Text-to-Speech Solution on AWS with Polly, CloudFront, and S3
- AWS profile used to deploy CloudFormation stacks.
- Dockerhub account and personal access token configured.
- Registered domain (preferably hosted in Route53 for easy ACM validation)
- Clone this repo.
- Checkout your branch name. The branch name is used to create a unique stack and environment for deployment. The app is configured for
developandmainbranch names. - Install your requirements
pip3 install -r ./app/requirements.txt- Create .env file in the root of the repo and populate the following variables (note the trailing dot on the dns domain):
APP_DNS_DOMAIN=example.domain.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=appCredentialsPopulatMeAfterCfnDeployment
AWS_ACCOUNT_NAME=account-name
AWS_ACCOUNT_NUMBER=123456789123
AWS_DEFAULT_PROFILE=account-profile-configured in ~./aws
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=appCredentialsPopulatMeAfterCfnDeployment
- Generate your Cloudformation template
python3 cloudformation/template.py- Deploy your CloudFormation stack using the profile configured in .env using the shell script below.
branch_name=$(git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD)
if [[ "$branch_name" == "main" ]]; then
ENVIRONMENT="production"
else
ENVIRONMENT="$branch_name"
fi
echo "Running in $ENVIRONMENT environment"
source .env && aws cloudformation deploy --template-file cloudformation/$ENVIRONMENT-template.json --stack-name $ENVIRONMENT-cloudchirp --region us-east-1 --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM CAPABILITY_AUTO_EXPAND- Ensure your ACM validation completes. AWS certificate manager will require you to validate your domain. If hosted in Route53 this is a 1 click deployment.
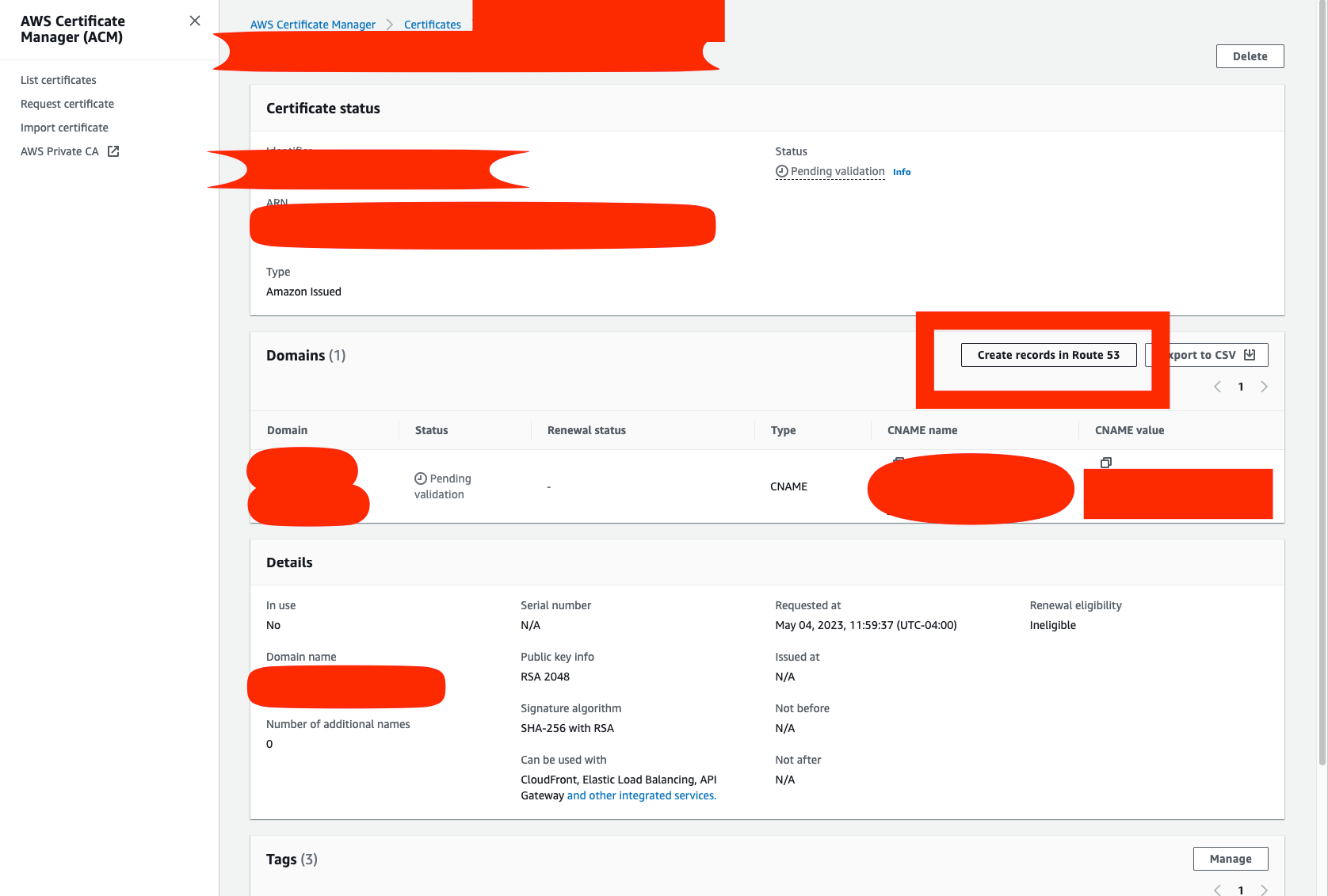
- Fetch your aws access keys from the stack outputs and store Github actions secrets as
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY. Also add these to your .env file you want to test locally. - You will now need to configure your Dockerhub credentials
DOCKERHUB_USERNAMEandDOCKERHUB_TOKENfor CI to push to Dockerhub. - Configure your secrets in the GitHub actions menu. Take note that each environment key has a unique prefix.
