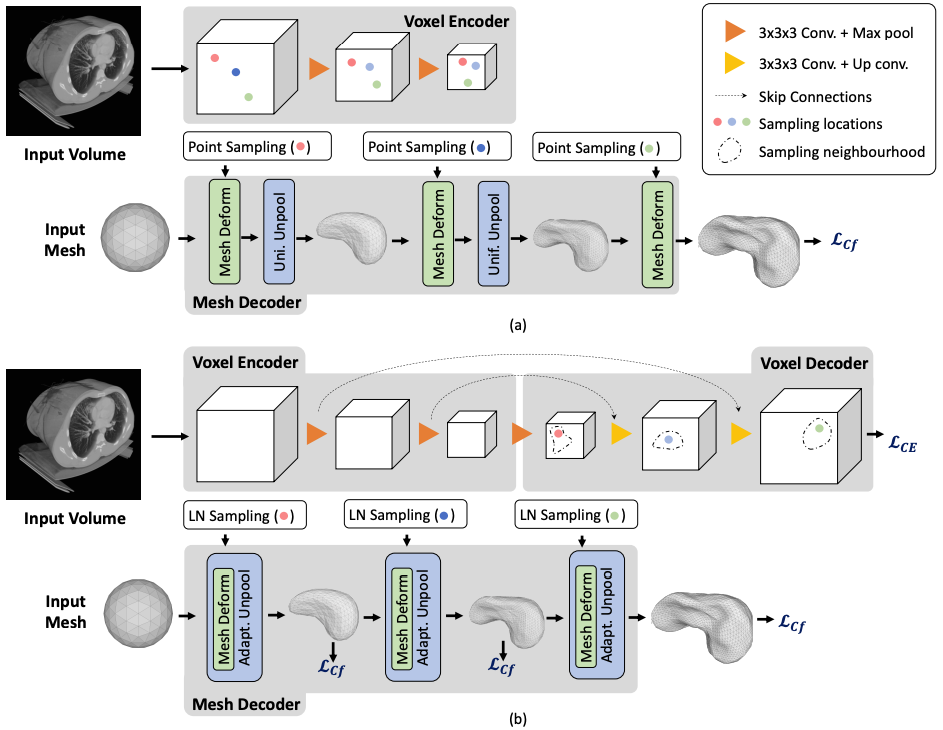
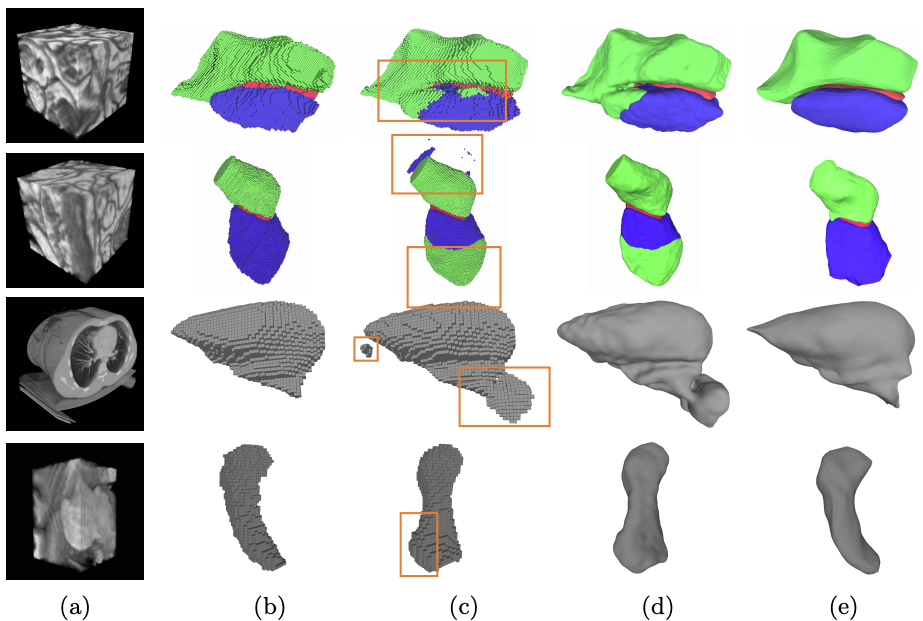
Fig. 1. Architectures (a) The Pixel2Mesh-3D architecture, a straightforward extension of [20], uses a surface decoder but no voxel decoder. (b) By contrast, our Voxel2Mesh architecture takes as input an image and spherical mesh. They are jointly encoded and then decoded into cubes and meshes of increasing resolution. At each mesh decoding stage, the decoder first receives as input the current mesh and a set of features sampled from the cube of corresponding resolution. Then the mesh is deformed and refined non-uniformly by adding vertices only where they are needed.Fig. 2. Qualitative results. (a) Input volumes. EM (row 1,2), CT(row 3), MRI(row 4) (b) Ground truth (c) CNN baseline (d) CNN baseline + post processing (e) Voxel2Mesh. The orange boxes highlight false positive regions.
PyTorch 1.4
Python 3.6.9
1. CHAOS dataset .
3. Synaptic junction dataset will be made available soon.
Step 1: First, it's recommended to do necessary preprocessing and saving the data to disk. You can use pre_process_dataset function to do that. Uncomment pre_process_dataset in main.py and execute python main.py
Step 2: Once the dataset is ready, comment pre_process_dataset and uncomment quick_load_data function in main.py. Then re-execute python main.py and this will start training the network. All the parameters used in the training are listed in config.py.
For any questions regard this paper/code, please directly contact Udaranga Wickramasinghe.