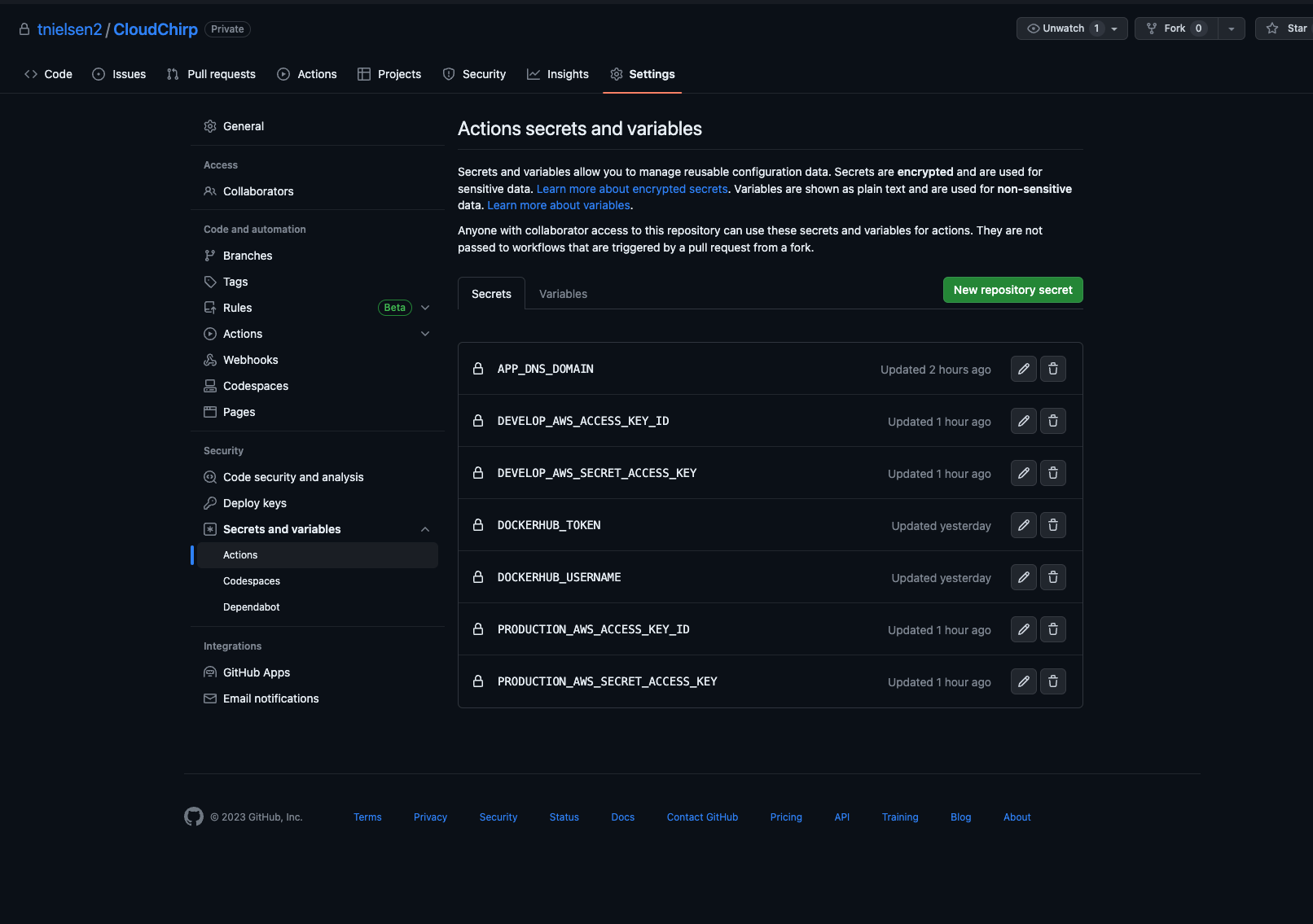
- Re-run Actions to build and populate the files.